From The Center Square
Reciprocal tariffs higher on many nations
President Donald Trump on Wednesday put the biggest piece of his new trade policy in effect by signing executive orders that place a 10% baseline tariff on all imports and much higher rates on nations that put taxes on U.S. products.
It could be the opening salvo in a global trade war, or, as Trump sees it, the beginning of a “Golden Age” for U.S. trade.
Trump also closed the small value packages loophole that allowed China to avoid taxes on packages valued at less than $800. Companies such as Temu and Shein used the loophole to ship billions of dollars worth of products directly to U.S. consumers and avoid paying the tax, as The Center Square previously reported.
President Trump speaks about tariffs at a Make America Wealthy Again event
Trump’s moves on Wednesday, which he termed “Liberation Day” for U.S. trade, marked the most significant shift in U.S. trade policy since the end of World War II.
In a speech from the White House’s Rose Garden, Trump said foreign nations for decades have stolen American jobs, factories and industries. He said the tariffs would bring in new jobs, factories and industries and return the U.S. to a manufacturing superpower.
“Our country and its taxpayers have been ripped off for more than 50 years,” Trump said. “But it is not going to happen anymore.”
Trump’s supporters praised the trade overhaul. U.S. Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene said it was time for foreign nations to pay up.
“If you want to do business in America, you need to play by our rules,” she said. “For too long, American businesses, big and small, have been ripped off by bad trade deals and unfair competition. President Trump is putting a stop to it. He’s standing up for our workers, our companies and our consumers.”
Critics slammed Trump’s trade plans.
“Donald Trump may want to call this ‘Liberation Day,’ but there is nothing liberating for working families who are grappling with the high costs of food, housing, and utilities,” said Illinois Gov. J.B. Pritzker, a Democrat. “Tariffs are a tax. They are a tax on working families, a tax on groceries, and a tax on other everyday necessities.”
Other countries planned their own responses. The European Union plans to retaliate with its own measures.
“Europe has not started this confrontation,” EU boss Ursula von der Leyen said in a speech. “We do not necessarily want to retaliate but, if it is necessary, we have a strong plan to retaliate and we will use it.”
She said tariffs are taxes “paid by the people.”
“But Europe has everything to protect our people and our prosperity,” she wrote on X. “We will always promote & defend our interests and values. And we will always stand up for Europe.”
China, the world’s second-largest economy, said Monday that it was planning to coordinate its response to U.S. tariffs with Japan and South Korea.
Japan’s Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba said Tuesday that he was willing to fly to the U.S. to meet with Trump to get an exemption for Japanese vehicle makers. He also said the government will take steps to minimize the impact of U.S. tariffs on Japanese industries and jobs.
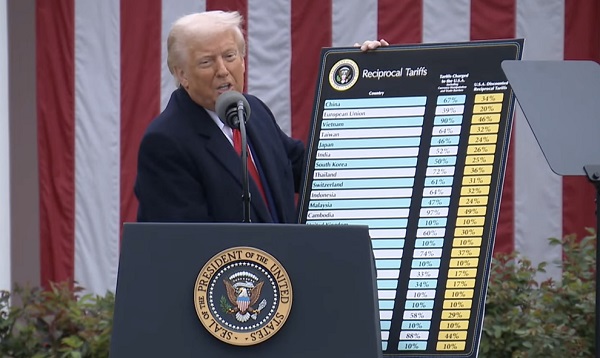
Trump will impose a 10% tariff on all countries that will take effect April 5, 2025 at 12:01 a.m. EDT. Trump will impose an individualized reciprocal tariff on the countries with which the United States has the largest trade deficits, including China, India and Vietnam, among others. All other countries will continue to be subject to the 10% tariff baseline, according to the White House.
“These tariffs will remain in effect until such a time as President Trump determines that the threat posed by the trade deficit and underlying nonreciprocal treatment is satisfied, resolved, or mitigated,” according to a White House fact sheet.
Trump’s executive order also gives him authority to increase the tariffs
“if trading partners retaliate” or “decrease the tariffs if trading partners take significant steps to remedy non-reciprocal trade arrangements and align with the United States on economic and national security matters,” according to the White House.
“Foreign cheaters have stolen our jobs, ransacked our factories and foreign scavengers have torn apart our once beautiful American dream,” Trump said in the Rose Garden.
For China, the tariff rate will be about 34% on imports from the world’s most populous nation. For European Union countries, it will be 20%. For Japan, the duty will be 24%. Imports from India will get a 26% tariff. Cambodia will get hit with a 49% tariff, among the highest Trump outlined on Wednesday.
For months, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce has warned that tariffs could increase costs for U.S. consumers and hurt businesses. Neil Bradley, the chamber’s chief policy officer, said businesses large and small don’t want tariffs.
“What we have heard from business of all sizes, across all industries, from around the country is that these broad tariffs are a tax increase that will raise prices for American consumers and hurt the economy,” he said.
Last week, Trump announced a 25% tariff on imported automobiles and auto parts, duties that he said would be “permanent.” The White House said it expects the auto tariffs on cars and light-duty trucks will generate up to $100 billion in federal revenue.
Trump said he hopes to bring in $600 billion to $1 trillion in tariff revenue in the next year or two. Trump also said the tariffs would lead to a manufacturing boom in the U.S., with auto companies building new plants, expanding existing plants and adding jobs.