Break The Needle
Canada-US border mayors react to new border security initiative

US President Donald Trump has linked his threat to impose 25-per-cent tariffs on Canadian goods to Canada’s failure to address drug trafficking and illegal migration at the Canada-US border.
Ontario has responded with a border security initiative, Operation Deterrence, which is drawing tepid support from Ontario mayors of border communities.
“Absence of leadership from Ottawa has created this [scenario] where the provinces are all going in to be Captain, or Miss Captain, Canada,” said Mike Bradley, the mayor of Sarnia, Ont., a city of 75,000 that sits on the Ontario-Michigan border.
“[But] anything that helps on the policing side to deal with the black plague of fentanyl is welcome,” Bradley said.
Operation Deterrence
On Dec. 6, Ontario redeployed 200 Ontario Provincial Police officers to unpoliced border areas near the 14 official Ontario-US border crossings, which are staffed by the Canada Border Services Agency.
Officers are using aircraft, drones, boats, off-road vehicles and foot patrols to “deter, detect and disrupt” the illegal trafficking of drugs, guns and people, a Jan. 7 provincial press release says.
Premier Ford’s office and Ontario Solicitor General Michael Kerzner declined to provide further details about the operation in response to requests for comment.
But a spokesperson for the Ontario RCMP said there is little evidence that fentanyl trafficking is a significant issue at the Canada-US border.
“There is limited to no evidence or data from law enforcement agencies in the U.S. or Canada to support the claim that Canadian-produced fentanyl is an increasing threat to the U.S.,” the spokesperson told Canadian Affairs in an emailed statement.
The spokesperson highlighted that fentanyl trafficking frequently occurs by mail, rather than at physical border crossings.
“Reports state fentanyl produced in Canada is being exported in micro shipments, most often through the mail. Micro traffickers are most often found on the dark web,” the spokesperson said.
As Canadian Affairs reported last week, seizures of fentanyl at the Canada-US border remain relatively low. But Canadian authorities have seized significant volumes of precursor chemicals used in the production of fentanyl, and key sources say Canada is a major player in the global fentanyl trade.
Data also show illegal migration is a concern along the Canada-US border.
The U.S. Customs and Border Protection reported nearly 200,000 cases of individuals in Canada trying to illegally enter the US in the 2024 fiscal year.
Canada Border Services Agency data indicate just under 5,000 individuals were detained trying to enter Canada from the US in 2023-24.
Borderlands
Jim Diodati, the mayor of Niagara Falls, says he is supportive of Ontario launching Operation Deterrence in response to Trump’s tariff threats.
“I’m glad at least we’re reacting,” he said. “The concerns, of course, are that things are slipping through the cracks … both for drugs, guns and human smuggling as well.”
But Diodati stressed that border concerns go both ways. He hopes Operation Deterrence will also address firearms trafficking from the US into Canada.
“Ninety percent of illegal guns that come into Canada come from the US side, across our borders,” he said.
Diodati blames Ottawa for underfunding the Canada Border Services Agency, the federal agency responsible for border security and immigration enforcement. “CBSA needs more resources,” he said.
“The US sees our border as porous, not as secure as theirs, and now, with the incoming president, they’re looking to punish us over it.”
Bev Hand is the mayor of Point Edward, a 2,500-person village located a short drive north of Sarnia, on the southern tip of Lake Huron. The community connects to Port Huron, Mich., by the Blue Water Bridge, a key Canada-US border crossing.
Hand expressed cautious support for Operation Deterrence’s aims of addressing drug trafficking.
She noted that, since 2019, there have been 16 major drug busts at the Point Edward border, including two significant cocaine seizures by U.S. Customs and Border Protection. In December 2023, US authorities found nearly 500 kg of cocaine in a truck entering the US. In August 2024, US authorities discovered over 120 kg of cocaine hidden in the wall of a truck bound for Canada.
“Fifteen of the seizures were in transport trucks,” she said. “This represents millions of dollars in illegal drugs, and we don’t know what wasn’t captured.”
Hand noted, however, that funds allocated to border security might be better spent on addressing the root causes of drug trafficking, such as addiction.
In December, Ottawa announced it would spend an additional $1.3 billion over six years on enhancing its border security. Ontario has not disclosed how much Operation Deterrence will cost.
Like Diodati, Hand also emphasized the role Operation Deterrence could play in helping to curb firearms trafficking from the US.
She referenced a May 2022 case where a resident discovered a bag with 11 handguns in a tree near Port Lambton, Ont., a city approximately 15 kilometres south of Point Edward.
“The package had fallen from a drone that is assumed to have come from the US side,” she said.
Our content is always free. Subscribe to get BTN’s latest news and analysis, or donate to our journalism fund.
‘Fentanyl Czar’
Bradley, Sarnia’s mayor, said border security initiatives must be balanced against the need to facilitate trade, particularly at critical crossings like the CN Rail tunnel — which runs beneath the St. Clair River and connects Canada to Michigan — and Blue Water Bridge.
“We want security, but you also want trade, and that’s the balance right now that we’re struggling with,” Bradley said.
A 13-year review by professors at Carleton University found that tighter Canada-US border security following the 9/11 attacks increased inspection times and delays at the border. This has “negatively impacted” bilateral trade and cost the Canadian economy billions in foregone economic opportunities and productivity.
Diodati, of Niagara Falls, said he would prefer to see Canada and the US take a bilateral approach to border security that focuses on bolstering security around the continent.
“We want to take a perimeter approach around North America, rather than the borders between us,” he said.
While diplomatic relations between Canada and the US are tense, further collaboration on border security may be on the horizon.
On Feb. 3, Trump paused the imposition of tariffs on Canada after Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau promised Canada would send nearly 10,000 frontline personnel to protect the border.
“Canada is making new commitments to appoint a Fentanyl Czar, we will list cartels as terrorists, ensure 24/7 eyes on the border, launch a Canada-U.S. Joint Strike Force to combat organized crime, fentanyl and money laundering,” Trudeau wrote in a post on social media platform X.
“I have also signed a new intelligence directive on organized crime and fentanyl and we will be backing it with $200 million.
“Proposed tariffs will be paused for at least 30 days while we work together.”
This article was produced through the Breaking Needles Fellowship Program, which provided a grant to Canadian Affairs, a digital media outlet, to fund journalism exploring addiction and crime in Canada. Articles produced through the Fellowship are co-published by Break The Needle and Canadian Affairs.
Our content is always free – but if you want to help us commission more high-quality journalism, consider getting a voluntary paid subscription.
Break The Needle
Why psychedelic therapy is stuck in the waiting room
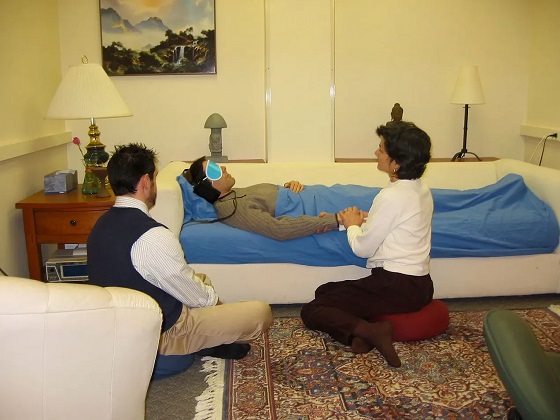

There is mounting evidence of psychedelics’ effectiveness at treating mental disorders. But researchers face obstacles conducting rigorous studies
In a move that made international headlines, America’s top drug regulator denied approval last year for psychedelic-assisted therapy to treat post-traumatic stress disorder.
In its decision, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration cited concerns about study design and inadequate evidence to assess the benefits and harms of using the drug MDMA.
The decision was a significant setback for psychedelics researchers and veterans’ groups who had been advocating for the therapy to be approved. It is also reflective of a broader challenge faced by researchers keen to validate the therapeutic potential of psychedelics.
“Sometimes I feel like it’s death by 1,000 paper cuts,” said Leah Mayo, a researcher at the University of Calgary.
“If the regulatory burden were a little bit less, that would be helpful,” added Mayo, who holds the Parker Psychedelics Research Chair at the Psychedelic and Cannabinoid Therapeutics Lab. The lab develops new treatments for mental health disorders using psychedelics and cannabinoids.
Sources say the weak research body behind psychedelics is due to a complex interplay of factors. But they would like to see more research conducted to make psychedelics more accessible to people who could benefit from them.
“If you want [psychedelics] to work within existing health-care infrastructure, you have to play by [Canadian research] rules,” said Mayo.
“Therapy has to be reproducible, it has to be evidence-based, it has to be grounded in reality.”
Psychedelics in Canada
Psychedelics are hallucinogenic substances such as psilocybin, MDMA and ketamine that alter people’s perceptions, mood and thought processes. Psychedelic therapy involves the use of psychedelics in guided sessions with therapists to treat mental health conditions.
Psychedelics are generally banned for possession, production and distribution in Canada. However, two per cent of Canadians consumed hallucinogens in 2019, according to the latest Canadian Alcohol and Drugs Survey. Psychedelics are also used in Canada and abroad in unregulated clinics and settings to treat conditions such as substance use disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and various mental disorders.
“The cat’s out of the bag, and people are using this,” said Zachary Walsh, a professor in the Department of Psychology at the University of British Columbia.
Within Canada, there are three ways for psychedelics to be accessed legally.
The federal health minister can approve their use for medical, scientific or public interest purposes. Health Canada runs a Special Access Program that allows doctors to request the use of unapproved drugs for patients with serious conditions that have not responded to other treatments. And Health Canada can approve psychedelics for use in clinical trials.
Researchers interested in conducting clinical trials involving psychedelics face significant hurdles.
“There’s been a concerted effort — and it’s just fading now — to mischaracterize the risks of these substances,” said Walsh, who has conducted several studies on the therapeutic uses of psychedelics. These include studies on MDMA-assisted therapy for PTSD, and the effects of microdosing psilocybin on stress, anxiety and depression.
This Substack is reader-supported.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
The U.S. government demonized psychedelic substances during its War on Drugs in the 1970s, exaggerating their risks and blocking research into their medical potential. Influenced by this war, Canada adopted similar tough-on-drugs policies and restricted research.
Today, younger researchers are pushing forward.
“New ideas really come into the forefront when the people in charge of the old ideas retire and die,” said Norman Farb, an associate professor in the Department of Psychology at the University of Toronto.
But it remains a challenge to secure funding for psychedelic research. Government funding is limited, and pharmaceutical companies are often hesitant to invest because psychedelic-assisted therapy does not generally fit the traditional pharmaceutical model.
“It’s not something that a pharmaceutical company wants to pay for, because it’s not going to be a classic pharmaceutical,” said Walsh.
As a result, many researchers rely on private donations or venture capital. This makes it difficult to fund large-scale studies, says Farb, who has faced institutional obstacles researching microdosing for treatment-resistant depression.
“No one wants to be that first cautionary tale,” he said. “No one wants to invest a lot of money to do the kind of study that would be transparent if it didn’t work.”
Difficulties in clinical trials
But funding is not the only challenge. Sources also pointed to the difficulty of designing clinical trials for psychedelics.
In particular, it can be difficult to implement a blind trial process, given the potent effects of psychedelics. Double blind trials are the gold standard of clinical trials, where neither the person administering the drug or patient knows if the patient is receiving the active drug or placebo.
Health Canada also requires researchers to meet strict trial criteria, such as demonstrating that the benefits outweigh the risks, that the drug treats an ongoing condition with no other approved treatments, and that the drug’s effects exceed any placebo effect.
It is especially difficult to isolate the effects of psychedelics. Psychotherapy, for example, can play a crucial role in treatment, making it difficult to disentangle the role of therapy from the drugs.
Mayo, of the University of Calgary, worries the demands of clinical trial models are not practical given the limitations of Canada’s health-care system.
“The way we’re writing these clinical trials, it’s not possible within our existing health-care infrastructure,” she said. She cited as one example the expectation that psychiatrists in clinical trials spend eight or more hours with each patient.
Ethical issues
Psychedelics research can also raise ethical concerns, particularly where it involves individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions.
A 2024 study found that people who visited an emergency room after using hallucinogens were at a significantly increased risk of developing schizophrenia — raising concerns that trials could harm vulnerable participants.
Another problem is a lack of standardization in psychedelic therapy. “We haven’t standardized it,” said Mayo. “We don’t even know what people are being taught psychedelic therapy is.”
This concern was underscored in a 2015 clinical trial on MDMA in Canada, where one of the trial participants was subjected to inappropriate physical contact and questioning by two unlicensed therapists.
Mayo advocates for the creation of a regulatory body to standardize therapist training and prevent misconduct.
Others have raised concerns about whether the research exploits Indigenous knowledge or cultural practices.
“There’s no psychedelic science without Indigenous communities,” said Joseph Mays, a doctorate candidate at the University of Saskatchewan.
“Whether it’s medicalized or ceremonial, there’s a direct continuity with Indigenous practices.”
Mays is an advisor to the Indigenous Reciprocity Initiative, which funnels psychedelic investments back to Indigenous communities. He believes those working with psychedelics must incorporate reciprocity into their work.
“If you’re using psychedelics in any way, it only makes sense that you would also have a commitment to fighting for the rights of [Indigenous] communities, which are still lacking basic necessities,” said Mays, suggesting that companies profiting from psychedelic medicine should contribute to Indigenous causes.
Despite these various challenges, sources remained optimistic that psychedelics would eventually be legalized — although not due to their work.
“It’s inevitable,” said Mays. “They’re already widespread, being used underground.”
Farb agrees. “A couple more research studies is not going to change the law,” he said. “Power is going to change the law.”
This article was produced through the Breaking Needles Fellowship Program, which provided a grant to Canadian Affairs, a digital media outlet, to fund journalism exploring addiction and crime in Canada. Articles produced through the Fellowship are co-published by Break The Needle and Canadian Affairs.
Subscribe to Break The Needle.
Our content is always free – but if you want to help us commission more high-quality journalism, consider getting a voluntary paid subscription.
Addictions
There’s No Such Thing as a “Safer Supply” of Drugs

By Adam Zivo
Sweden, the U.K., and Canada all experimented with providing opioids to addicts. The results were disastrous.
[This article was originally published in City Journal, a public policy magazine and website published by the Manhattan Institute for Policy Research. We encourage our readers to subscribe to them for high-quality analysis on urban issues]
Last August, Denver’s city council passed a proclamation endorsing radical “harm reduction” strategies to address the drug crisis. Among these was “safer supply,” the idea that the government should give drug users their drug of choice, for free. Safer supply is a popular idea among drug-reform activists. But other countries have already tested this experiment and seen disastrous results, including more addiction, crime, and overdose deaths. It would be foolish to follow their example.
The safer-supply movement maintains that drug-related overdoses, infections, and deaths are driven by the unpredictability of the black market, where drugs are inconsistently dosed and often adulterated with other toxic substances. With ultra-potent opioids like fentanyl, even minor dosing errors can prove fatal. Drug contaminants, which dealers use to provide a stronger high at a lower cost, can be just as deadly and potentially disfiguring.
Because of this, harm-reduction activists sometimes argue that governments should provide a free supply of unadulterated, “safe” drugs to get users to abandon the dangerous street supply. Or they say that such drugs should be sold in a controlled manner, like alcohol or cannabis—an endorsement of partial or total drug legalization.
But “safe” is a relative term: the drugs championed by these activists include pharmaceutical-grade fentanyl, hydromorphone (an opioid as potent as heroin), and prescription meth. Though less risky than their illicit alternatives, these drugs are still profoundly dangerous.
The theory behind safer supply is not entirely unreasonable, but in every country that has tried it, implementation has led to increased suffering and addiction. In Europe, only Sweden and the U.K. have tested safer supply, both in the 1960s. The Swedish model gave more than 100 addicts nearly unlimited access through their doctors to prescriptions for morphine and amphetamines, with no expectations of supervised consumption. Recipients mostly sold their free drugs on the black market, often through a network of “satellite patients” (addicts who purchased prescribed drugs). This led to an explosion of addiction and public disorder.
Most doctors quickly abandoned the experiment, and it was shut down after just two years and several high-profile overdose deaths, including that of a 17-year-old girl. Media coverage portrayed safer supply as a generational medical scandal and noted that the British, after experiencing similar problems, also abandoned their experiment.
While the U.S. has never formally adopted a safer-supply policy, it experienced something functionally similar during the OxyContin crisis of the 2000s. At the time, access to the powerful opioid was virtually unrestricted in many parts of North America. Addicts turned to pharmacies for an easy fix and often sold or traded their extra pills for a quick buck. Unscrupulous “pill mills” handed out prescriptions like candy, flooding communities with OxyContin and similar narcotics. The result was a devastating opioid epidemic—one that rages to this day, at a cumulative cost of hundreds of thousands of American lives. Canada was similarly affected.
The OxyContin crisis explains why many experienced addiction experts were aghast when Canada greatly expanded access to safer supply in 2020, following a four-year pilot project. They worried that the mistakes of the recent past were being made all over again, and that the recently vanquished pill mills had returned under the cloak of “harm reduction.”
Subscribe for free to get BTN’s latest news and analysis – or donate to our investigative journalism fund.
Most Canadian safer-supply prescribers dispense large quantities of hydromorphone with little to no supervised consumption. Patients can receive up to 40 eight-milligram pills per day—despite the fact that just two or three are enough to cause an overdose in someone without opioid tolerance. Some prescribers also provide supplementary fentanyl, oxycodone, or stimulants.
Unfortunately, many safer-supply patients sell or trade a significant portion of these drugs—primarily hydromorphone—in order to purchase more potent illicit substances, such as street fentanyl.
The problems with safer supply entered Canada’s consciousness in mid-2023, through an investigative report I wrote for the National Post. I interviewed 14 addiction physicians from across the country, who testified that safer-supply diversion is ubiquitous; that the street price of hydromorphone collapsed by up to 95 percent in communities where safer supply is available; that youth are consuming and becoming addicted to diverted safer-supply drugs; and that organized crime traffics these drugs.
Facing pushback, I interviewed former drug users, who estimated that roughly 80 percent of the safer-supply drugs flowing through their social circles was getting diverted. I documented dozens of examples of safer-supply trafficking online, representing tens of thousands of pills. I spoke with youth who had developed addictions from diverted safer supply and adults who had purchased thousands of such pills.
After months of public queries, the police department of London, Ontario—where safer supply was first piloted—revealed last summer that annual hydromorphone seizures rose over 3,000 percent between 2019 and 2023. The department later held a press conference warning that gangs clearly traffic safer supply. The police departments of two nearby midsize cities also saw their post-2019 hydromorphone seizures increase more than 1,000 percent.
The Canadian government quietly dropped its support for safer supply last year, cutting funding for many of its pilot programs. The province of British Columbia (the nexus of the harm-reduction movement) finally pulled back support last month, after a leaked presentation confirmed that safer-supply drugs are getting sold internationally and that the government is investigating 60 pharmacies for paying kickbacks to safer-supply patients. For now, all safer-supply drugs dispensed within the province must be consumed under supervision.
Harm-reduction activists have insisted that no hard evidence exists of widespread diversion of safer-supply drugs, but this is only because they refuse to study the issue. Most “studies” supporting safer supply are produced by ideologically driven activist-scholars, who tend to interview a small number of program enrollees. These activists also reject attempts to track diversion as “stigmatizing.”
The experiences of Sweden, the United Kingdom, and Canada offer a clear warning: safer supply is a reliably harmful policy. The outcomes speak for themselves—rising addiction, diversion, and little evidence of long-term benefit.
As the debate unfolds in the United States, policymakers would do well to learn from these failures. Americans should not be made to endure the consequences of a policy already discredited abroad simply because progressive leaders choose to ignore the record. The question now is whether we will repeat others’ mistakes—or chart a more responsible course.
Our content is always free –
but if you want to help us commission more high-quality journalism,
consider getting a voluntary paid subscription.
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoRCMP Whistleblowers Accuse Members of Mark Carney’s Inner Circle of Security Breaches and Surveillance
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoMEI-Ipsos poll: 56 per cent of Canadians support increasing access to non-governmental healthcare providers
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoAI-Driven Election Interference from China, Russia, and Iran Expected, Canadian Security Officials Warn
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoTrump admin directs NIH to study ‘regret and detransition’ after chemical, surgical gender transitioning
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoBureau Exclusive: Chinese Election Interference Network Tied to Senate Breach Investigation
-
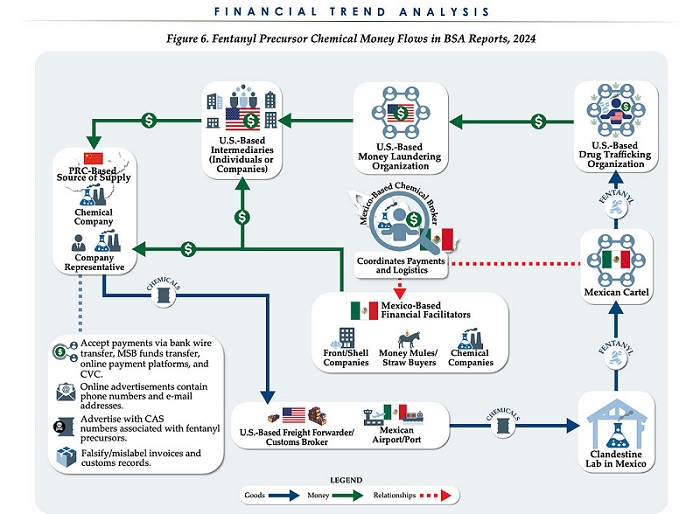
 Business6 hours ago
Business6 hours agoChina, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
-

 2025 Federal Election16 hours ago
2025 Federal Election16 hours agoTucker Carlson Interviews Maxime Bernier: Trump’s Tariffs, Mass Immigration, and the Oncoming Canadian Revolution
-

 Daily Caller4 hours ago
Daily Caller4 hours agoTrump Executive Orders ensure ‘Beautiful Clean’ Affordable Coal will continue to bolster US energy grid