Economy
Reliance on fossil fuels remains virtually unchanged despite trillions for ‘clean energy’

From the Fraser Institute
By Elmira Aliakbari, Julio Mejía, and Jason Clemens
” after tens of trillions of dollars spent on the transition away from fossil fuels, consumption declined by 3.8 percentage points as a share of total global energy. “
At COP28, the recent United Nations climate change conference in the United Arab Emirates, bureaucrats, politicians and activists from nearly 200 countries gathered to push for a “transition away from fossil fuels” and continue and indeed expedite efforts to achieve a global net-zero “carbon footprint” by 2050. However, despite significant spending on clean energy, the world’s dependence on fossil fuels remains largely unaffected, calling into question how realistic the commitment to zero emissions by 2050 is in the real world.
The UN staged the first “COP” conference in Berlin in 1995, marking the beginning of a collaborative international effort of energy transition and decarbonization. According to one report, global investment in renewable energy totalled US$7 billion in 1995.
Today, according to the latest data from the International Energy Agency (IEA), investment in “clean energy” by both governments and private industry reached more than US$1.7 trillion in 2023. That’s roughly the equivalent of the entire Australian economy this year. This spending includes more than just renewable power (wind, solar, etc.), which totalled $659 billion in 2023, but also electric vehicles, battery storage, nuclear, carbon capture and more.
More broadly, according to the IEA numbers, from 2015 to 2023, governments and industry worldwide have spent $11.7 trillion (inflation-adjusted) on clean energy. For context, this is basically the equivalent of all the goods and services produced in Germany, Japan and the United Kingdom combined in 2023. Simply put, an extraordinary amount of money and resources have been allocated to the transition away from fossil fuels for the better part of three decades.
So, what’s the return on this investment?
According to data from the Statistical Review of World Energy, from 1995 to 2022, the amount of fossil fuels (oil, gas and coal) consumed worldwide actually increased by 58.6 per cent. Specifically, oil consumption increased by 34.2 per cent, natural gas by 86.7 per cent and coal by 72.7 per cent.
There was, however, a small decline in the share of total energy provided by oil, gas and coal during that time period, falling from 85.6 per cent of total energy use in 1995 to 81.8 per cent in 2022. In other words, after tens of trillions of dollars spent on the transition away from fossil fuels, consumption declined by 3.8 percentage points as a share of total global energy.
Meanwhile, renewables increased from 0.6 per cent of total energy to 7.5 per cent over the same period but both nuclear and hydro declined (6.5 per cent to 4.0 per cent and 7.3 per cent to 6.7 per cent, respectively). In other words, the 3.8-percentage point decline in fossil fuels as a share of total energy in 2022 was offset by a net increase in clean energy of the same amount.
In addition to the massive amounts of spending, much of it paid for by taxpayers, this transition has come with other costs. Renewable sources such as wind and solar are not always available and therefore require back-up energy systems. Lack of investment in back-up systems and required infrastructure has resulted in marked price increases in energy and/or blackouts in parts of Europe and the United States.
At COP28, conference attendees including Canada’s Environment Minister Steven Guilbeault pledged to reach net-zero emissions—that our economy will emit no greenhouse gas emissions or offset its emissions—in 26 years. But given the trillions spent, the limited progress in reducing global reliance on fossil fuels, and the price increases and reduced energy reliability in countries that have meaningfully transitioned, that goal seems unrealistic in the real world.
Authors:
2025 Federal Election
Canada drops retaliatory tariffs on automakers, pauses other tariffs

 MxM News
MxM News
Quick Hit:
Canada has announced it will roll back retaliatory tariffs on automakers and pause several other tariff measures aimed at the United States. The move, unveiled by Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne, is designed to give Canadian manufacturers breathing room to adjust their supply chains and reduce reliance on American imports.
Key Details:
- Canada will suspend 25% tariffs on U.S. vehicles for automakers that maintain production, employment, and investment in Canada.
- A broader six-month pause on tariffs for other U.S. imports is intended to help Canadian sectors transition to domestic sourcing.
- A new loan facility will support large Canadian companies that were financially stable before the tariffs but are now struggling.
Diving Deeper:
Ottawa is shifting its approach to the escalating trade war with Washington, softening its economic blows in a calculated effort to stabilize domestic manufacturing. On Tuesday, Finance Minister François-Philippe Champagne outlined a new set of trade policies that provide conditional relief from retaliatory tariffs that have been in place since March. Automakers, the hardest-hit sector, will now be eligible to import U.S. vehicles duty-free—provided they continue to meet criteria that include ongoing production and investment in Canada.
“From day one, the government has reacted with strength and determination to the unjust tariffs imposed by the United States on Canadian goods,” Champagne stated. “We’re giving Canadian companies and entities more time to adjust their supply chains and become less dependent on U.S. suppliers.”
The tariff battle, which escalated in April with Canada slapping a 25% tax on U.S.-imported vehicles, had caused severe anxiety within Canada’s auto industry. John D’Agnolo, president of Unifor Local 200, which represents Ford employees in Windsor, warned the BBC the situation “has created havoc” and could trigger a recession.
Speculation about a possible Honda factory relocation to the U.S. only added to the unrest. But Ontario Premier Doug Ford and federal officials were quick to tamp down the rumors. Honda Canada affirmed its commitment to Canadian operations, saying its Alliston facility “will operate at full capacity for the foreseeable future.”
Prime Minister Mark Carney reinforced the message that the relief isn’t unconditional. “Our counter-tariffs won’t apply if they (automakers) continue to produce, continue to employ, continue to invest in Canada,” he said during a campaign event. “If they don’t, they will get 25% tariffs on what they are importing into Canada.”
Beyond the auto sector, Champagne introduced a six-month tariff reprieve on other U.S. imports, granting time for industries to explore domestic alternatives. He also rolled out a “Large Enterprise Tariff Loan Facility” to support big businesses that were financially sound prior to the tariff regime but have since been strained.
While Canada has shown willingness to ease its retaliatory measures, there’s no indication yet that the U.S. under President Donald Trump will reciprocate. Nevertheless, Ottawa signaled its openness to further steps to protect Canadian businesses and workers, noting that “additional measures will be brought forward, as needed.”
Business
DOGE Is Ending The ‘Eternal Life’ Of Government


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By David Bossie
In his 1964 “A Time For Choosing” speech, Ronald Reagan famously said, “a government bureau is the nearest thing to eternal life we’ll ever see on this earth.” And for more than 60 years, President Reagan’s words have proven to be true. However, with the historic re-election of President Donald Trump and the creation of the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) under the leadership of Elon Musk, the Gipper’s contention is finally being challenged – and not a moment too soon.
The Trump Administration inherited a horribly bloated federal government in dire need of common sense streamlining from top to bottom. For decades, the executive branch has expanded at an incomprehensible rate and along with it, so has waste, fraud, and abuse. Presidents on both sides of the aisle have made promises to tighten the government’s belt, shrink the bureaucracy, and return power to the people where it belongs. Those efforts for the most part – however well-intentioned – never got off the ground. The reality is that when politicians have been forced to choose between a legislative priority and cutting government spending, cuts are always the first casualty. But currently, with our $36 trillion national debt spiraling out of control, reining in the size and scope of government is no longer a choice, but a necessity.
President Trump is the perfect leader for these trying times. He’s battletested and fears nothing – and no challenge is too large. Whether it’s securing the border, growing the economy, forging peace in Ukraine and the Middle East, or negotiating fair trade deals, this president is on a mission to save America. And if any chief executive is going to have success at deconstructing the administrative state, it’s Trump the steel-spined change agent. The shadowy deep state doesn’t scare him, the biased liberal media can’t intimidate him, and this time there are no phony partisan investigations aiming to sidetrack him. Trump made a promise to bring fiscal responsibility back to governing, and along with Musk and DOGE, they’re finally conducting the “audit with teeth” that the American people have been waiting for, and their hard work is turning out to be infectious.
Dear Readers:
As a nonprofit, we are dependent on the generosity of our readers.
Please consider making a small donation of any amount here. Thank you!
With each passing day, a different member of the cabinet is announcing a new cut, discovering a duplicative program, or updating an antiquated system to steer us away from the fiscal cliff that’s rapidly approaching. When the president also happens to be a highly successful businessman, making the business operate more smoothly and for less money is the name of the game. Trump has brought this mindset to the White House and according to recent polling 77 percent favor a full review of government spending.
President Trump is going back to the basics that have become taboo in Washington, like asking fundamental questions about whether an agency has been successful in its mission or if a program is still necessary. In the case of the Education Department, Trump sees an emergency and is not willing to kick the can down the road any longer. The president believes that education excellence for our children is essential so America can compete for generations to come. Drastic reform is long overdue and that means moving education decisions back to state and local officials – and parents. That’s why President Trump is taking the steps to confront the failed status quo and close the underperforming department so we can turnaround lackluster public schools and low-test scores.
Similarly, with the decision to end USAID and slash foreign aid, Trump and DOGE are simply putting America first. America is handing out billions upon billions in taxpayer dollars around the globe on programs that should be spent on fixing our own domestic problems. The plan to decentralize and modernize the Agriculture Department is another great example of thinking outside the box. The American people understand the rationale that downtown Washington, D.C. is the last place decisions about farming should be made. Relocating the department to various hubs around the heartland is common sense.
Additionally, the announcement that the Department of Health and Human Services will cut 20,000 full-time employees is part of President Trump’s vision to “right-size the federal government and unleash the private sector again” in the words of Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent. And word that the Trump Administration is planning to work with Congress to finally defund National Public Radio and the Public Broadcasting Service is welcome news to millions of Americans who believe sending taxpayer funds to biased news outlets is wrong.
DOGE is also doing courageous work at the Social Security Administration (SSA). The amazing efforts to identify individuals who are either deceased, in the country illegally, or otherwise ineligible will help stave off the program’s insolvency, which experts predict is only ten years away. When a DOGE official disclosed that 40 percent of the calls made to SSA are from would-be fraudsters trying to exploit the system, it’s become all too obvious that new safeguards must be adopted.
When it comes to the question of how much money DOGE will ultimately end up saving taxpayers, in the context of our $36 trillion debt crisis, the more the better. However, the overall change in mindset – forcing government to operate efficiently and responsibly like businesses and families – and passing that mindset onto future administrations is perhaps the most critical shift that can be made. In fact, in an ideal scenario, every state, county, and city would have its very own DOGE operation. We must get serious about cutting government waste now or we’ll go bankrupt. That’s just the reality of the situation and President Trump knows it.
David Bossie is the president of Citizens United and served as a senior adviser to the Trump-Pence 2020 campaign. In 2016, Bossie served as deputy campaign manager for Donald J. Trump for President and deputy executive director for the Trump-Pence Transition Team.
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoTrump Executive Orders ensure ‘Beautiful Clean’ Affordable Coal will continue to bolster US energy grid
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoBREAKING from THE BUREAU: Pro-Beijing Group That Pushed Erin O’Toole’s Exit Warns Chinese Canadians to “Vote Carefully”
-
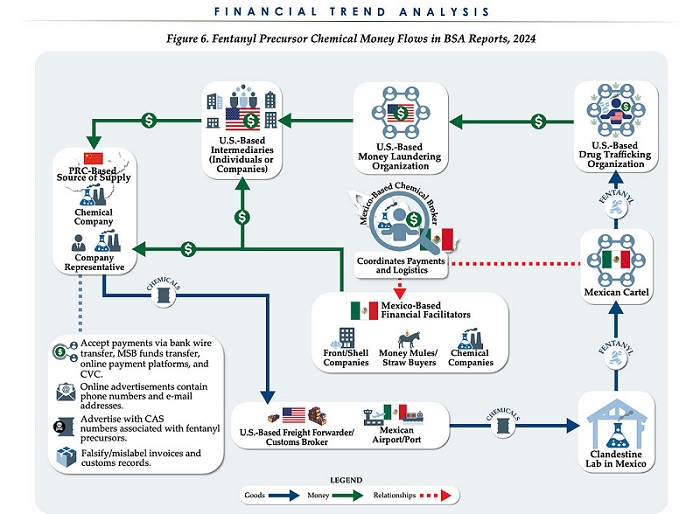
 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoChina, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoTamara Lich and Chris Barber trial update: The Longest Mischief Trial of All Time continues..
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoTucker Carlson Interviews Maxime Bernier: Trump’s Tariffs, Mass Immigration, and the Oncoming Canadian Revolution
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoAllegations of ethical misconduct by the Prime Minister and Government of Canada during the current federal election campaign
-

 Energy1 day ago
Energy1 day agoStraits of Mackinac Tunnel for Line 5 Pipeline to get “accelerated review”: US Army Corps of Engineers
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDOGE Is Ending The ‘Eternal Life’ Of Government









