Energy
Houses passes bill to protect domestic oil production, protect Iñupiat community

From T
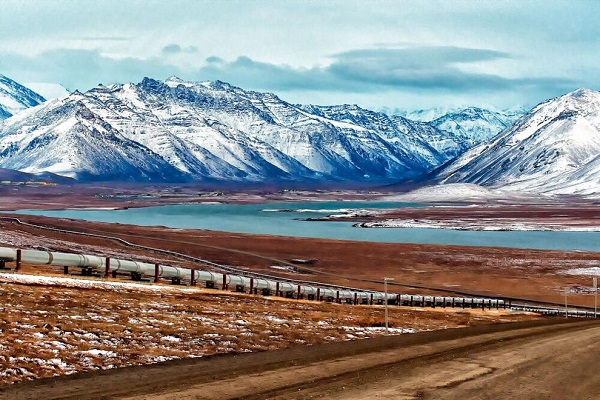
Indigenous communities are advocating for economic development projects in the North Slope, explaining that more than 95% of their tax base comes from resource development infrastructure.
The U.S. House passed another a bill to advance domestic energy production, this time in response to cries for help from an indigenous community living in the Alaska North Slope.
The bill’s cosponsor, a Democrat from Alaska, did not vote for her own bill. It passed with the support of five Democrats, including two from Texas who are strong supporters of the U.S. oil and natural gas industry.
The U.S. House has advanced several bills and resolutions to support domestic U.S. oil and natural gas production, supported by Texas Democrats. They’ve done so after the Biden administration has taken more than 200 actions against the industry, The Center Square reported.
One includes the Department of the Interior restricting development on over 50% of the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge (ANWR), directly impacting the Iñupiat North Slope community.
The Alaska North Slope region includes a part of ANWR and National Petroleum Reserve-Alaska (NPRA). Both are home to the indigenous Iñupiat community who maintain that the Biden administration is trying to “silence indigenous voices in the Arctic.”
The plan to halt North Slope production was done through a federal agency rule change, a tactic the administration has used to change federal law bypassing Congress. The rule cancels seven oil and gas leases issued by the Trump administration in the name of “climate change.” Interior Secretary Deb Haaland said canceling the leases was “based on the best available science and in recognition of the Indigenous Knowledge of the original stewards of this area, to safeguard our public lands for future generations.”
The indigenous community strongly disagrees, saying they weren’t consulted before, during or after the rule change.
Nagruk Harcharek, president of the Voice of Arctic Iñupiat, a nonprofit that represents a collective elected Iñupiaq leadership, says the administration’s mandate “to ‘protect’ 13 million acres of our ancestral homelands was made without fulfilling legal consultative obligations to our regional tribal governments, without engaging our communities about the decision’s impact, and with an incomplete economic analysis that undercuts North Slope communities.”
He argues the administration has overlooked “the legitimate concerns of elected Indigenous leaders from Alaska’s North Slope. This is a continuation of the onslaught of being blindsided by the federal government about unilateral decisions affecting our homelands.”
Restricting NPR-A oil production is “yet another blow to our right to self-determination in our ancestral homelands, which we have stewarded for over 10,000 years. Not a single organization or elected leader on the North Slope, which fully encompasses the NPR-A, supports this proposed rule,” he said, adding that they asked for it to be rescinded.
In response, U.S. Reps. Mary Sattler Peltola, D-Alaska, and Pete Stauber, R-Minn., introduced HR 6285, “Alaska’s Right to Produce Act.” The U.S. House Committee on Natural Resources Subcommittee on Energy and Natural Resources held a hearing on the issue; members of the Iñupiat Community of the Arctic Slope and the Kaktovik Iñupiat Corporation testified.
Kaktovik Iñupiat Corporation president Charles Lampe said they “refuse to become conservation refugees on our own homelands and unapologetically stand behind the Alaska’s Right to Produce Act.”
The Kaktovik is the only community located in the ANWR. The North Slope Iñupiat have stewarded their ancestral homelands for thousands of years, predating the creation of the U.S. federal government, the Interior Department and the state of Alaska, they argue.
The indigenous communities are advocating for economic development projects in the North Slope, explaining that more than 95% of their tax base comes from resource development infrastructure. Tax revenue funds public school education, health clinics, water and sewage systems, wildlife management and research and other services that otherwise would not exist, they argue. Eliminating their tax base, will directly impact their lives and jeopardize their long-term economic security, they argue.
The House passed Alaska’s Right to Produce Act on Wednesday to reverse the rule change and establish the Coastal Plain oil and gas leasing program. It authorizes and directs federal agencies to administer oil and natural gas leasing on 13 million acres of public land in the North Slope.
The bill passed by a vote of 214-199 without the support of its Democratic cosponsor from Alaska, Peltola, who voted “present.”
Five Democrats voted for it: Sanford D. Bishop, Jr. of Georgia, Henry Cuellar and Vincente Gonzalez of Texas, Jared Golden of Maine and Marie Gluesenkamp Perez of Washington. One Republican voted against it, Rep. Brian Fitzpatrick of Pennsylvania.
After it passed, Harcharek said, “Since the Biden administration announced this decision in September, our voices, which overwhelmingly reject the federal government’s decisions, have been consistently drowned out and ignored. This administration has not followed its well-documented promises to work with Indigenous people when crafting policies affecting their lands and people. We are grateful to Congress for exercising its legislative authority to correct the federal government’s hypocrisy and advance Iñupiaq self-determination in our ancestral homelands.”
Kaktovik Mayor Nathan Gordon, Jr. said the administration “is regulating our homelands in a region they do not understand and without listening to the people who live here.” The new law is “a vital corrective measure that will prevent our community from being isolated and protect our Iñupiaq culture in the long term.”
The bill heads to the Democratic controlled Senate, where it is unlikely to pass.
Business
Looks like the Liberals don’t support their own Pipeline MOU
From Pierre Poilievre
Alberta
They never wanted a pipeline! – Deputy Conservative Leader Melissa Lantsman

From Melissa Lantsman
Turns out the anti-development wing of the Liberal Party never stopped running the show.
Today, we’ll see if the Liberals vote for the pipeline they just finished bragging about.
Spoiler: they won’t. Because with the Liberals, the announcements are real, but the results never are.
-

 Focal Points2 days ago
Focal Points2 days agoCommon Vaccines Linked to 38-50% Increased Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer’s
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoLoblaws Owes Canadians Up to $500 Million in “Secret” Bread Cash
-

 Business24 hours ago
Business24 hours agoThe EU Insists Its X Fine Isn’t About Censorship. Here’s Why It Is.
-

 Dan McTeague2 days ago
Dan McTeague2 days agoWill this deal actually build a pipeline in Canada?
-

 Economy20 hours ago
Economy20 hours agoAffordable housing out of reach everywhere in Canada
-

 Business20 hours ago
Business20 hours agoCanada invests $34 million in Chinese drones now considered to be ‘high security risks’
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex2 days ago
Censorship Industrial Complex2 days agoUS Condemns EU Censorship Pressure, Defends X
-

 Banks2 days ago
Banks2 days agoTo increase competition in Canadian banking, mandate and mindset of bank regulators must change




