Alberta
Summer Vacation Idea – Central Alberta’s collection of Train stations preserved along the Highway 56 Corridor

Article submitted by Paul O’Neil
For decades, the railroad station or “depot” was the transportation hub of many communities across North America. As the “storefront” for the railway company, the depot was the town’s gateway, handling express freight, serving travelers, and providing vital communication in an erathat is now almost forgotten. In Canada’s West, the remaining small-town depots that continue to exist are now museums, private businesses or residences, or in the worst cases have been left to deteriorate as hulks on private property.
There is however a special historical railway on the Prairies that has developed into a true “historic railway district”. A visit to the depots preserved by the Canadian Northern Society in Central Alberta provides a glimpse into the past – an entire collection of classic railroad station designs, carefully and lovingly maintained by a dedicated group of volunteers.

History Background:
Members of the Canadian Northern Society include historians, community volunteers, gardeners, and other local supporters who have since 1987 been active in the preservation of its namesake railway’s history, and in particular its depots. The Canadian Northern Railway (CNoR) traces its origins to Manitoba in 1896. Visionary founders Sir William Mackenzie and Sir Donald Mann – both instrumental as contractors in the completion of the Canadian Pacific Railway – grew the company from a modest short line between Gladstone and the Dauphin district of Manitoba into to a 9500 mile transcontinental system.
Despite the relative business success of the CNoR’s branchline network, negative financial impacts created by the First World War, together with mounting debt from the over-expansion led to the company being nationalized in late 1918. By 1924, operations in Central Alberta were amalgamated with the rival Grand Trunk Pacific Railway under the newly formed Canadian National Railways (CN) banner.
DEPOTS
Similar to other western railroads, the CNoR designed standard plans to be used at individual locations based on the size and importance of the locality to be served. In Alberta, the most common CNoR design was the combination freight and passenger “Third Class” station. Several “Second Class” depots intended primarily for divisional points were constructed, and a single-story “Fourth Class” depot design were also found. The designs were flexible enough that additions could be constructed as traffic or operations warranted. The distinctive pyramid or “semi-pyramid” roofline of a CNoR depot, a feature designed by company architect Ralph Benjamin Pratt, created a unique and pleasing image.
By the late 1960’s the depot-era on the former CNoR Battle River Subdivision (a large portion had by then been renamed the “Stettler Subdivision”) was drawing to a close. However, the presence of a branch line passenger service in the form of a Budd RDC service between Edmonton and Drumheller ensured the continued existence of several depots as passenger shelters that otherwise would most certainly face demolition. The Edmonton to Drumheller service lasted into VIA Rail Canada times until the Trudeau Government service cuts of November 1981 gutted passenger service across Canada.
ENTER THE CANADIAN NORTHERN SOCIETY
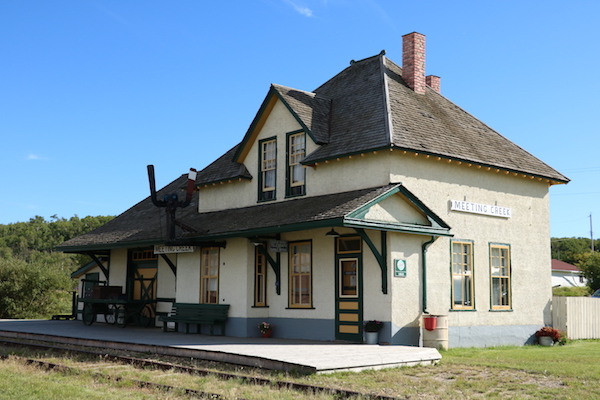
Meeting Creek, MP 21.2

My beautiful picture

By 1986, the CNoR Third Class depot at Meeting Creek was surviving on borrowed time, vandalized and yet escaping the fate of several identical structures in neighboring towns. As a result of an interest by a small group of younger railroaders and rail historians, powered perhaps by a few pints enjoyed in a Stettler pub, the Canadian Northern Society (CNoS) was soon established with the intent to save this classic structure from imminent destruction.
Armed with enthusiasm, some grant money, and the support of short-line Central Western Railway; the CNoS got to work repairing the roof, floors, rebuilding the wooden platform, painting, and replacing missing windows, doors and chimneys. By 1989 the Meeting Creek depot was resurrected from a sad state to her today’s 1940’s-era appearance.
Complimenting the station today is another vanishing prairie icon. A 1917 Alberta Pacific Grain elevator located across from the depot was purchased by CNoS from the Alberta Wheat Pool in 1992. Over the years, it too has been conserved by the Society and work continues into its second century. A second grain elevator, while privately owned, ensures that Meeting Creek continues to feature two classic prairie elevators that dominate the skyline in this picturesque location.
Donalda, MP 30.9:

9.7 miles south of Meeting Creek lies the Village of Donalda. Always an agrarian-based community, Donalda was never larger than 500 souls, and as such rated a Canadian Northern Railway “Third Class Depot”. Unfortunately, the original depot at Donalda was demolished in 1984.
Thanks to the efforts of the CNoS, the group was able to relocate an original CNoR “Fourth-Class” type depot, donated by a Saskatchewan farmer many miles to the east. All the Societyhad to do was physically move this building 700 miles from her location at Vandura, Saskatchewan to Donalda! Through fundraising and community support, the building was moved to Donalda in 1991. The depot was restored to her CN oxide red paint scheme, with cream trim on the windows and facia boards. The interior of the depot was refurbished to her heyday as a depot and is now included in the present-day collection of the Donalda & District Museum. Like Meeting Creek, a short section of original CNoR 60-pound steel main track remains preserved in front of the depot.
Warden MP 55.8:

Five miles south of Stettler is the one-time important junction of the CNoR Brazeau Subdivision, its westward extension into the coal fields at the foot of the Rockies. Originally, a “Fourth Class” station was located here, being destroyed by fire and replaced with a standard later version of the company’s “Third Class” design in 1919. This structure was sold and demolished in the 1980’s, and was recently replaced by a “representative” train order office/depot built entirely by CNoS volunteers, that features design features, artifacts, and “parts” of the original depot. It is used for educational purposes in a peaceful park-like setting along what is now short-line Alberta Prairie Railway.
Big Valley, MP 72.1:


Established in 1911, Big Valley was once hub of the division for the CNoR. By 1921 this one-time bustling terminal boasted well over 300 employees on payroll and featured a 10 stallroundhouse, coaling plant, water tank, and other terminal facilities. Big Valley’s 1912-built depot was a large “Second Class” design commonly constructed by the CNoR at divisionalpoints across the system. The main floor handled passenger and LCL business, while the second-floor housed accommodations for the agent – and later crews and offices.
The Big Valley depot was the second major conservation project for the Canadian Northern Society in 1989. Encouraged by the Village of Big Valley, CNoS began refurbishment of the station, and was able to raise funding from Alberta Historical Resources Foundation and various temporary job creation programs to restore the depot to today’s attractive 1940’s-era exterior appearance.
At the same time, short–line operator Central Western Railway was launching Alberta’s first tourist railroad service. Big Valley, like in her previous railroad life, again had the infrastructure to accommodate steam powered trains into the community. In addition, the 10-stall roundhouse,by then in ruins with only the concrete walls showing her prominence to the community was preserved as an interpretive park through the efforts of CNoS, Central Western, and the Village of Big Valley. Volunteers cleared and excavated the site, allowing the view of the ash and turntable pits, boiler room and machine shop. You can imagine the one-time bustling activity of Ten-Wheelers and Consolidations locomotives receiving service at the Roundhouse.
Big Valley today is the centerpiece of this rich CNoR heritage, plus a restored grain elevator to complete the scene of a bustling prairie railroad terminal. The Big Valley Historical Society also operates an excellent local museum in a classic garage on Railway Avenue, together with maintaining St. Edmund’s Church – a spiritual home of many of the community’s early railroaders. Serving as primary destination for Stettler based Alberta Prairie Railway, seasonal excursion trains arrive at Big Valley on a scheduled basis, where passengers spend a few hours in the community, experiencing the magic of its railway, ranching, and mining historical attractions.
Further along the line in the ghost town of Rowley is another preserved CNoR Third Class depot, built to a similar floor plan as Meeting Creek’s railway station. While not part of the Canadian Northern Society’s collection, it is certainly worth a visit while in historic “Rowleywood”.
Other Projects
In addition to its Stettler Subdivision projects, the Canadian Northern Society has and continues to support other railway preservation efforts.
Over the years the preservation of depots at Rowley, Smoky Lake, Viking, Canora in Saskatchewan, and Dauphin in Manitoba have all been supported by CNoS. A roundhouse project at the former CNoR divisional point of Hanna has also been aided by the CNoS. While the 1909 Viking depot is in fact a rival GTP station, the CNoS was instrumental in its 1991 preservation – and remarkably you can still catch a train here – with VIA Rail Canada’s flagship train “The Canadian” stopping upon request.
The CNoS collection of depots and the corresponding regional history that they represent has become part of the historical fabric of Western Canada. It is proud to have left this legacy – and its true hope is that future generations will continue to be educated by its efforts, and will perhaps contribute to the further preservation of each of these wonderful historic structures.
This summer the Canadian Northern Railway Historical Society invites you to visit these historic buildings along Alberta’s Highway 56 corridor.
Alberta
Federal budget: It’s not easy being green

From Resource Works
Canada’s climate rethink signals shift from green idealism to pragmatic prosperity.
Bill Gates raised some eyebrows last week – and probably the blood pressure of climate activists – when he published a memo calling for a “strategic pivot” on climate change.
In his memo, the Microsoft founder, whose philanthropy and impact investments have focused heavily on fighting climate change, argues that, while global warming is still a long-term threat to humanity, it’s not the only one.
There are other, more urgent challenges, like poverty and disease, that also need attention, he argues, and that the solution to climate change is technology and innovation, not unaffordable and unachievable near-term net zero policies.
“Unfortunately, the doomsday outlook is causing much of the climate community to focus too much on near-term emissions goals, and it’s diverting resources from the most effective things we should be doing to improve life in a warming world,” he writes.
Gates’ memo is timely, given that world leaders are currently gathered in Brazil for the COP30 climate summit. Canada may not be the only country reconsidering things like energy policy and near-term net zero targets, if only because they are unrealistic and unaffordable.
It could give some cover for Canadian COP30 delegates, who will be at Brazil summit at a time when Prime Minister Mark Carney is renegotiating his predecessor’s platinum climate action plan for a silver one – a plan that contains fewer carbon taxes and more fossil fuels.
It is telling that Carney is not at COP30 this week, but rather holding a summit with Alberta Premier Danielle Smith.
The federal budget handed down last week contains kernels of the Carney government’s new Climate Competitiveness Strategy. It places greater emphasis on industrial strategy, investment, energy and resource development, including critical minerals mining and LNG.
Despite his Davos credentials, Carney is clearly alive to the fact it’s a different ballgame now. Canada cannot afford a hyper-focus on net zero and the green economy. It’s going to need some high octane fuel – oil, natural gas and mining – to prime Canada’s stuttering economic engine.
The prosperity promised from the green economy has not quite lived up to its billing, as a recent Fraser Institute study reveals.
Spending and tax incentives totaling $150 billion over a decade by Ottawa, B.C, Ontario, Alberta and Quebec created a meagre 68,000 jobs, the report found.
“It’s simply not big enough to make a huge difference to the overall performance of the economy,” said Jock Finlayson, chief economist for the Independent Contractors and Business Association and co-author of the report.
“If they want to turn around what I would describe as a moribund Canadian economy…they’re not going to be successful if they focus on these clean, green industries because they’re just not big enough.”
There are tentative moves in the federal budget and Climate Competitiveness Strategy to recalibrate Canada’s climate action policies, though the strategy is still very much in draft form.
Carney’s budget acknowledges that the world has changed, thanks to deglobalization and trade strife with the U.S.
“Industrial policy, once seen as secondary to market forces, is returning to the forefront,” the budget states.
Last week’s budget signals a shift from regulations towards more investment-based measures.
These measures aim to “catalyse” $500 billion in investment over five years through “strengthened industrial carbon pricing, a streamlined regulatory environment and aggressive tax incentives.”
There is, as-yet, no commitment to improve the investment landscape for Alberta’s oil industry with the three reforms that Alberta has called for: scrapping Bill C-69, a looming oil and gas emissions cap and a West Coast oil tanker moratorium, which is needed if Alberta is to get a new oil pipeline to the West Coast.
“I do think, if the Carney government is serious about Canada’s role, potentially, as an global energy superpower, and trying to increase our exports of all types of energy to offshore markets, they’re going to have to revisit those three policy files,” Finlayson said.
Heather Exner-Pirot, director of energy, natural resources and environment at the Macdonald-Laurier Institute, said she thinks the emissions cap at least will be scrapped.
“The markets don’t lie,” she said, pointing to a post-budget boost to major Canadian energy stocks. “The energy index got a boost. The markets liked it. I don’t think the markets think there is going to be an emissions cap.”
Some key measures in the budget for unlocking investments in energy, mining and decarbonization include:
- incentives to leverage $1 trillion in investment over the next five years in nuclear and wind power, energy storage and grid infrastructure;
- an expansion of critical minerals eligible for a 30% clean technology manufacturing investment tax credit;
- $2 billion over five years to accelerate critical mineral production;
- tax credits for turquoise hydrogen (i.e. hydrogen made from natural gas through methane pyrolysis); and
- an extension of an investment tax credit for carbon capture utilization and storage through to 2035.
As for carbon taxes, the budget promises “strengthened industrial carbon pricing.”
This might suggest the government’s plan is to simply simply shift the burden for carbon pricing from the consumer entirely onto industry. If that’s the case, it could put Canadian resource industries at a disadvantage.
“How do we keep pushing up the carbon price — which means the price of energy — for these industries at a time when the United States has no carbon pricing at all?” Finlayson wonders.
Overall, Carney does seem to be moving in the right direction in terms of realigning Canada’s energy and climate policies.
“I think this version of a Liberal government is going to be more focused on investment and competitiveness and less focused around the virtue-signaling on climate change, even though Carney personally has a reputation as somebody who cares a lot about climate change,” Finlayson said.
“It’s an awkward dance for them. I think they are trying to set out a different direction relative to the Trudeau years, but they’re still trying to hold on to the Trudeau climate narrative.”
Pictured is Mark Carney at COP26 as UN Special Envoy on Climate Action and Finance. He is not at COP30 this week. UNRIC/Miranda Alexander-Webber
Resource Works News
Alberta
ChatGPT may explain why gap between report card grades and standardized test scores is getting bigger

From the Fraser Institute
By Paige MacPherson and Max Shang
In Alberta, the gap between report card grades and test/exam scores increased sharply in 2022—the same year ChatGPT came out.
Report card grades and standardized test scores should rise and fall together, since they measure the same group of students on the same subjects. But in Alberta high schools, report card grades are rising while scores on Provincial Achievement Tests (PAT) and diploma exams are not.
Which raises the obvious question—why?
Report card grades partly reflect student performance in take-home assignments. Standardized tests and diploma exams, however, quiz students on their knowledge and skills in a supervised environment. In Alberta, the gap between report card grades and test/exam scores increased sharply in 2022—the same year ChatGPT came out. And polling shows Canadian students now rely heavily on ChatGPT (and other AI platforms).
Here’s what the data show.
In Alberta, between 2016 and 2019 (the latest year of available comparable data), the average standardized test score covering math, science, social study, biology, chemistry, physics, English and French language arts was just 64, while the report card grade 73.3—or 14.5 per cent higher. Data for 2020 and 2021 are unavailable due to COVID-19 school closures, but between 2022 and 2024, the gap widened to 20 per cent. This trend holds regardless of school type, course or whether the student was male or female. Across the board, since 2022, students in Alberta high schools are performing significantly better in report card grades than on standardized tests.
Which takes us back to AI. According to a recent KPMG poll, 73 per cent of students in Canada (high school, vocational school, college and university) said they use generative AI in their schoolwork, an increase from the previous year. And 71 per cent say their grades improved after using generative AI.
If AI is simply used to aid student research, that’s one thing. But more than two-thirds (66 per cent) of those using generative AI said that although their grades increased, they don’t think they’re learning or retaining as much knowledge. Another 48 per cent say their “critical thinking” skills have deteriorated since they started using AI.
Acquiring knowledge is the foundation of higher-order thinking and critical analysis. We’re doing students a deep disservice if we don’t ensure they expand their knowledge while in school. And if teachers award grades, which are essentially inflated by AI usage at home, they set students up for failure. It’s the academic equivalent of a ski coach looking at a beginner and saying, “You’re ready for the black diamond run.” That coach would be fired. Awarding AI-inflated grades is not fair to students who will later struggle in college, the workplace or life beyond school.
Finally, the increasing popularity of AI underscores the importance of standardized testing and diploma exams. And parents knew this even before the AI wave. A 2022 Leger poll found 95 per cent of Canadian parents with kids in K-12 schools believe it’s important to know their child’s academic performance in the core subjects by a fair and objective measure. Further, 84 per cent of parents support standardized testing, specifically, to understand how their children are doing in reading, writing and mathematics. Alberta is one of the only provinces to administer standardized testing and diploma exams every year.
Clearly, parents should oppose any attempt to reduce accountability and objective testing in Alberta schools.
-

 Fraser Institute1 day ago
Fraser Institute1 day agoCourts and governments caused B.C.’s property crisis—they’re not about to fix it
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoChatGPT may explain why gap between report card grades and standardized test scores is getting bigger
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoIs America drifting toward civil war? Joe Rogan thinks so
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex2 days ago
Censorship Industrial Complex2 days agoEU’s “Democracy Shield” Centralizes Control Over Online Speech
-

 Alberta16 hours ago
Alberta16 hours agoFederal budget: It’s not easy being green
-

 Energy8 hours ago
Energy8 hours agoIt should not take a crisis for Canada to develop the resources that make people and communities thrive.
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoBondi and Patel deliver explosive “Clinton Corruption Files” to Congress
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoUS announces Operation Southern Spear, targeting narco-terrorists