Censorship Industrial Complex
JK Rowling dares Scottish police to arrest her over new ‘hate crime’ law threatening free speech

From LifeSiteNews
‘If what I’ve written here qualifies as an offence under the terms of the new act, I look forward to being arrested when I return to the birthplace of the Scottish Enlightenment,’ the ‘Harry Potter’ creator said.
Harry Potter creator J.K. Rowling is striking a defiant tone in the face of a new Scottish law that many fear will effectively criminalize free speech on subjects such as biological sex and “gender identity.”
The Hate Crime and Public Order (Scotland) Act, passed in 2021 but only now taking effect, consolidates various preexisting “hate crime” statutes while also creating a new offense, “threatening or abusive behaviour which is intended to stir up hatred” on the basis of age, disability, religion, sexual orientation, transgender identity, or variations in sex characteristics.
As covered by The Guardian and The Scotsman, various individuals and groups have raised objections to the law, including MP Joanna Cherry, who predicts it “will be weaponized by trans rights activists to try to silence, and worse still criminalize, women who do not share their beliefs”; said the Scottish Family Party, who says it will mean the “death” of free speech; and the Association of Scottish Police Superintendents and Scottish Police Federation, who fear it will overtax police forces inadequately trained to handle the influx of new offenses.
Scotland First Minister Humza Yousaf, who championed the law, insists that abuse will be prevented by a “very high threshold” for prosecuting cases and protects freedom of expression in a variety of ways, including a “reasonableness” defense. Ex-Tory MSP Adam Tomkins claims that simply “asserting that sex is a biological fact or that it is not changed just by virtue of the gender by which someone chooses to identify is not and never can be a hate crime under this legislation.”
Such assurances hit a snag, however, when calls to prosecute Rowling under the law prompted Scotland’s Community Safety Minister Siobhian Brown to walk back her initial assurances that “misgendering” would “not at all” violate the law, The Telegraph reported. “It could be reported and it could be investigated,” she said, “whether or not the police would think it was criminal is up to Police Scotland for that.”
On Monday, Rowling shared a lengthy Twitter/X thread of examples of “trans women” (i.e., men) and pro-LGBT activists she suggested were now a “protected category” despite their violent, abusive acts and/or hateful behavior, using the hashtag #ArrestMe to effectively dare the authorities to persecute her.
“The new legislation is wide open to abuse by activists who wish to silence those of us speaking out about the dangers of eliminating women’s and girls’ single-sex spaces, the nonsense made of crime data if violent and sexual assaults committed by men are recorded as female crimes, the grotesque unfairness of allowing males to compete in female sports, the injustice of women’s jobs, honours and opportunities being taken by trans-identified men, and the reality and immutability of biological sex,” she wrote. “For several years now, Scottish women have been pressured by their government and members of the police force to deny the evidence of their eyes and ears, repudiate biological facts and embrace a neo-religious concept of gender that is unprovable and untestable.”
“I’m currently out of the country, but if what I’ve written here qualifies as an offence under the terms of the new act, I look forward to being arrested when I return to the birthplace of the Scottish Enlightenment,” Rowling added.
Scotland's Hate Crime Act comes into effect today. Women gain no additional protections, of course, but well-known trans activist Beth Douglas, darling of prominent Scottish politicians, falls within a protected category. Phew! 1/11 pic.twitter.com/gCKGwdjr5m
— J.K. Rowling (@jk_rowling) April 1, 2024
Fragile flower Katie Dolatowski, 6'5", was rightly sent to a women's prison in Scotland after conviction. This ensured she was protected from violent, predatory men (unlike the 10-year-old girl Katie sexually assaulted in a women's public bathroom.) 3/11 pic.twitter.com/13J5XfRo3a
— J.K. Rowling (@jk_rowling) April 1, 2024
Scottish woman and butcher Amy George abducted an 11-year-old girl while dressed in female clothing. No idea why this was mentioned in court – of course she was wearing women’s clothing, she's a woman! Amy took the girl home and sexually abused her over a 27-hour period. 5/11 pic.twitter.com/xy3DmnqZrc
— J.K. Rowling (@jk_rowling) April 1, 2024
Mridul Wadhwa, head of a Scottish rape crisis centre, says, ‘sexual violence happens to bigoted people as well.’ She has no gender recognition certificate, but was still appointed to a job advertised for women only. Time to be ‘challenged on your prejudices’, rape victims! 7/11 pic.twitter.com/YfxUhbh6cw
— J.K. Rowling (@jk_rowling) April 1, 2024
Katie Neeves has been appointed as the UN Women UK delegate. She switched from straight man to lesbian at the age of 48 and, in a leaked 2022 webinar, described how she used to enjoy stealing and wearing her sister’s underwear. A truly relatable representative! 9/11 pic.twitter.com/VKzF7IuJTU
— J.K. Rowling (@jk_rowling) April 1, 2024
🎉🌼🌸April Fools! 🌸🌼🎉
Only kidding. Obviously, the people mentioned in the above tweets aren't women at all, but men, every last one of them.
In passing the Scottish Hate Crime Act, Scottish lawmakers seem to have placed higher value on the feelings of men performing their…
— J.K. Rowling (@jk_rowling) April 1, 2024
Rowling, whose Potter novels are the best-selling book series in the world, has long been known as a doctrinaire liberal on most issues, in 2007 going so far as to retroactively add a same-sex relationship to the backstory of Harry’s mentor Albus Dumbledore, despite the character’s sexual attraction not being referenced in the books themselves or their film adaptations (until briefly being alluded to in the third film of the Fantastic Beasts spinoff series).
Even so, Rowling has been deemed a bigot by pro-LGBT activists for refusing to go along with the notions that gender is a social construct that may be changed at will, or that life-altering surgical or chemical “transition” procedures are appropriate for confused minors. In recent years, despite intense cultural pressure, she has only grown bolder in opposing the transgender lobby’s detrimental impacts on children as well as actual women.
2025 Federal Election
Mark Carney Vows Internet Speech Crackdown if Elected


By
Mark Carney dodges Epstein jabs in Hamilton while reviving failed Liberal plans for speech control via Bill C-36 and Bill C-63.
|
It was supposed to be a routine campaign pit stop, the kind of low-stakes political affair where candidates smile like used car salesmen and dish out platitudes thicker than Ontario maple syrup. Instead, Mark Carney found himself dodging verbal bricks in a Hamilton hall, facing hecklers who lobbed Jeffrey Epstein references like Molotovs. No rebuttal, no denial. Just a pivot worthy of an Olympic gymnast, straight to the perils of digital discourse.
“There are many serious issues that we’re dealing with,” he said, ignoring the criticism that had just lobbed his way. “One of them is the sea of misogyny, antisemitism, hatred, and conspiracy theories — this sort of pollution online that washes over our virtual borders from the United States.”
Ah yes, the dreaded digital tide. Forget inflation or the fact that owning a home now requires a GoFundMe. According to Carney, the real catastrophe is memes from Buffalo.
The Ghost of Bills Past
Carney’s new plan to battle the internet; whatever it may be, because details are apparently for peasants, would revive a long-dead Liberal Party obsession: regulating online speech in a country that still pretends to value free expression.
It’s an effort so cursed, it’s been killed more times than Jason Voorhees. First, there was Bill C-36, which flopped in 2021. Then came its undead cousin, Bill C-63, awkwardly titled the Online Harms Act, which proposed giving the Canadian Human Rights Commission the power to act as digital inquisitors, sniffing out content that “foments detestation or vilification.”
Naturally, it died too, not from public support, but because Parliament decided it had better things to do, like not passing it in time.
But as every horror franchise teaches us, the villain never stays away for long. Carney’s speech didn’t include specifics, which is usually code for “we’ll make it up later,” but the intent is clear: the Liberals are once again oiling up the guillotine of speech regulation, ready to let it fall on anything remotely edgy, impolite, or, God forbid, unpopular.
“Won’t Someone Think of the Children?”
“The more serious thing is when it affects how people behave — when Canadians are threatened going to their community centers or their places of worship or their school or, God forbid, when it affects our children,” Carney warned, pulling the emergency brake on the national sympathy train. It’s the same tired tactic every aspiring control freak uses, wrap the pitch in the soft fuzz of public safety and pray nobody notices the jackboot behind the curtain.
Nothing stirs the legislative loins like invoking the children. But vague terror about online contagion infecting impressionable minds has become the go-to excuse for internet crackdowns across the Western world. Canada’s Liberals are no different. They just dress it up and pretend it’s for your own good.
“Free Speech Is Important, But…”
Former Heritage Minister Pascale St-Onge, doing her best impression of a benevolent censor, also piped up earlier this year with a classic verbal pretzel: “We need to make sure [freedom of expression] exists and that it’s protected. Yet the same freedom of expression is currently being exploited and undermined.”
Protecting free speech by regulating it is the sort of logic that keeps satire writers out of work.
St-Onge’s lament about algorithms monetizing debate sounds suspiciously like a pitch from someone who can’t get a word in on X. It’s the familiar cry of technocrats and bureaucrats who can’t fathom a world where regular people might say things that aren’t government-approved. “Respect is lacking in public discourse,” she whined on February 20. She’s right. People are tired of pretending to respect politicians who think governing a country means babysitting the internet.
|
|
|
|
Powerful forces want to silence independent voices online
|
|
Governments and corporations are working hand in hand to control what you can say, what you can read; and soon, who you are allowed to be.
New laws promise to “protect” you; but instead criminalize dissent.
Platforms deplatform, demonetize, and disappear accounts that step out of line.
AI-driven surveillance tracks everything you do, feeding a system built to monitor, profile, and ultimately control.
Now, they’re pushing for centralized digital IDs; a tool that could link your identity to everything you say and do online. No anonymity. No privacy. No escape.
This isn’t about safety, it’s about power.
If you believe in a truly free and open internet; where ideas can be debated without fear, where privacy is a right, and where no government or corporation dictates what’s true; please become a supporter.
By becoming a supporter, you’ll help us:
We don’t answer to advertisers or political elites.
If you can, please become a supporter. It takes less than a minute to set up, you’ll get a bunch of extra features, guides, analysis and solutions, and every donation strengthens the fight for online freedom.
|
|
2025 Federal Election
Mark Carney To Ban Free Speech if Elected


 Dan Knight
Dan Knight
The former central banker, who now postures as a man of the people, made it clear that if the Liberals are re-elected, the federal government will intensify efforts to regulate what Canadians are allowed to see, say, and share online.
At a campaign rally in Hamilton, Ontario, Liberal leader Mark Carney unveiled what can only be described as a coordinated assault on digital freedom in Canada. Behind the slogans, applause lines, and empty rhetoric about unity, one portion of Carney’s remarks stood out for its implications: a bold, unapologetic commitment to controlling online speech under the guise of “safety” and “misinformation.”
“We announced a series of measures with respect to online harm… a sea of misogyny, anti-Semitism, hatred, conspiracy theories—the sort of pollution that’s online that washes over our virtual borders from the United States.”
He then made clear his intention to act:
“My government, if we are elected, will be taking action on those American giants who come across [our] border.”
The former central banker, who now postures as a man of the people, made it clear that if the Liberals are re-elected, the federal government will intensify efforts to regulate what Canadians are allowed to see, say, and share online. His language was deliberate. Carney condemned what he called a “sea of misogyny, anti-Semitism, hatred, conspiracy theories” polluting Canada’s internet space—language borrowed directly from the Trudeau-era playbook. But this wasn’t just a moral denunciation. It was a legislative preview.
Carney spoke of a future Liberal government taking “action on those American giants who come across our borders.” Translation: he wants to bring Big Tech platforms under federal control, or at least force them to play the role of speech enforcers for the Canadian state. He blamed the United States for exporting “hate” into Canada, reinforcing the bizarre Liberal narrative that the greatest threat to national unity isn’t foreign actors like the CCP or radical Islamists—it’s Facebook memes and American podcasts.
But the most revealing moment came when Carney linked online speech directly to violence. He asserted that digital “pollution” affects how Canadians behave in real life, specifically pointing to conjugal violence, antisemitism, and drug abuse. This is how the ground is prepared for censorship: first by tying speech to harm, then by criminalizing what the state deems harmful.
What Carney didn’t say is just as important. He made no distinction between actual criminal incitement and political dissent. He offered no assurance that free expression—a right enshrined in Canada’s Charter of Rights and Freedoms—would be respected. He provided no definition of what constitutes a “conspiracy theory” or who gets to make that determination. Under this framework, any criticism of government policy, of global institutions, or of the new technocratic order could be flagged, throttled, and punished.
And that’s the point.
Mark Carney isn’t interested in dialogue. He wants obedience. He doesn’t trust Canadians to discern truth from fiction. He believes it’s the job of government—his government—to curate the national conversation, to protect citizens from wrongthink, to act as referee over what is and isn’t acceptable discourse. In short, he wants Ottawa to become the Ministry of Truth.
Why They Don’t Actually Care About Antisemitism
The Liberal establishment talks a big game about fighting hate—but when it comes to actual antisemitic violence, they’ve shown nothing but selective enforcement and political cowardice.
Let’s look at the facts.
In 2023, B’nai Brith Canada recorded nearly 6,000 antisemitic incidents, including 77 violent attacks—from firebombed synagogues to shots fired at Jewish schools in Montreal and Toronto. This wasn’t a marginal increase. It was a 208% spike in violent antisemitism in a single year.
Statistics Canada echoed the same alarm bells. Jews—who make up just 1% of Canada’s population—were the victims of 70% of all religiously motivated hate crimes. That’s nearly 900 recorded incidents, up 71% from the previous year. Then came October 2023, when Hamas launched its attack on Israel—and the wave of hate turned into a tsunami: a 670% increase in antisemitic incidents across the country. Jewish schools, synagogues, and community centers were hit with bomb threats, arson attempts, and intimidation campaigns. This was a national security issue, not just a policing matter.
And yet, the government’s response? Virtually nonexistent.
Case in point: the Montreal Riot, November 2024. A 600-person mob, waving anti-NATO and pro-Palestinian banners, turned violent—setting fires, smashing windows, and attacking police. Amid this chaos, a man was filmed screaming “Final Solution”—a direct reference to the Nazi plan to exterminate the Jews. It went viral. There was no ambiguity, no misunderstanding. It was a public call for genocide.
So what happened?
Three arrests. None for hate crimes. None related to antisemitism. Montreal Police Chief Fady Dagher insisted there were “no confirmed antisemitic acts,” and as of early 2025, no hate crime charges have been filed against the individual caught on camera.
That man, as it turns out, owned a Second Cup franchise. His punishment? His café was shut down by the company. Not by law enforcement. Not by hate crime investigators. A corporate HR department showed more backbone than Canada’s justice system.
And this is what reveals the truth: they don’t care. They’ll enforce hate speech laws when it’s politically convenient—when it can be used to silence critics, crush dissent, or placate woke constituencies. But when Jewish communities are being threatened, attacked, and terrorized? The same laws suddenly go limp. The same political class that claims to protect minorities becomes paralyzed. They won’t touch it. Because confronting real antisemitism would require standing up to their political allies in activist circles, university campuses, and radical protest movements.
This isn’t an accident. It’s a pattern.
The Liberals aren’t weak on antisemitism because they’re unaware of it. They’re weak on it because they don’t see political value in enforcing the law when it conflicts with their ideological allies. Their obsession isn’t with hate speech—it’s with controlling “wrong” speech. And what qualifies as “wrong” isn’t defined by law or principle. It’s defined by what the Liberal establishment deems unacceptable.
Their target isn’t violent bigotry. It’s dissent. They’ll chase down citizens for questioning carbon taxes or criticizing globalist policy—but when Jewish schools get shot at, or someone calls for genocide in the street, they shrug.
This isn’t leadership. It’s selective justice. And it proves, beyond any doubt, that their agenda was never about protecting Canadians. It was always about protecting control.
The Online Harms Act: Carney’s Blueprint for Speech Control
This isn’t hypothetical. Mark Carney’s remarks in Hamilton mirror the exact logic and intent behind the Online Harms Act (Bill C-63)—legislation drafted under the Liberal banner and introduced in 2024 that pushes Canada into territory no free society should accept.
At its core, Bill C-63 hands the federal government sweeping powers to police digital speech. It creates a Digital Safety Commission, an unelected bureaucratic authority empowered to monitor, investigate, and punish online platforms and individuals for content deemed “harmful.” That word—harmful—is never concretely defined. It includes things like “hate speech,” “conspiracy theories,” and vague notions of “harm to children,” but it’s written broadly enough to be used as a political weapon.
The most chilling provision? Preemptive imprisonment. Under this law, Canadians could be jailed for up to a year—without having committed a crime—if a judge believes they might post something harmful in the future. This isn’t law enforcement. This is thought policing.
Carney didn’t just echo this approach—he amplified it. In his Hamilton rally, he described the internet as being flooded with “misogyny, anti-Semitism, hatred, conspiracy theories,” and laid blame on foreign content “washing over our borders from the United States.” He didn’t argue for open debate or for empowering users to challenge dangerous ideas. He argued for the state to intervene and shut them down.
He told Canadians that these ideas are “changing how people behave” and claimed his government will go after “those American giants” that allow this content to circulate. There’s no ambiguity here: this is a public declaration that a Liberal government under Mark Carney intends to censor, de-platform, and penalize dissenting views. Not illegal ones—just ones they don’t like.
And this isn’t new for him. Back in 2022, during the Freedom Convoy, Carney referred to protesters as committing “sedition” and demanded the government “thoroughly punish” them. These weren’t violent rioters or foreign agitators—these were working-class Canadians honking their horns and standing in the cold, protesting vaccine mandates. For Carney, their real crime was disobedience.
Carney’s view of speech is simple: if it challenges the ruling order, it’s dangerous. And now, with Bill C-63 on the table and Carney at the helm, he’s building the legal infrastructure to lock down the digital public square—not to protect Canadians from violence, but to protect the Liberal establishment from criticism.
That law is real. Carney’s agenda is real. And if he wins, enforcement is coming.
Final thoughts
This is the Canada Mark Carney envisions—one where citizens can’t speak freely online without first checking their views against government guidelines. A country where speech is no longer a right but a privilege granted by bureaucrats. A country where opposition isn’t argued with, it’s labeled harmful and erased.
There was a time when Liberals championed civil liberties. That era is over. The new Liberalism is authoritarian—cloaked in the language of safety and inclusion, but animated by control. Carney’s rally in Hamilton wasn’t a policy rollout. It was a warning to anyone who still thinks they live in a country where dissent is allowed.
They don’t want to fight hate. They want to define “wrong” speech—and then eliminate it. And by “wrong,” they mean anything the Liberal establishment disapproves of. Criticize the government, question the orthodoxy, challenge the state’s narrative, and you’ll be branded a threat. Not a citizen. Not a participant. A threat.
So here we are.
The speech laws are written. The censors are waiting. And Mark Carney is ready to pull the trigger.
This election isn’t about tax credits or campaign slogans. It’s about whether Canada remains a free country or slides deeper into soft tyranny, one regulation, one commission, one silenced voice at a time.
There is a choice. And the choice is this: bring it home—restore freedom, restore sanity, restore this country.
Or: hand the keys to the same people who think you’re the problem for having the nerve to think for yourself.
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoRCMP Whistleblowers Accuse Members of Mark Carney’s Inner Circle of Security Breaches and Surveillance
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoMEI-Ipsos poll: 56 per cent of Canadians support increasing access to non-governmental healthcare providers
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoAI-Driven Election Interference from China, Russia, and Iran Expected, Canadian Security Officials Warn
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoTrump admin directs NIH to study ‘regret and detransition’ after chemical, surgical gender transitioning
-
 Business6 hours ago
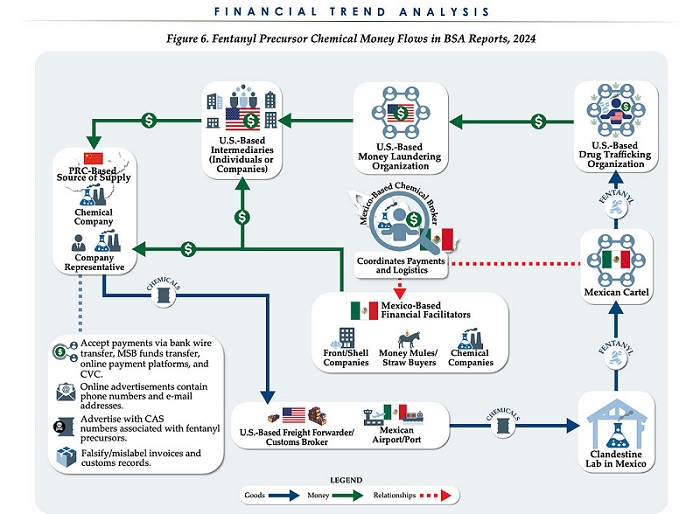
Business6 hours agoChina, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoBureau Exclusive: Chinese Election Interference Network Tied to Senate Breach Investigation
-

 2025 Federal Election16 hours ago
2025 Federal Election16 hours agoTucker Carlson Interviews Maxime Bernier: Trump’s Tariffs, Mass Immigration, and the Oncoming Canadian Revolution
-

 Daily Caller4 hours ago
Daily Caller4 hours agoTrump Executive Orders ensure ‘Beautiful Clean’ Affordable Coal will continue to bolster US energy grid