Housing
Trudeau’s 2024 budget could drive out investment as housing bubble continues

From LifeSiteNews
By David James
The extent to which the Canadian economy is distorted by a property bubble can be seen by comparing government debt with household debt, with the latter being 130 percent of GDP, nearly twice as much as American households.
Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s federal government has brought in its 2024 budget, which projects C$53 billion in new spending over the next 5 years. It includes a significant capital gains tax increase, which some are warning will drive away investment, and a plan for more government-controlled public housing.
The Trudeau government is wrestling with a problem that is afflicting most English-speaking economies: how to deal with the consequences of a 20-year house price bubble that has led to deep social divisions, especially between baby boomers and people under 40.
House prices have tripled over the last 20 years on average, fuelled by the combination of aggressive bank lending and, until recently, falling interest rates. Neither is directly controlled by the federal government. There is no avenue to restrict how much banks lend and the Bank of Canada sets interest rates independently.
Accordingly, the Trudeau government is left to tinker at the edges. It will legislate an increase, from one half to two-thirds, in the share of capital gains subject to taxation for annual investment profits greater than C$250,000. The change will apply to individuals, companies and trusts.
Christina Freeland, Canada’s minister for finance, claimed improbably that only 0.13 percent of Canadians with an average income of $1.42 million are expected to pay more income tax on their capital gains in any given year.
That is a dubious forecast. The average house price in Canada 20 years ago was C$241,000; it is now C$719,000. Any Canadians who bought an investment property (family homes are exempt) before about 2015 are likely to have a capital gain larger than C$250,000 should they sell.
The government’s claim that the change will only affect a tiny proportion of Canada’s population is also belied by the government’s own forecast that the tax change will raise over C$20 billion over five years.
The extent to which the Canadian economy is distorted by a property bubble can be seen by comparing government debt with household debt. Canada’s government debt is fairly modest by current international standards: 67.8 percent of GDP in March 2023, down from 73 percent in the previous year. That is about half the U.S. government debt and half the average for G7 countries.
Canada’s budget deficit is also cautious by Western standards. In 2023-24 it was C$40 billion, equivalent to 1.4 percent of GDP. The U.S. budget deficit is currently over 6 percent of GDP.
By contrast Canada’s household debt, inflated by large mortgages, is at over 130 percent of GDP, making borrowers vulnerable to rising interest rates. U.S. household debt is about 75 percent of GDP. Attracted by rising house prices and the advantages of negative gearing (deducting rental losses from a property investment from income tax), Canadians have seen property as their preferred investment option.
Investors account for 30 percent of home buying in Canada, and about one in five properties is owned by an investor. Worse, the enthusiasm for property investment seems to be intensifying. According to one survey, 23 percent of Canadians who do not own a residential investment property say that they are likely to purchase one in the next five years, and 51 percent of current investors say that they are likely to purchase an additional residential investment property within the same time frame.
The problem with the bias towards property investment is that it is actually a punt on land values – and land is inherently unproductive. Business groups have criticized the government’s capital gains hike as a disincentive for investment and innovation, but the far bigger issue is investors’ focus on property, which is crowding out interest in other kinds of investments.
That means the main source investment capital for businesses will tend to come from institutions, such as mutual funds, which typically have a global, rather than local, orientation.
Faced with forces largely out of its control, the Trudeau government is fiddling at the edges. It has announced the introduction of what it calls “Canada’s Housing Plan”, which is aimed at unlocking over 3.8 million homes by 2031. Two million are expected to be new homes, with the government contributing to more than half of them. This will be done by converting underused federal offices into homes, building homes on Canada Post properties, redeveloping National Defence lands, creating more loans for building apartments in Ottawa, and looking at taxing vacant land.
The initiatives may have some effect on supply and demand, but the property price excesses are mainly a financial problem caused by unrestrained bank lending that has been fuelled by low interest rates. When a correction does occur, it will most likely be because of changed global financial conditions, not government policy or fiscal changes.
There are other measures that could be taken to address the property bubble such as reducing, or removing, negative gearing or more heavily taxing capital gains only on property but not other types of investments. But these policies would no doubt would be politically unsalable, so the Trudeau government is instead making minor changes, probably hoping that the problem will fix itself.
2025 Federal Election
Homebuilding in Canada stalls despite population explosion

From the Fraser Institute
By Austin Thompson and Steven Globerman
Between 1972 and 2019, Canada’s population increased by 1.8 residents for every new housing unit started compared to 3.9 new residents in 2024. In other words, Canada must now house more than twice as many new residents per new housing unit as it did during the five decades prior to the pandemic
In many parts of Canada, the housing affordability crisis continues with no end in sight. And many Canadians, priced out of the housing market or struggling to afford rent increases, are left wondering how much longer this will continue.
Simply put, too few housing units are being built for the country’s rapidly growing population, which has exploded due to record-high levels of immigration and the federal government’s residency policies.
As noted in a new study published by the Fraser Institute, the country added an all-time high 1.2 million new residents in 2023—more than double the previous record in 2019—and another 951,000 new residents in 2024. Altogether, Canada’s population has grown by about 3 million people since 2022—roughly matching the total population increase during the 1990s.
Meanwhile, homebuilding isn’t keeping up. In 2024, construction started on roughly 245,000 new housing units nationwide—down from a recent peak of 272,000 in 2021. By contrast, in the 1970s construction started on more than 240,000 housing units (on average) per year—when Canada’s population grew by approximately 280,000 people annually.
In fact, between 1972 and 2019, Canada’s population increased by 1.8 residents for every new housing unit started compared to 3.9 new residents in 2024. In other words, Canada must now house more than twice as many new residents per new housing unit as it did during the five decades prior to the pandemic. And of course, housing follows the laws of supply and demand—when a lot more prospective buyers and renters chase a limited supply of new homes, prices increase.
This key insight should guide the policy responses from all levels of government.
For example, the next federal government—whoever that may be—should avoid policies that merely fuel housing demand such as home savings accounts. And provincial governments (including in Ontario and British Columbia) should scrap any policies that discourage new housing supply such as rent controls, which reduce incentives to build rental housing. At the municipal level, governments across the country should ensure that permit approval timelines and building fees do not discourage builders from breaking ground. Increasing housing supply is, however, only part of the solution. The next federal government should craft immigration and residency policies so population growth doesn’t overwhelm available housing supply, driving up costs for Canadians.
It’s hard to predict how long Canada’s housing affordability crisis will last. But without more homebuilding, slower population growth, or both, there’s little reason to expect affordability woes to subside anytime soon.
2025 Federal Election
Housing starts unchanged since 1970s, while Canadian population growth has more than tripled
From the Fraser Institute
By: Austin Thompson and Steven Globerman
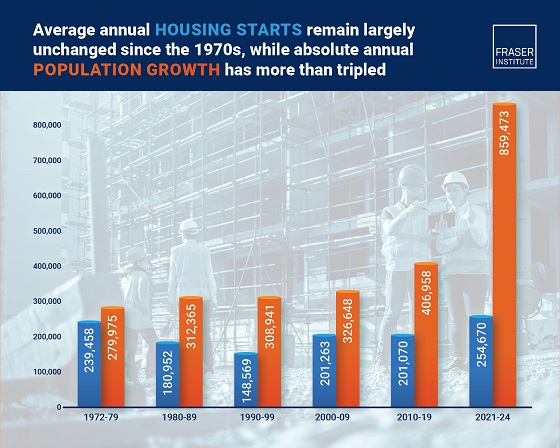
The annual number of new homes being built in Canada in recent years is virtually the same as it was in the 1970s, despite annual population growth
now being three times higher, finds a new study published today by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think tank.
“Despite unprecedented levels of immigration-driven population growth following the COVID-19 pandemic, Canada has failed to ramp up homebuilding sufficiently to meet housing demand,” said Steven Globerman, Fraser Institute senior fellow and co-author of The Crisis in Housing Affordability: Population Growth and Housing Starts 1972–2024.
Between 2021 and 2024, Canada’s population grew by an average of 859,473 people per year, while only 254,670 new housing units were started annually. From 1972 to 1979, a similar number of new housing units were built—239,458—despite the population only growing by 279,975 people a year.
As a result, more new residents are competing for each new home than in the past, which is driving up housing costs.
“The evidence is clear—population growth has been outpacing housing construction for decades, with predictable results,” Globerman said.
“Unless there is a substantial acceleration in homebuilding, a slowdown in population growth, or both, Canada’s housing affordability crisis is unlikely to improve.”
The Crisis in Housing Affordability: Population Growth and Housing Starts 1972–2024
- Canada experienced unprecedented population growth following the COVID-19 pandemic without a commensurately large increase in new homebuilding.
- The imbalance between population growth and new housing construction is reflected in a significant gap between housing demand and supply, which is driving up housing costs.
- Canada’s population grew by a record 1.23 million new residents in 2023 almost entirely due to immigration. That growth was more than double the pre-pandemic record set in 2019.
- Population growth slowed to 951,517 in 2024, still well above any year before 2023.
- Nationally, construction began on about 245,367 new housing units in 2024, down from a recent high of 271,198 starts in 2021—Canada’s annual number of housing starts peaked at 273,203 in 1976.
- Canada’s annual number of housing starts regularly exceeded 200,000 in past decades, when absolute population growth was much lower.
- In 2023, Canada added 5.1 new residents for every housing unit started, which was the highest ratio over the study’s timeframe and well above the average rate of 1.9 residents for every unit started observed over the study period (1972–2024).
- This ratio improved modestly in 2024, with 3.9 new residents added per housing start. However, the ratio remains far higher than at any point prior to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- These national trends are broadly mirrored across all 10 provinces, where annual population growth relative to housing starts is, to varying degrees, elevated when compared to long-run averages.
- Without an acceleration in homebuilding, a slowdown in population growth, or both, Canada’s housing affordability crisis will likely persist.
Austin Thompson
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoTrump Has Driven Canadians Crazy. This Is How Crazy.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCarney’s Hidden Climate Finance Agenda
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoThe Anhui Convergence: Chinese United Front Network Surfaces in Australian and Canadian Elections
-

 Automotive19 hours ago
Automotive19 hours agoHyundai moves SUV production to U.S.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoStudy links B.C.’s drug policies to more overdoses, but researchers urge caution
-

 Entertainment1 day ago
Entertainment1 day agoPedro Pascal launches attack on J.K. Rowling over biological sex views
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoWhen it comes to pipelines, Carney’s words flow both ways
-

 2025 Federal Election16 hours ago
2025 Federal Election16 hours agoAs PM Poilievre would cancel summer holidays for MP’s so Ottawa can finally get back to work





