International
Ghislaine Maxwell to be sentenced in Epstein sex abuse case
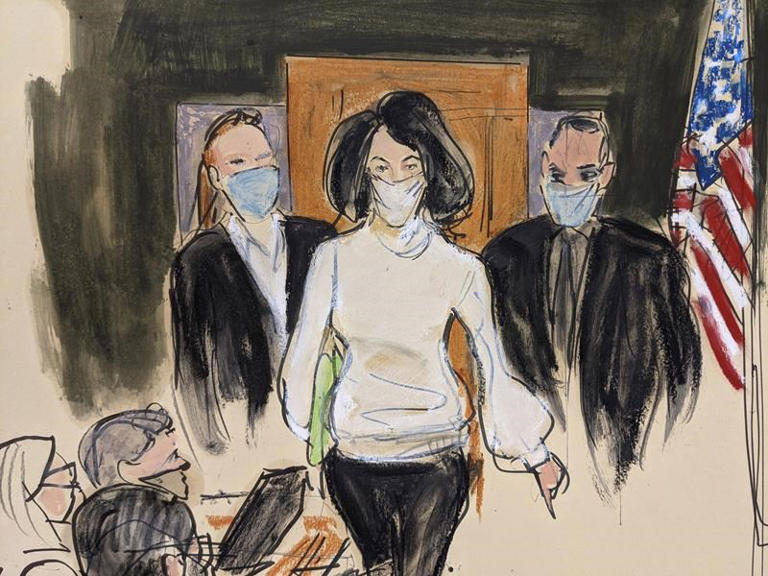

NEW YORK (AP) — Ghislaine Maxwell, the jet-setting socialite who once consorted with royals, presidents and billionaires, is set to be sentenced Tuesday for helping the wealthy financier Jeffrey Epstein sexually abuse underage girls.
The 11 a.m. sentencing in New York is the culmination of a prosecution that detailed how the power couple flaunted their riches and prominent connections to lure vulnerable girls as young as 14, and then exploit them.
Prosecutors said Epstein, who killed himself in 2019 while awaiting trial, sexually abused children hundreds of times over more than a decade, and couldn’t have done so without the help of Maxwell, his longtime companion and onetime girlfriend.
“Maxwell’s conduct was shockingly predatory. She was a calculating, sophisticated, and dangerous criminal who preyed on vulnerable young girls and groomed them for sexual abuse,” prosecutors wrote in a court filing.
In December, a jury convicted Maxwell of sex trafficking, transporting a minor to participate in illegal sex acts and two conspiracy charges. Prosecutors say she deserves 30 to 55 years in prison.
Maxwell, 60, has denied abusing anyone. Her lawyers have asked U.S. District Judge Alison J. Nathan to impose a sentence of no more than five years.
“The witnesses at trial testified about Ms. Maxwell’s facilitation of Epstein’s abuse, but Epstein was always the central figure: Epstein was the mastermind, Epstein was the principal abuser, and Epstein orchestrated the crimes for his personal gratification,” they wrote in a court filing.
Epstein and Maxwell’s associations with some of the world’s most famous people were not a prominent part of the trial, but mentions of friends like Bill Clinton, Donald Trump and Britain’s Prince Andrew showed how the pair exploited their connections to impress their prey.
Over the past 17 years, scores of women have accused Epstein of abusing them. Many described Maxwell as acting as a madam who recruited them to give massages to Epstein.
The trial, though, revolved around allegations from only a handful of those women.
Four testified that they were abused as teens in the 1990s and early 2000s at Epstein’s mansions in Florida, New York, New Mexico and the Virgin Islands.
Three were identified in court only by their first names or pseudonyms to protect their privacy: Jane, a television actress; Kate, an ex-model from the U.K.; and Carolyn, now a mom recovering from drug addiction. The fourth was Annie Farmer, who identified herself in court by her real name after speaking out publicly.
They described how Maxwell charmed them with conversation and gifts and promises that Epstein could use his wealth and connections to help fulfill their dreams.
Then, they testified, she led them to give massages to Epstein that turned sexual and played it off as normal.
Carolyn testified that she was one of several underprivileged teens who lived near Epstein’s Florida home in the early 2000s and took up an offer to massage him in exchange for $100 bills in what prosecutors described as “a pyramid of abuse.”
Maxwell made all the arrangements, Carolyn told the jury, even though she knew the girl was only 14 at the time.
The allegations against Epstein first surfaced publicly in 2005. He pleaded guilty to sex charges in Florida and served 13 months in jail, much of it in a work-release program as part of a deal criticized as lenient. Afterward, he was required to register as a sex offender.
In the years that followed, many women sued Epstein over alleged abuse. One, Virginia Giuffre, claimed that Epstein and Maxwell had also pressured her into sexual trysts with other powerful men, including Prince Andrew. All of those men denied the allegations and Giuffre ultimately settled a lawsuit against Andrew out of court.
Federal prosecutors in New York revived the case against Epstein after stories by the Miami Herald in 2018 brought new attention to his crimes. He was arrested in 2019, but killed himself a month later.
Eleven months later after his death, Maxwell was arrested at a New Hampshire estate. A U.S., British and French citizen, she has remained in a federal jail in New York City since then as her lawyers repeatedly criticize her treatment, saying she was even unjustly placed under suicide watch days before sentencing. Prosecutors say the claims about the jail are exaggerated and that Maxwell has been treated better than other prisoners.
Her lawyers also fought to have her conviction tossed on the grounds of juror misconduct.
Days after the verdict, one juror gave media interviews in which he disclosed he had been sexually abused as a child — something he hadn’t told the court during jury selection. Maxwell’s lawyers said she deserved a new trial. A judge disagreed.
At least eight women have submitted letters to the judge, describing the sexual abuse they said they endured for having met Maxwell and Epstein. Four of them plan to make oral statements at sentencing, including two women — Annie Farmer and Kate — who testified at the trial.
In letters to the judge, six of Maxwell’s seven living siblings pleaded for leniency.
Anne Holve and Philip Maxwell, her eldest siblings, wrote that her relationship with Epstein began soon after the 1991 death of their father, the British newspaper magnate Robert Maxwell.
They said Robert Maxwell had subjected her daughter to “frequent rapid mood swings, huge rages and rejections.”
“This led her to becoming very vulnerable to abusive and powerful men who would be able to take advantage of her innate good nature,” they wrote.
Prosecutors called Maxwell’s shifting of blame to Epstein “absurd and offensive.”
“Maxwell was an adult who made her own choices,” they wrote to the court. “She made the choice to sexually exploit numerous underage girls. She made the choice to conspire with Epstein for years, working as partners in crime and causing devastating harm to vulnerable victims. She should be held accountable for her disturbing role in an extensive child exploitation scheme.”
Larry Neumeister And Tom Hays, The Associated Press
Daily Caller
Daily Caller EXCLUSIVE: Trump’s Broad Ban On Risky Gain-Of-Function Research Nears Completion


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Emily Kopp
President Donald Trump could sign a sweeping executive order banning gain-of-function research — research that makes viruses more dangerous in the lab — as soon as May 6, according to a source who has worked with the National Security Council on the issue.
The executive order will take a broad strokes approach, banning research amplifying the infectivity or pathogenicity of any virulent and replicable pathogen, according to the source, who requested anonymity to speak candidly about the anticipated executive action. But significant unresolved issues remain, according to the source, including whether violators will be subject to criminal penalties as bioweaponeers.
The executive order is being steered by Gerald Parker, head of the White House Office of Pandemic Preparedness and Response Policy, which has been incorporated into the NSC. Parker did not respond to requests for comment.
Dear Readers:
As a nonprofit, we are dependent on the generosity of our readers.
Please consider making a small donation of any amount here. Thank you!
In the process of drafting the executive order, Parker has frozen out the federal agencies that have for years championed gain-of-function research and staved off regulation — chiefly Anthony Fauci’s former institute, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases at the National Institutes of Health.
The latest policy guidance on gain-of-function research, unveiled under the Biden administration in 2024, was previously expected to go into effect May 6. According to a March 25 letter cosigned by the American Society for Microbiology, the Association for Biosafety and Biosecurity International, and Council on Governmental Relations, organizations that conduct pathogen research have not received direction from the NIH on that guidance — suggesting the executive order would supersede the May 6 deadline.
The 2024 guidance altered the scope of experiments subject to more rigorous review, but charged researchers, universities and funding agencies like NIH with its implementation, which critics say disincentivizes reporting. Many scientists say that researchers and NIH should not be the primary entities conducting cost–benefit analyses of pandemic virus studies.
Parker previously served as the head of the National Science Advisory Board for Biosecurity (NSABB), a group of outside experts that advises NIH on biosecurity matters, and in that role recommended that Congress stand up a new government agency to advise on gain-of-function research. Former Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Director Robert Redfield has also endorsed moving gain-of-function research decision making out of the NIH to an independent commission.
“Given the well documented lapses in the NIH review process, policymakers should … remove final approval of any gain-of function research grants from NIH,” Redfield said in a February op-ed.
It remains to be seen whether the executive order will articulate carveouts for gain-of-function research without risks of harm such as research on non-replicative pseudoviruses, which can be used to study viral evolution without generating pandemic viruses.
It also remains to be seen whether the executive order will define “gain-of-function research” tightly enough to stand up to legal scrutiny should a violator be charged with a crime.
Risky research on coronaviruses funded by the NIH at the Wuhan Institute of Virology through the U.S. nonprofit EcoHealth Alliance typifies the loopholes in NIH’s existing regulatory framework, some biosecurity experts say.
Documents obtained through the Freedom of Information Act in 2023 indicated that EcoHealth Alliance President Peter Daszak submitted a proposal to the Pentagon in 2018 called “DEFUSE” describing gain-of-function experiments on viruses similar to SARS-CoV-2 but downplayed to his intended funder the fact that many of the tests would occur in Wuhan, China.
Daszak and EcoHealth were both debarred from federal funding in January 2025 but have faced no criminal charges.
“I don’t know that criminal penalties are necessary. But we do need more sticks in biosafety as well as carrots,” said a biosecurity expert who requested anonymity to avoid retribution from his employer for weighing in on the expected policy. “For instance, biosafety should be a part of tenure review and whether you get funding for future work.”
Some experts say that it is likely that the COVID-19 crisis was a lab-generated pandemic, and that without major policy changes it might not be the last one.
“Gain-of-function research on potential pandemic pathogens caused the COVID-19 pandemic, killing 20 million and costing $25 trillion,” said Richard Ebright, a Rutgers University microbiologist and longtime critic of high-risk virology, to the Daily Caller News Foundation. “If not stopped, gain-of-function research on potential pandemic pathogens likely will cause future lab-generated pandemics.”
Daily Caller
DOJ Releases Dossier Of Deported Maryland Man’s Alleged MS-13 Gang Ties

From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By Katelynn Richardson
The Department of Justice (DOJ) released documents Wednesday demonstrating Kilmar Armando Abrego Garcia’s membership in the MS-13 gang.
Abrego Garcia’s police interview, immigration court rulings and Department of Homeland Security (DHS) deportable/inadmissible alien record highlighting his membership in the gang, which he has disputed in court, are included in the release.
In a December 2019 decision, the Board of Immigration Appeals dismissed Abrego Garcia’s challenge to an immigration judge’s factual finding that he is “a verified member of MS-13.”
The board found the immigration judge “appropriately considered allegations of gang affiliation against the respondent in determining that he has not demonstrated that he is not a danger to property or persons.”
Officers found Abrego Garcia loitering in a Home Depot parking lot on March 28, 2019, wearing “a Chicago Bulls hat and a hoodie with rolls of money covering the eyes, ears and mouth of the presidents on the separate denominations,” the initial Prince George’s County Police Department Gang Field Interview Sheet states.
“Wearing the Chicago Bulls hat represents that they are a member in good standing with the MS-13,” the document states. “Officers contacted a past proven and reliable source of information, who advised Kilmar Armando ABREGO-GARCIA is an active member of MS-13 with the Westerns clique. The confidential source further advised that he is the rank of ‘Chequeo’ with the moniker of ‘Chele.’”
The administration became embroiled in a legal dispute after Abrego Garcia, who entered the country illegally in 2011, was deported in March to El Salvador as a result of an error. In court records, they argued Abrego Garcia could not “relitigate the finding that he is a danger to the community.”
A lower court ordered his return, but the Supreme Court required it to clarify the order and directed the administration to “facilitate” Abrego Garcia’s release.
The Department of Justice (DOJ) indicated Wednesday that it would appeal the amended order Judge Paula Xinis issued which directed the government to “take all available steps to facilitate the return of Abrego Garcia to the United States as soon as possible.”
During a Monday meeting with President Donald Trump, El Salvadoran President Nayib Bukele said he would not “smuggle” a terrorist into the U.S.
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) also released court filings Wednesday showing Abrego Garcia’s wife requested a domestic violence restraining order against him.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoRCMP Whistleblowers Accuse Members of Mark Carney’s Inner Circle of Security Breaches and Surveillance
-

 Daily Caller20 hours ago
Daily Caller20 hours agoTrump Executive Orders ensure ‘Beautiful Clean’ Affordable Coal will continue to bolster US energy grid
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoBureau Exclusive: Chinese Election Interference Network Tied to Senate Breach Investigation
-
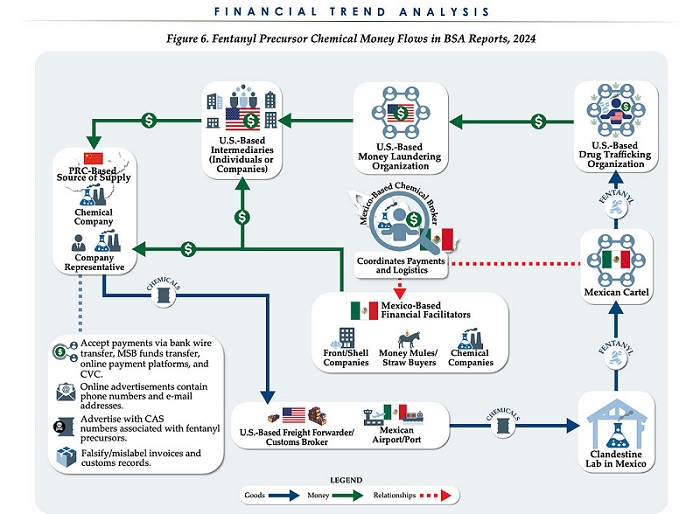
 Business21 hours ago
Business21 hours agoChina, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
-

 2025 Federal Election20 hours ago
2025 Federal Election20 hours agoBREAKING from THE BUREAU: Pro-Beijing Group That Pushed Erin O’Toole’s Exit Warns Chinese Canadians to “Vote Carefully”
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoTucker Carlson Interviews Maxime Bernier: Trump’s Tariffs, Mass Immigration, and the Oncoming Canadian Revolution
-

 2025 Federal Election18 hours ago
2025 Federal Election18 hours agoAllegations of ethical misconduct by the Prime Minister and Government of Canada during the current federal election campaign
-

 COVID-1915 hours ago
COVID-1915 hours agoTamara Lich and Chris Barber trial update: The Longest Mischief Trial of All Time continues..





