Alberta
Taking Action Against Climate Change with Emissions Reduction Alberta

As the climate conversation continues to expand in the public space, ambitious goals for reducing emissions are being communicated at regional and international levels. The burning of fossil fuels has substantially contributed to the build up of greenhouse gases (GHG) in our atmosphere, resulting in the climate changes currently impacting major industries, ecosystems, weather patterns, natural resources and biodiversity around the world. According to Climate Change in Alberta, “97% of climate scientists now agree that human activity is responsible for most temperature increases over the past 250 years.”
In Alberta, over 50% of GHG emissions are the result of “industrial, manufacturing and construction activity, as well as producing the electricity we consume … the remainder comes from heating our homes and businesses, transportation and from agriculture, forestry and municipal waste” (1). As a part of a multi-level provincial strategy aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions in Alberta, the government currently partners with various organizations and funds a number of programs designed to accelerate emissions reduction initiatives and technology development.
One Alberta organization that has played a significant role in furthering emissions reduction in our province for more than a decade is Emissions Reduction Alberta (ERA), based in Edmonton.
Established in 2009, Emissions Reduction Alberta “takes action on climate change and supports economic growth by investing in the pilot, demonstration and deployment of clean technology solutions that reduce GHGs, lower costs and attract investment, and create jobs in Alberta.” For more than 10 years, ERA has been facilitating Alberta’s transition to a low carbon economy by supporting and furthering the most innovative approaches to emissions reduction.
“Alberta’s industries have ambitious goals around emissions reductions that can’t be achieved without deploying new technology,” says Steve MacDonald, CEO of Emissions Reduction Alberta, “Our goal is to identify and accelerate the innovation Alberta needs to grow the economy and cut emissions.”

Steve MacDonald – CEO of Emissions Reduction Alberta
ERA’s funding comes from the carbon price paid by large final emitters in Alberta. With this funding, ERA operates a challenge structure that calls innovative companies to respond to pertinent industry challenges with original solutions. “Challenges are always well over-subscribed,” says MacDonald. “This gives us the ability to really select the best of the best and get a good understanding of the range of ideas that are out there.”
To date, ERA has invested $607 million in the development of 183 unique projects dedicated to reducing emissions across various industries. ERA funding is leveraged and for every dollar invested by the organization, another $6.40 is invested by industry, innovators and other project funders. As a result, the total value of these projects is over $4 billion. ERA estimates this will lead to a total reduction of 34,800,000 tonnes of CO2e by the year 2030.
In October 2019, ERA announced their Natural Gas Challenge, a campaign committed to improving cost competitiveness and reducing emissions in Alberta’s natural gas sector. On July 21, 2020, ERA pledged $58.4 million to the 20 winning projects, valued at over $155 million. According to ERA, these projects will create 760 new jobs and, “if successful, these technology innovations will lead to cumulative GHG reductions of almost one million tonnes of CO2e by 2030 – equivalent to the GHG emissions from 750,000 passenger vehicles driven for one year.”
Moving forward, the ERA expects to see the first round of Expression of Interest for their latest $40 million Food, Farming and Forestry Challenge by August 27, 2020. In the meantime, the organization will continue to focus on aiding Alberta’s economic recovery through diversification and job creation, and the pursuit of innovation.
“We are supporting the actions required to help Alberta achieve its economic and environmental goals,” says MacDonald. “Our investments are making a real difference; one that is fundamental to Alberta’s future success. From incremental change to game-changers, we are developing the solutions Alberta and the world need.”
To learn more about Emissions Reduction Alberta, visit https://eralberta.ca.
For more stories, visit Todayville Calgary.
Alberta
Ottawa-Alberta agreement may produce oligopoly in the oilsands

From the Fraser Institute
By Jason Clemens and Elmira Aliakbari
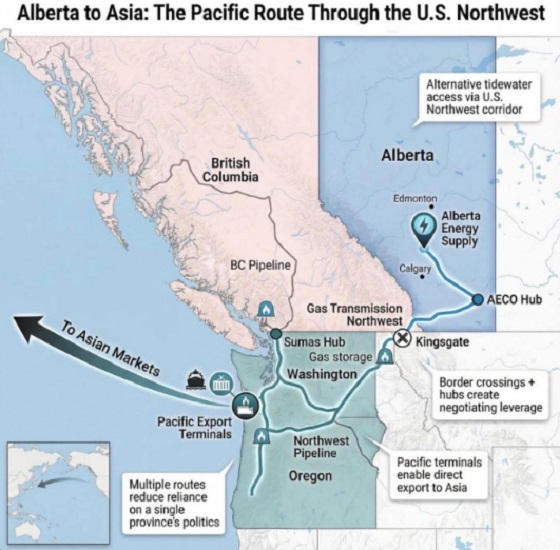
The federal and Alberta governments recently jointly released the details of a memorandum of understanding (MOU), which lays the groundwork for potentially significant energy infrastructure including an oil pipeline from Alberta to the west coast that would provide access to Asia and other international markets. While an improvement on the status quo, the MOU’s ambiguity risks creating an oligopoly.
An oligopoly is basically a monopoly but with multiple firms instead of a single firm. It’s a market with limited competition where a few firms dominate the entire market, and it’s something economists and policymakers worry about because it results in higher prices, less innovation, lower investment and/or less quality. Indeed, the federal government has an entire agency charged with worrying about limits to competition.
There are a number of aspects of the MOU where it’s not sufficiently clear what Ottawa and Alberta are agreeing to, so it’s easy to envision a situation where a few large firms come to dominate the oilsands.
Consider the clear connection in the MOU between the development and progress of Pathways, which is a large-scale carbon capture project, and the development of a bitumen pipeline to the west coast. The MOU explicitly links increased production of both oil and gas (“while simultaneously reaching carbon neutrality”) with projects such as Pathways. Currently, Pathways involves five of Canada’s largest oilsands producers: Canadian Natural, Cenovus, ConocoPhillips Canada, Imperial and Suncor.
What’s not clear is whether only these firms, or perhaps companies linked with Pathways in the future, will have access to the new pipeline. Similarly, only the firms with access to the new west coast pipeline would have access to the new proposed deep-water port, allowing access to Asian markets and likely higher prices for exports. Ottawa went so far as to open the door to “appropriate adjustment(s)” to the oil tanker ban (C-48), which prevents oil tankers from docking at Canadian ports on the west coast.
One of the many challenges with an oligopoly is that it prevents new entrants and entrepreneurs from challenging the existing firms with new technologies, new approaches and new techniques. This entrepreneurial process, rooted in innovation, is at the core of our economic growth and progress over time. The MOU, though not designed to do this, could prevent such startups from challenging the existing big players because they could face a litany of restrictive anti-development regulations introduced during the Trudeau era that have not been reformed or changed since the new Carney government took office.
And this is not to criticize or blame the companies involved in Pathways. They’re acting in the interests of their customers, staff, investors and local communities by finding a way to expand their production and sales. The fault lies with governments that were not sufficiently clear in the MOU on issues such as access to the new pipeline.
And it’s also worth noting that all of this is predicated on an assumption that Alberta can achieve the many conditions included in the MOU, some of which are fairly difficult. Indeed, the nature of the MOU’s conditions has already led some to suggest that it’s window dressing for the federal government to avoid outright denying a west coast pipeline and instead shift the blame for failure to the Smith government.
Assuming Alberta can clear the MOU’s various hurdles and achieve the development of a west coast pipeline, it will certainly benefit the province and the country more broadly to diversify the export markets for one of our most important export products. However, the agreement is far from ideal and could impose much larger-than-needed costs on the economy if it leads to an oligopoly. At the very least we should be aware of these risks as we progress.

Elmira Aliakbari
Alberta
A Christmas wish list for health-care reform

From the Fraser Institute
By Nadeem Esmail and Mackenzie Moir
It’s an exciting time in Canadian health-care policy. But even the slew of new reforms in Alberta only go part of the way to using all the policy tools employed by high performing universal health-care systems.
For 2026, for the sake of Canadian patients, let’s hope Alberta stays the path on changes to how hospitals are paid and allowing some private purchases of health care, and that other provinces start to catch up.
While Alberta’s new reforms were welcome news this year, it’s clear Canada’s health-care system continued to struggle. Canadians were reminded by our annual comparison of health care systems that they pay for one of the developed world’s most expensive universal health-care systems, yet have some of the fewest physicians and hospital beds, while waiting in some of the longest queues.
And speaking of queues, wait times across Canada for non-emergency care reached the second-highest level ever measured at 28.6 weeks from general practitioner referral to actual treatment. That’s more than triple the wait of the early 1990s despite decades of government promises and spending commitments. Other work found that at least 23,746 patients died while waiting for care, and nearly 1.3 million Canadians left our overcrowded emergency rooms without being treated.
At least one province has shown a genuine willingness to do something about these problems.
The Smith government in Alberta announced early in the year that it would move towards paying hospitals per-patient treated as opposed to a fixed annual budget, a policy approach that Quebec has been working on for years. Albertans will also soon be able purchase, at least in a limited way, some diagnostic and surgical services for themselves, which is again already possible in Quebec. Alberta has also gone a step further by allowing physicians to work in both public and private settings.
While controversial in Canada, these approaches simply mirror what is being done in all of the developed world’s top-performing universal health-care systems. Australia, the Netherlands, Germany and Switzerland all pay their hospitals per patient treated, and allow patients the opportunity to purchase care privately if they wish. They all also have better and faster universally accessible health care than Canada’s provinces provide, while spending a little more (Switzerland) or less (Australia, Germany, the Netherlands) than we do.
While these reforms are clearly a step in the right direction, there’s more to be done.
Even if we include Alberta’s reforms, these countries still do some very important things differently.
Critically, all of these countries expect patients to pay a small amount for their universally accessible services. The reasoning is straightforward: we all spend our own money more carefully than we spend someone else’s, and patients will make more informed decisions about when and where it’s best to access the health-care system when they have to pay a little out of pocket.
The evidence around this policy is clear—with appropriate safeguards to protect the very ill and exemptions for lower-income and other vulnerable populations, the demand for outpatient healthcare services falls, reducing delays and freeing up resources for others.
Charging patients even small amounts for care would of course violate the Canada Health Act, but it would also emulate the approach of 100 per cent of the developed world’s top-performing health-care systems. In this case, violating outdated federal policy means better universal health care for Canadians.
These top-performing countries also see the private sector and innovative entrepreneurs as partners in delivering universal health care. A relationship that is far different from the limited individual contracts some provinces have with private clinics and surgical centres to provide care in Canada. In these other countries, even full-service hospitals are operated by private providers. Importantly, partnering with innovative private providers, even hospitals, to deliver universal health care does not violate the Canada Health Act.
So, while Alberta has made strides this past year moving towards the well-established higher performance policy approach followed elsewhere, the Smith government remains at least a couple steps short of truly adopting a more Australian or European approach for health care. And other provinces have yet to even get to where Alberta will soon be.
Let’s hope in 2026 that Alberta keeps moving towards a truly world class universal health-care experience for patients, and that the other provinces catch up.
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoGeorgia county admits illegally certifying 315k ballots in 2020 presidential election
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoCommunist China arrests hundreds of Christians just days before Christmas
-

 Energy22 hours ago
Energy22 hours agoThe Top News Stories That Shaped Canadian Energy in 2025 and Will Continue to Shape Canadian Energy in 2026
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoSome Of The Wackiest Things Featured In Rand Paul’s New Report Alleging $1,639,135,969,608 In Gov’t Waste
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoCalgary’s new city council votes to ban foreign flags at government buildings
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoWarning Canada: China’s Economic Miracle Was Built on Mass Displacement
-

 International21 hours ago
International21 hours ago$2.6 million raised for man who wrestled shotgun from Bondi Beach terrorist
-
 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoWhat are the odds of a pipeline through the American Pacific Northwest




