Business
It’s Time for Canadians to Challenge the American Domination of the LNG Space

From EnergyNow.Ca
By Susan McArthur
Canada is now among the top 10 countries with natural gas reserves. It’s time to take advantage of that
Canadians are starting to understand the Americans ate our breakfast, lunch and dinner when it comes to selling liquefied natural gas (LNG) on the global market while simultaneously undermining our national security.
They are finally waking up to the importance of the urgent request by oil and gas CEOs to all federal party leaders calling for the removal of legislation and regulation impeding and capping the development of our resources.
The LNG story in the United States is one of unprecedented growth, according to a recent Atlantic Council report by Daniel Yergin and Madeline Jowdy. Ten years ago, the U.S. did not export a single tonne of LNG. Today, U.S. exports account for 25 per cent of the global market and have contributed US$400 billion to its gross domestic product (GDP) over the past decade.
The U.S. is now the world’s largest LNG supplier, edging out Qatar and Australia, and according to Yergin and Jowdy, its export market is on track to contribute US$1.3 trillion to U.S. GDP by 2040 and create an average of 500,000 jobs annually.
Last week, Alberta announced a sixfold increase in its proven natural gas reserves to 130 trillion cubic feet (tcf). The new figures push Canada into the top 10 countries with natural gas reserves.
Unfortunately, notwithstanding this vast resource, Canada didn’t even make it to the LNG party and the Americans have been laughing all the way to the bank at Canada’s expense. Our decade-long anti-pipeline and natural resource agenda has cost us dearly and Donald Trump’s trade tariffs are a stake to the heart.
As the world grapples with global warming, natural gas is the perfect transition fuel. It generates half the CO2 emissions of coal, provides needed grid backup for intermittent renewable wind and solar power, and it is relatively easy to commission.
Canada has extensive natural gas reserves, but these reserves are less valuable if we can’t get them to offshore markets where countries will pay a premium for energy generation. Canadian gas is abundant, but, given our smaller market, typically trades at a discount to U.S. gas and a massive discount to European and Asian markets.
The capital-intensive nature of LNG facilities requires long-term supply contracts. Generally, 20-year supply contracts with creditworthy counterparties are required to secure the financing required to build gas infrastructure and liquefaction plants.
For example, as part of a larger strategic deal, Houston-based LNG company NextDecade Corp. signed a 20-year offtake agreement to supply 5.4 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) to French multinational TotalEnergies SE.
As the market grows and matures, the spot market is gaining share, but term contracts continue to represent most of the market. This is a problem for Canada as it tries to break into the market, as much of current and future demand is already committed.
More than half the current LNG market demand, or 225 mtpa, is under contract until 2040, according to Shell PLC’s LNG outlook report for 2024. A further 100 mtpa is contracted to 2045. Shell recently revised its LNG market growth forecast upward to 700 mtpa by 2040 and it estimates the LNG supply currently in operation or under construction already accounts for about 525 mtpa, or almost 75 per cent of the estimated market in 2040.
Even if Canada secured 100 per cent of the available market share (impossible), this represents a fraction of the 130 trillion cubic feet of reserves in Alberta and an infinitesimal amount of Canada’s natural gas reserve.
If Canada wants to sell its LNG to the global market, it needs to be at the starting line now. Canada has seven LNG export projects in various stages of development. They are all in British Columbia. The capacity of these export plants is 50 mtpa and the capital cost is estimated to be $110 billion.
After significant delays and cost overruns, our first export facility, LNG Canada’s 14 mtpa Phase 1 in Kitimat, is set to ship its first cargo to Asia later this year. Phase 2, representing a further 14 mtpa, is still awaiting a final investment decision. The Cedar LNG, Ksi Lisims LNG and Woodfibre LNG projects are licensed, at various stages of development and represent a further 17 mtpa.
Canada’s LNG exports today are a drop in the bucket compared to both our potential and the 88 mtpa exported by the U.S. in 2024. We have one project completed and, if history repeats itself and Canada doesn’t get its act together, the runway for the remaining licensed projects will be long, painful and costly.
Financing large capital projects requires predictability with respect to timing and cost. This is also a problem for Canada. As the oil and gas CEOs have pointed out, LNG market players have lost trust in Canada as an investible jurisdiction for these projects.
In the face of Trump’s trade war, Canadians have become pipeline evangelists. Wishful thinking and political talking points won’t be enough if we repeat our decade of own goals on this file. We have literally left billions on the table.
Governments should fast-track all licensed projects, limit special interest distractions and provide the required muscle and financial support to get these projects up and running as soon as possible.
From Churchill, Man., to Quebec to the Maritimes to British Columbia, we should be making plans for LNG terminals and the required pipeline infrastructure to get this valuable and clean resource to market. And Canadians should pray we haven’t totally missed the market.
Susan McArthur is a former venture capital investor, investment banker and current corporate director. She has previously served on a chemical logistics and oil service board.
2025 Federal Election
MEI-Ipsos poll: 56 per cent of Canadians support increasing access to non-governmental healthcare providers

-
Most believe private providers can deliver services faster than government-run hospitals
-
77 per cent of Canadians say their provincial healthcare system is too bureaucratic
Canadians are increasingly in favour of breaking the government monopoly over health care by opening the door to independent providers and cross-border treatments, an MEI-Ipsos poll has revealed.
“Canadians from coast to coast are signalling they want to see more involvement from independent health providers in our health system,” explains Emmanuelle B. Faubert, economist at the MEI. “They understand that universal access doesn’t mean government-run, and that consistent failures to deliver timely care in government hospitals are a feature of the current system.”
Support for independent health care is on the rise, with 56 per cent of respondents in favour of allowing patients to access services provided by independent health entrepreneurs. Only 25 per cent oppose this.
In Quebec, support is especially strong, with 68 per cent endorsing this change.
Favourable views of accessing care through a mixed system are widespread, with three quarters of respondents stating that private entrepreneurs can deliver healthcare services faster than hospitals managed by the government. This is up four percentage points from last year.
Countries like Sweden and France combine universal coverage with independent providers and deliver faster, more accessible care. When informed about how these health systems run, nearly two in three Canadians favour adopting such models.
The poll also finds that 73 per cent of Canadians support allowing patients to receive treatment abroad with provincial coverage, which could help reduce long wait times at home.
Common in the European Union, this “cross-border directive” enabled 450,000 patients to access elective surgeries in 2022, with costs reimbursed as if they had been treated in their home country.
There’s a growing consensus that provincial healthcare systems are overly bureaucratic, with the strongest agreement in Alberta, B.C., and Quebec. The proportion of Canadians holding this view has risen by 16 percentage points since 2020.
Nor do Canadians see more spending as being a solution: over half say the current pace of healthcare spending in their province is unsustainable.
“Governments shouldn’t keep doubling down on what isn’t working. Instead, they should look at what works abroad,” says Ms. Faubert. “Canadians have made it clear they want to shift gears; now it’s up to policymakers to show they’re listening.”
A sample of 1,164 Canadians aged 18 and older was polled between March 24th and March 28th, 2025. The margin of error is ±3.3 percentage points, 19 times out of 20.
The results of the MEI-Ipsos poll are available here.
* * *
The MEI is an independent public policy think tank with offices in Montreal, Ottawa, and Calgary. Through its publications, media appearances, and advisory services to policymakers, the MEI stimulates public policy debate and reforms based on sound economics and entrepreneurship.
Education
Schools should focus on falling math and reading skills—not environmental activism

From the Fraser Institute
In 2019 Toronto District School Board (TDSB) trustees passed a “climate emergency” resolution and promised to develop a climate action plan. Not only does the TDSB now have an entire department in their central office focused on this goal, but it also publishes an annual climate action report.
Imagine you were to ask a random group of Canadian parents to describe the primary mission of schools. Most parents would say something along the lines of ensuring that all students learn basic academic skills such as reading, writing and mathematics.
Fewer parents are likely to say that schools should focus on reducing their environmental footprints, push students to engage in environmental activism, or lobby for Canada to meet the 2016 Paris Agreement’s emission-reduction targets.
And yet, plenty of school boards across Canada are doing exactly that. For example, the Seven Oaks School Division in Winnipeg is currently conducting a comprehensive audit of its environmental footprint and intends to develop a climate action plan to reduce its footprint. Not only does Seven Oaks have a senior administrator assigned to this responsibility, but each of its 28 schools has a designated climate action leader.
Other school boards have gone even further. In 2019 Toronto District School Board (TDSB) trustees passed a “climate emergency” resolution and promised to develop a climate action plan. Not only does the TDSB now have an entire department in their central office focused on this goal, but it also publishes an annual climate action report. The most recent report is 58 pages long and covers everything from promoting electric school buses to encouraging schools to gain EcoSchools certification.
Not to be outdone, the Vancouver School District (VSD) recently published its Environmental Sustainability Plan, which highlights the many green initiatives in its schools. This plan states that the VSD should be the “greenest, most sustainable school district in North America.”
Some trustees want to go even further. Earlier this year, the British Columbia School Trustees Association released its Climate Action Working Group report that calls on all B.C. school districts to “prioritize climate change mitigation and adopt sustainable, impactful strategies.” It also says that taking climate action must be a “core part” of school board governance in every one of these districts.
Apparently, many trustees and school board administrators think that engaging in climate action is more important than providing students with a solid academic education. This is an unfortunate example of misplaced priorities.
There’s an old saying that when everything is a priority, nothing is a priority. Organizations have finite resources and can only do a limited number of things. When schools focus on carbon footprint audits, climate action plans and EcoSchools certification, they invariably spend less time on the nuts and bolts of academic instruction.
This might be less of a concern if the academic basics were already understood by students. But they aren’t. According to the most recent data from the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), the math skills of Ontario students declined by the equivalent of nearly two grade levels over the last 20 years while reading skills went down by about half a grade level. The downward trajectory was even sharper in B.C., with a more than two grade level decline in math skills and a full grade level decline in reading skills.
If any school board wants to declare an emergency, it should declare an academic emergency and then take concrete steps to rectify it. The core mandate of school boards must be the education of their students.
For starters, school boards should promote instructional methods that improve student academic achievement. This includes using phonics to teach reading, requiring all students to memorize basic math facts such as the times table, and encouraging teachers to immerse students in a knowledge-rich learning environment.
School boards should also crack down on student violence and enforce strict behaviour codes. Instead of kicking police officers out of schools for ideological reasons, school boards should establish productive partnerships with the police. No significant learning will take place in a school where students and teachers are unsafe.
Obviously, there’s nothing wrong with school boards ensuring that their buildings are energy efficient or teachers encouraging students to take care of the environment. The problem arises when trustees, administrators and teachers lose sight of their primary mission. In the end, schools should focus on academics, not environmental activism.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoASK YOURSELF! – Can Canada Endure, or Afford the Economic Stagnation of Carney’s Costly Climate Vision?
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoMade in Alberta! Province makes it easier to support local products with Buy Local program
-

 2025 Federal Election22 hours ago
2025 Federal Election22 hours agoEuthanasia is out of control in Canada, but nobody is talking about it on the campaign trail
-

 2025 Federal Election9 hours ago
2025 Federal Election9 hours agoMEI-Ipsos poll: 56 per cent of Canadians support increasing access to non-governmental healthcare providers
-

 2025 Federal Election17 hours ago
2025 Federal Election17 hours agoAI-Driven Election Interference from China, Russia, and Iran Expected, Canadian Security Officials Warn
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCSIS Warned Beijing Would Brand Conservatives as Trumpian. Now Carney’s Campaign Is Doing It.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoInside Buttongate: How the Liberal Swamp Tried to Smear the Conservative Movement — and Got Exposed
-
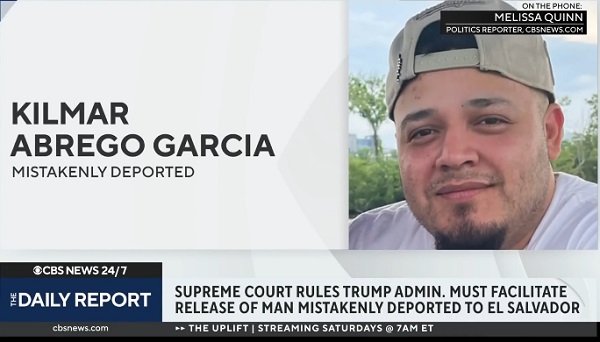
 illegal immigration1 day ago
illegal immigration1 day agoDespite court rulings, the Trump Administration shows no interest in helping Abrego Garcia return to the U.S.