Alberta
Transit safety and violent crime: Enough is enough

Alberta’s government is taking action to restore order and improve public safety in response to increasing crime and disorder in the province’s big cities.
In both Edmonton and Calgary, criminal activity is on the rise. Between July 2022 and January 2023, Edmonton’s LRT and transit centres experienced an increase in violent criminal incidents of 75 per cent. In Calgary, overall criminal occurrences at LRT stations increased 46 per cent between 2021 and 2022.
Premier Danielle Smith has directed Public Safety and Emergency Services Minister Mike Ellis to work with his cabinet colleagues to develop a plan to hire 100 more street-level police officers over the next 18 months to increase the visible law enforcement presence and tackle criminal activity in high-crime locations in Calgary and Edmonton.
“Safety on public streets is never negotiable. We can address root causes like mental health and addiction at the same time, but we will not compromise on security for all Calgarians and Edmontonians. This starts with the federal government reforming its broken catch-and-release bail system and includes us working with cities and police services to fight back against criminals.”
In addition to increasing the number of street-level police officers on city streets, Alberta’s government is encouraging the City of Calgary and the City of Edmonton to transfer command and control of transit peace officers to the Calgary and Edmonton police services. This transfer would enable the police to better lead a coordinated and strategic response to the increase in violent crime on public transit.
“Enough is enough – the rising crime levels in Edmonton and Calgary are unacceptable. Albertans have a right to use public transit and walk the streets without fear. We are working with our partners to develop a clear plan to take our cities back from those who seek to cause harm.”
Improving public safety on the cities’ transit networks also involves stations and vehicles that are clean of drug paraphernalia and debris. Through a new $5-million grant to each city, municipal governments will be able to provide the services needed to keep station platforms and vehicles clean, safe and welcoming for law-abiding Calgarians and Edmontonians.
“The safety and security of our transit systems and downtowns will remain a top priority. No single order of government can solve this issue alone. We will continue to work together by deploying our safety resources in an integrated and collaborative way.”
“We are seeing a significant portion of those who are improperly using transit and other public spaces becoming entrenched, with many displaying resistance to offers for services, as well as reduced cooperation and compliance with authority figures. For those people, consequences will follow.”
Police and crisis teams
As part of building strong recovery-oriented systems of mental health and addiction care, Alberta’s government is investing almost $8 million over three years to increase the number of police and crisis teams (PACT) in Calgary and Edmonton. PACT pairs police constables with mental health therapists from Alberta Health Services to respond to 911 calls where there is a mental health concern. Police and mental health therapists work together to assess a client’s mental health challenge and determine what support is required to keep the individual and the community safe.
“We are taking a fair, firm and compassionate approach to keeping our communities safe while treating mental health and addiction as health-care issues. By working with our partners in the Calgary and Edmonton police services, we can connect people in need with critical mental health services and better address the social issues affecting our two largest cities.”
With this funding, Alberta’s government is adding 12 new PACT partnerships in each city. This will double the number of PACT teams in Calgary, increasing from 12 to 24, and triple them in Edmonton, increasing from six to 18. These partnerships will better support Albertans struggling with mental health challenges while improving public safety for everyone.
“These additional resources will help us to gather what we need to get ahead of the concerning spike in crime and particularly violent crime that we are witnessing in areas like our downtown core and transit stations across Edmonton. The support, not just for police but for PACT, means prioritizing those who need support while ensuring appropriate focus on safety. Centring police as leaders within this work shows a key understanding that we cannot have well-being if we don’t have safety.”
Quick facts
Edmonton crime:
- The average crime severity index in downtown Edmonton has increased 29 per cent, to 116 in December 2022 from 90 in July 2022, driven primary by an increase in serious criminal offences, in particular second-degree murder, assault causing bodily harm with a weapon, robbery and aggravated assault.
- In Edmonton, a person is about twice as likely to be victimized by a stranger at a transit centre than for the city as a whole (70 per cent at LRT transit versus 36 per cent citywide).
Calgary crime:
- Property crime occurrences in Calgary nearly doubled – increasing 95 per cent to 463 in 2022, up from 238 in 2021.
- Total calls for service to Calgary LRT stations increased to 9,317 in 2022, up 39 per cent from 6,706 in 2021.
- Public-generated calls for service to LRT stations increased to 5,012 in 2022, up 20 per cent from 4,160 in 2021.
- Officer-generated calls for service to LRT stations increased to 4,305, up 69 per cent from 2,546 in 2021.
PACT facts:
- Police and crisis teams (PACT) offer mental health assessment, support and/or consultation in crisis situations. Mental health therapists work with police constables to assess mental health needs and determine appropriate action in accordance with the Mental Health Act and the criminal justice system.
Alberta
‘Weird and wonderful’ wells are boosting oil production in Alberta and Saskatchewan
From the Canadian Energy Centre
Multilateral designs lift more energy with a smaller environmental footprint
A “weird and wonderful” drilling innovation in Alberta is helping producers tap more oil and gas at lower cost and with less environmental impact.
With names like fishbone, fan, comb-over and stingray, “multilateral” wells turn a single wellbore from the surface into multiple horizontal legs underground.
“They do look spectacular, and they are making quite a bit of money for small companies, so there’s a lot of interest from investors,” said Calin Dragoie, vice-president of geoscience with Calgary-based Chinook Consulting Services.
Dragoie, who has extensively studied the use of multilateral wells, said the technology takes horizontal drilling — which itself revolutionized oil and gas production — to the next level.
“It’s something that was not invented in Canada, but was perfected here. And it’s something that I think in the next few years will be exported as a technology to other parts of the world,” he said.
Dragoie’s research found that in 2015 less than 10 per cent of metres drilled in Western Canada came from multilateral wells. By last year, that share had climbed to nearly 60 per cent.
Royalty incentives in Alberta have accelerated the trend, and Saskatchewan has introduced similar policy.
Multilaterals first emerged alongside horizontal drilling in the late 1990s and early 2000s, Dragoie said. But today’s multilaterals are longer, more complex and more productive.
The main play is in Alberta’s Marten Hills region, where producers are using multilaterals to produce shallow heavy oil.
Today’s average multilateral has about 7.5 horizontal legs from a single surface location, up from four or six just a few years ago, Dragoie said.
One record-setting well in Alberta drilled by Tamarack Valley Energy in 2023 features 11 legs stretching two miles each, for a total subsurface reach of 33 kilometres — the longest well in Canada.
By accessing large volumes of oil and gas from a single surface pad, multilaterals reduce land impact by a factor of five to ten compared to conventional wells, he said.
The designs save money by skipping casing strings and cement in each leg, and production is amplified as a result of increased reservoir contact.
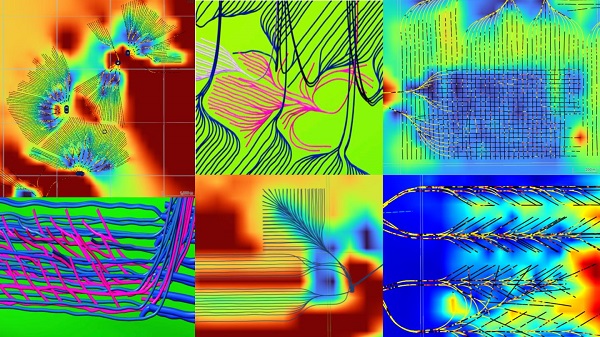
Here are examples of multilateral well design. Images courtesy Chinook Consulting Services.
Parallel
Fishbone
Fan
Waffle
Stingray
Frankenwells
Alberta
Alberta to protect three pro-family laws by invoking notwithstanding clause

From LifeSiteNews
Premier Danielle Smith said her government will use a constitutional tool to defend a ban on transgender surgery for minors and stopping men from competing in women’s sports.
Alberta Premier Danielle Smith said her government will use a rare constitutional tool, the notwithstanding clause, to ensure three bills passed this year — a ban on transgender surgery for minors, stopping men from competing in women’s sports, and protecting kids from extreme aspects of the LGBT agenda — stand and remain law after legal attacks from extremist activists.
Smith’s United Conservative Party (UCP) government stated that it will utilize a new law, Bill 9, to ensure that laws passed last year remain in effect.
“Children deserve the opportunity to grow into adulthood before making life-altering decisions about their gender and fertility,” Smith said in a press release sent to LifeSiteNews and other media outlets yesterday.
“By invoking the notwithstanding clause, we’re ensuring that laws safeguarding children’s health, education and safety cannot be undone – and that parents are fully involved in the major decisions affecting their children’s lives. That is what Albertans expect, and that is what this government will unapologetically defend.”
Alberta Justice Minister and Attorney General Mickey Amery said that the laws passed last year are what Albertans voted for in the last election.
“These laws reflect an overwhelming majority of Albertans, and it is our responsibility to ensure that they will not be overturned or further delayed by activists in the courts,” he noted.
“The notwithstanding clause reinforces democratic accountability by keeping decisions in the hands of those elected by Albertans. By invoking it, we are providing certainty that these protections will remain in place and that families can move forward with clarity and confidence.”
The Smith government said the notwithstanding clause will apply to the following pieces of legislation:
-
Bill 26, the Health Statutes Amendment Act, 2024, prohibits both gender reassignment surgery for children under 18 and the provision of puberty blockers and hormone treatments for the purpose of gender reassignment to children under 16.
-
Bill 27, the Education Amendment Act, 2024, requires schools to obtain parental consent when a student under 16 years of age wishes to change his or her name or pronouns for reasons related to the student’s gender identity, and requires parental opt-in consent to teaching on gender identity, sexual orientation or human sexuality.
-
Bill 29, the Fairness and Safety in Sport Act, requires the governing bodies of amateur competitive sports in Alberta to implement policies that limit participation in women’s and girls’ sports to those who were born female.”
Bill 26 was passed in December of 2024, and it amends the Health Act to “prohibit regulated health professionals from performing sex reassignment surgeries on minors.”
As reported by LifeSiteNews, pro-LGBT activist groups, with the support of Alberta’s opposition New Democratic Party (NDP), have tried to stop the bill via lawsuits. It prompted the Smith government to appeal a court injunction earlier this year blocking the province’s ban on transgender surgeries and drugs for gender-confused minors.
Last year, Smith’s government also passed Bill 27, a law banning schools from hiding a child’s pronoun changes at school that will help protect kids from the extreme aspects of the LGBT agenda.
Bill 27 will also empower the education minister to, in effect, stop the spread of extreme forms of pro-LGBT ideology or anything else to be allowed to be taught in schools via third parties.
Bill 29, which became law last December, bans gender-confused men from competing in women’s sports, the first legislation of its kind in Canada. The law applies to all school boards, universities, and provincial sports organizations.
Alberta’s notwithstanding clause is like all other provinces’ clauses and was a condition Alberta agreed to before it signed onto the nation’s 1982 constitution.
It is meant as a check to balance power between the court system and the government elected by the people. Once it is used, as passed in the legislature, a court cannot rule that the “legislation which the notwithstanding clause applies to be struck down based on the Charter of Rights and Freedoms, the Alberta Bill of Rights, or the Alberta Human Rights Act,” the Alberta government noted.
While Smith has done well on some points, she has still been relatively soft on social issues of importance to conservatives , such as abortion, and has publicly expressed pro-LGBT views, telling Jordan Peterson earlier this year that conservatives must embrace homosexual “couples” as “nuclear families.”
-

 Crime1 day ago
Crime1 day ago‘Modern-Day Escobar’: U.S. Says Former Canadian Olympian Ran Cocaine Pipeline with Cartel Protection and a Corrupt Toronto Lawyer
-

 National13 hours ago
National13 hours agoPsyop-Style Campaign That Delivered Mark Carney’s Win May Extend Into Floor-Crossing Gambits and Shape China–Canada–US–Mexico Relations
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoDemocrats Explicitly Tell Spy Agencies, Military To Disobey Trump
-

 COVID-1910 hours ago
COVID-1910 hours agoCovid Cover-Ups: Excess Deaths, Vaccine Harms, and Coordinated Censorship
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin11 hours ago
Bruce Dowbiggin11 hours agoBurying Poilievre Is Job One In Carney’s Ottawa
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoALAN DERSHOWITZ: Can Trump Legally Send Troops Into Our Cities? The Answer Is ‘Wishy-Washy’
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta on right path to better health care
-

 Alberta24 hours ago
Alberta24 hours ago‘Weird and wonderful’ wells are boosting oil production in Alberta and Saskatchewan










