Economy
Climate researchers show we’re actually “safer than ever from climate” catastrophes
The climate safety denial movement
I and others have documented that we’re safer than ever from climate. Catastrophists can’t refute us, so they’re now saying that disaster deaths don’t matter!
|
|
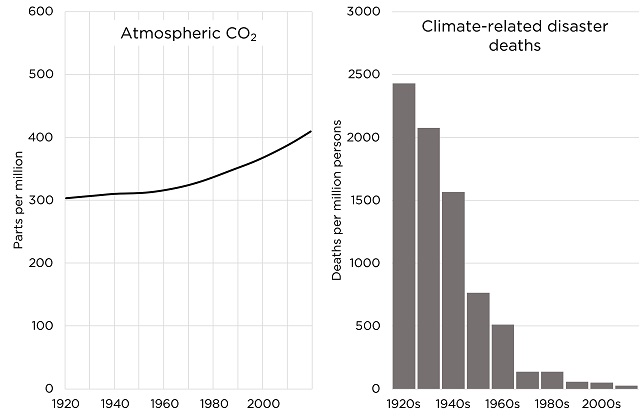
For decades climate catastrophists have portrayed climate disasters as getting deadlier and deadlier.
Now that I and others have documented that we’re safer than ever from climate, catastrophists are saying that disaster deaths don’t matter!
- Reuters says “Drop in climate-related disaster deaths not evidence against climate emergency.”
But a drop in deaths from something—here, a 98% drop—is obvious evidence against it being an emergency.
Would Reuters say: “98% drop in flu deaths not evidence against flu emergency”?¹
- Why is Reuters, along with The New York Times, PolitiFact, and USA Today, claiming that a 98% drop in climate disaster deaths doesn’t contradict their climate emergency narrative? Because it obviously does, and they can only save their narrative by intimidating us into denying the obvious.²
- The central narrative of climate catastrophists is that fossil fuels and their CO2 emissions are killing more and more people via climate disasters.
This narrative has always had a fatal weakness: it totally contradicts the data, which show plummeting climate disaster deaths.³
- Why are climate disaster deaths plummeting as fossil fuel use and CO2 emissions rise?
Because the enormous ability uniquely cost-effective and scalable fossil fuel energy gives us to master climate danger far outweighs any new climate challenges from CO2 emissions.
- An example of fossil-fueled climate mastery overwhelming CO2 impacts is drought.
Any contribution of rising CO2 to drought has been overwhelmed by fossil-fueled irrigation and crop transport, which have helped reduce drought deaths by over 100 times over 100 years as CO2 levels have risen.⁴
- Over the last decade, I and a number of others, including Bjorn Lomborg and Michael Shellenberger, have challenged catastrophism by pointing to declining climate disaster deaths.
Catastrophists couldn’t refute our argument. So instead they pretended it didn’t exist.
Until last year.⁵
- In 2023, climate catastrophists finally felt compelled to address the fact that climate disaster deaths have plummeted (driven by fossil-fueled climate mastery).
Because of honesty? No—because Presidential candidates started bringing it up and persuading people with it.
- Here is Vivek Ramaswamy during his Presidential campaign referring to a 98% decline in climate disaster deaths—and, crucially, giving fossil fuel energy credit.
- Here is Ron DeSantis during his Presidential campaign referring to a 98% decline in climate disaster deaths—and, crucially, giving fossil fuel energy credit.
- The 98% decline in climate disaster deaths, driven by fossil fuels, is a blockbuster fact: it shows that we are experiencing not fossil-fueled climate emergency but fossil-fueled climate safety.
But instead of being happy, catastrophists engage in climate safety denial.
- Here are 3 recent instances of climate safety denial—from Reuters, PolitiFact, and USA Today. All have long portrayed climate deaths as a fast-increasing problem. But now they claim deaths don’t matter.
https://www.reuters.com/fact-check/drop-climate-related- disaster-deaths-not-evidence- against-climate-emergency- 2023-09-19/ - Climate safety denial utilizes 5 main myths to evade the decline in disaster deaths:
1. Fossil fuels don’t deserve credit
2. Weather forecasting deserves the credit
3. 100 years is a misleading period
4. Damages are drastically increasing
5. There’s a major increase in reported disasters - Myth 1: Fossil fuels don’t deserve much credit for plummeting climate disaster deaths; it’s “resilience.”
Truth: Uniquely cost-effective and scalable fossil fuel energy makes us resilient through plentiful infrastructure-building, heating and cooling, irrigation, transportation, etc.⁶
- Myth 2: Storm warning systems deserve the credit for plummeting climate disaster deaths.
Truth: Drought, not storm, deaths are the leading source of reduced climate deaths. And fossil fuels power storm warning and evacuation systems (and more resilient infrastructure).⁷
- Myth 3: 100 years is a misleading period to measure plummeting climate disaster deaths.
Truth: 100 years is a standard, very meaningful period to look at. While we have data going back an additional two decades, those tend to underreport due to less global communication.⁸
- Contrary to the claim that starting analysis of climate disaster deaths in the 1920s overestimates the decline, it actually likely underestimates the decline due to insufficient past reporting; data before WWII extremely likely underreport deaths compared to data after 2000.
- Myth 4: There is an alarming increase in reported disasters, revealing an underlying climate emergency.
Truth: The increase in reported disasters over time is due overwhelmingly to increased global communication. Changes in fundamentals, such as storms, are extremely modest.⁹
- The claim that more reported disasters show an increasingly dangerous climate is absurd in light of the fact that underlying data show massive increases in reporting before significant human climate impacts and the reporting trend also massively goes up for non-climate causes!
- Other biases might inflate the number of reported disasters. E.g., governments of poor countries have an incentive to declare more disasters with increasing international relief.¹⁰
- Using obviously problematic disaster frequency reporting instead of direct climatological evidence to try and show increasing climate danger is a revealing choice by catastrophists. They are making it because the climate change we’ve experienced has been very modest—and masterable.
Do Not Declare a “Climate Emergency”
·AUGUST 17, 2023Read full story - An example of unalarming climate fundamentals: neither the frequency nor the energy in global hurricanes has changed significantly relative to the noisy average. There is also little evidence for more landfalling hurricanes.¹¹
- The catastrophist attempt to undermine the 98% decrease in disaster deaths by pointing to the increased reporting of disasters is actually self-defeating.
If disaster deaths are plummeting despite incomplete past reporting, that means they’ve declined by even more than 98%.
- Myth 5: Climate damages are drastically increasing, revealing an underlying climate emergency.
Truth: Even though there are many incentives for climate damages to go up—preferences for riskier areas, government bailouts—GDP-adjusted damages are flat.¹²
- We often hear that “billion-dollar disasters” have increased significantly. But this is a bogus metric. Of course, as GDP grows we’ll have more billion-dollar disasters because there is more wealth for disasters to strike. But when we adjust for GDP there’s no increase in damage.¹³
- A Reuters “fact check” alarmingly claims a 151% growth in disaster damages from a period starting in 1978 to a period ending in 2017.
But they evade that the global economy grew by over 200% during that period!
(And they evade that disaster and damage reporting increased.)¹⁴
- The stupidest climate safety denial myth (used by The New York Times): 2 million people died from extreme weather in the last 50 years; that’s obviously an emergency.
Truth: 2 million in 50 years is a rate of 40,000 per year—far, far less than 100 years ago, thus confirming today’s climate safety.¹⁵
- The last-gasp climate safety denial myth: Okay, we’re safer than ever from climate disasters, and it is driven by cheap energy from fossil fuels, but we can easily replace fossil fuels with solar and wind.
Truth: For the foreseeable future there is no cheap global energy without fossil fuels.
The ultimate debunking of “solar and wind are cheaper than fossil fuels.”
·JULY 19, 2023Read full story - Observe that all these seemingly scientific outlets, such as The New York Times, Reuters, and PolitiFact are totally unable to refute the death-blow to their “climate emergency” narrative that is the drastic decline in climate disaster deaths.
Science requires that they admit defeat.
Popular links
- EnergyTalkingPoints.com: Hundreds of concise, powerful, well-referenced talking points on energy, environmental, and climate issues.
- My new book Fossil Future: Why Global Human Flourishing Requires More Oil, Coal, and Natural Gas—Not Less.
- Speaking and media inquiries.
“Energy Talking Points by Alex Epstein” is my free Substack newsletter designed to give as many people as possible access to concise, powerful, well-referenced talking points on the latest energy, environmental, and climate issues from a pro-human, pro-energy perspective.
Share Energy Talking Points by Alex Epstein
UC San Diego – The Keeling Curve
For every million people on earth, annual deaths from climate-related causes (extreme temperature, drought, flood, storms, wildfires) declined 98%–from an average of 247 per year during the 1920s to 2.5 per year during the 2010s.
Data on disaster deaths come from EM-DAT, CRED / UCLouvain, Brussels, Belgium – www.emdat.be (D. Guha-Sapir).
Population estimates for the 1920s from the Maddison Database 2010, the Groningen Growth and Development Centre, Faculty of Economics and Business at University of Groningen. For years not shown, population is assumed to have grown at a steady rate.
Population estimates for the 2010s come from World Bank Data
Business
Budget 2025: Ottawa Fakes a Pivot and Still Spends Like Trudeau

It finally happened. Canada received a federal budget earlier this month, after more than a year without one. It’s far from a budget that’s great. It’s far from what many expected and distant from what the country needs. But it still passed.
With the budget vote drama now behind us, there may be space for some general observations beyond the details of the concerning deficits and debt. What kind of budget did Canada get?
Haultain’s Substack is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support our work, please consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Try it out.
For a government that built its political identity on social-program expansion and moralized spending, Budget 2025 arrives wearing borrowed clothing. It speaks in the language of productivity, infrastructure, and capital formation, the diction of grown-up economics, yet keeps the full spending reflex of the Trudeau era. The result feels like a cabinet trying to change its fiscal costume without changing the character inside it. Time will tell, to be fair, but it feels like more rhetoric, and we have seen this same rhetoric before lead to nothing. So, I remain skeptical of what they say and how they say it.
The government insists it has found a new path, one where public investment leads private growth. That sounds bold. However, it is more a rebranding than a reform. It is a shift in vocabulary, not in discipline.
A comparison with past eras makes this clear.
Jean Chrétien and Paul Martin did not flirt with restraint; they executed it. Their budgets were cut deeply, restored credibility, and revived Canada’s fiscal health when it was most needed. The Chrétien years were unsentimental. Political capital was spent so financial capital could return. Ottawa shrank so the country could grow. Budget 2025 tries to invoke their spirit but not their actions. Nothing in this plan resembles the structural surgery of the mid 1990s.
Stephen Harper, by contrast, treated balanced budgets as policy and principle. Even during the global financial crisis, his government used stimulus as a bridge, not a way of life. It cut taxes widely and consistently, limited public service growth, and placed the long-term burden on restraint rather than rhetoric. Budget 2025 nods toward Harper’s focus on productivity and capital assets, yet it rejects the tax relief and spending controls that made his budgets coherent.
Then there is Justin Trudeau, the high tide of redistribution, vacuous identity politics, and deficit-as-virtue posturing. Ottawa expanded into an ideological planner for everything, including housing, climate, childcare, inclusion portfolios, and every new identity category. Much of that ideological scaffolding consisted of mere words, weakening the principle of equality under the law and encouraging the government to referee culture rather than administer policy.
Budget 2025 is the first hint of retreat from that style. The identity program fireworks are dimmer, though they have not disappeared. The social policy boosterism is quieter. Perhaps fiscal gravity has begun to whisper in the prime minister’s ear.
However, one cannot confuse tone for transformation.
Spending is still vast. Deficits grew. The new fiscal anchor, balancing only the operating budget, is weaker than the one it replaced. The budget relies on the hopeful assumption that Ottawa’s capital spending will attract private investment on a scale that economists politely describe as ambitious.
The housing file illustrates the contradiction. The budget announces new funding for the construction of purpose-built rentals and a larger federal role in modular and subsidized housing builds. These are presented as productivity measures, yet they continue the Trudeau-era instinct to centralize housing policy rather than fix the levers that matter. Permitting delays, zoning rigidity, municipal approvals, and labour shortages continue to slow actual construction. Ottawa spends, but the foundations still cure at the same pace.
Defence spending tells the same story. Budget 2025 offers incremental funding and some procurement gestures, but it avoids the core problem: Canada’s procurement system is broken. Delays stretch across decades. Projects become obsolete before contracts are signed. The system cannot buy a ship, an aircraft, or an armoured vehicle without cost overruns and missed timelines. Spending more through this machinery will waste time and money. It adds motion, not capability.
Most importantly, the structural problems remain untouched: no regulatory reform for major projects, no tax competitiveness agenda, no strategy for shrinking a federal bureaucracy that has grown faster than the economy it governs. Ottawa presides over a low-productivity country but insists that a new accounting framework will solve what decades of overregulation and policy clutter have created. More bluster.
To receive new posts and support our work, please consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
From an Alberta vantage, the pivot is welcome but inadequate. The economy that pays for Confederation, energy, mining, agriculture, and transportation receives more rhetorical respect in Budget 2025, yet the same regulatory thicket that blocks pipelines and mines remains intact. The government praises capital formation but still undermines the key sectors that generate it.
Budget 2025 tries to walk like Chrétien and talk like Harper while spending like Trudeau. That is not a transformation; it is a costume change. The country needed a budget that prioritized growth rooted in tangible assets and real productivity. What it got instead is a rhetorical turn without the courage to cut, streamline, or reform.
Canada does not require a new budgeting vocabulary. It requires a government willing to govern in the best interest of the country.
Haultain’s Substack is a reader-supported publication.
Help us bring you more quality research and commentary.
Carbon Tax
Carney fails to undo Trudeau’s devastating energy policies

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill and Elmira Aliakbari
On the campaign trail and after he became prime minister, Mark Carney has repeatedly promised to make Canada an “energy superpower.” But, as evidenced by its first budget, the Carney government has simply reaffirmed the failed plans of the past decade and embraced the damaging energy policies of the Trudeau government.
First, consider the Trudeau government’s policy legacy. There’s Bill C-69 (the “no pipelines act”), the new electricity regulations (which aim to phase out natural gas as a power source starting this year), Bill C-48 (which bans large oil tankers off British Columbia’s northern coast and limit Canadian exports to international markets), the cap on emissions only from the oil and gas sector (even though greenhouse gas emissions have the same effect on the environment regardless of the source), stricter regulations for methane emissions (again, impacting the oil and gas sector), and numerous “net-zero” policies.
According to a recent analysis, fully implementing these measures under Trudeau government’s emissions reduction plan would result in 164,000 job losses and shrink Canada’s economic output by 6.2 per cent by the end of the decade compared to a scenario where we don’t have these policies in effect. For Canadian workers, this will mean losing $6,700 (annually, on average) by 2030.
Unfortunately, the Carney government’s budget offers no retreat from these damaging policies. While Carney scrapped the consumer carbon tax, he plans to “strengthen” the carbon tax on industrial emitters and the cost will be passed along to everyday Canadians—so the carbon tax will still cost you, it just won’t be visible.
There’s also been a lot of buzz over the possible removal of the oil and gas emissions cap. But to be clear, the budget reads: “Effective carbon markets, enhanced oil and gas methane regulations, and the deployment at scale of technologies such as carbon capture and storage would create the circumstances whereby the oil and gas emissions cap would no longer be required as it would have marginal value in reducing emissions.” Put simply, the cap remains in place, and based on the budget, the government has no real plans to remove it.
Again, the cap singles out one source (the oil and gas sector) of carbon emissions, even when reducing emissions in other sectors may come at a lower cost. For example, suppose it costs $100 to reduce a tonne of emissions from the oil and gas sector, but in another sector, it costs only $25 a tonne. Why force emissions reductions in a single sector that may come at a higher cost? An emission is an emission regardless of were it comes from. Moreover, like all these policies, the cap will likely shrink the Canadian economy. According to a 2024 Deloitte study, from 2030 to 2040, the cap will shrink the Canadian economy (measured by inflation-adjusted GDP) by $280 billion, and result in lower wages, job losses and a decline in tax revenue.
At the same time, the Carney government plans to continue to throw money at a range of “green” spending and tax initiatives. But since 2014, the combined spending and forgone revenue (due to tax credits, etc.) by Ottawa and provincial governments in Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia and Alberta totals at least $158 billion to promote the so-called “green economy.” Yet despite this massive spending, the green sector’s contribution to Canada’s economy has barely changed, from 3.1 per cent of Canada’s economic output in 2014 to 3.6 per cent in 2023.
In his first budget, Prime Minister Carney largely stuck to the Trudeau government playbook on energy and climate policy. Ottawa will continue to funnel taxpayer dollars to the “green economy” while restricting the oil and gas sector and hamstringing Canada’s economic potential. So much for becoming an energy superpower.
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoExpanding Canadian energy production could help lower global emissions
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoWill the Port of Churchill ever cease to be a dream?
-

 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoFreedom Convoy protestor Evan Blackman convicted at retrial even after original trial judge deemed him a “peacemaker”
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoBari Weiss Reportedly Planning To Blow Up Legacy Media Giant
-

 Daily Caller1 day ago
Daily Caller1 day agoTrump Gives Zelenskyy Until Thanksgiving To Agree On Peace Deal, With U.S. Weapons And Intel On The Line
-

 Business23 hours ago
Business23 hours agoI Was Hired To Root Out Bias At NIH. The Nation’s Health Research Agency Is Still Sick
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoThe numbers Canada uses to set policy don’t add up
-

 Carbon Tax4 hours ago
Carbon Tax4 hours agoCarney fails to undo Trudeau’s devastating energy policies



























