Canadian Energy Centre
Analyst says LNG Canada likely to start exports before year-end

Welders with JGC-Fluor following completion of the final weld on the first production train at the LNG Canada project, in Kitimat, B.C. in July 2024. Since construction began in 2018, upwards of 380 pipe welders have worked on the LNG Canada project. Photo courtesy JGC-Fluor
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
Canada’s first liquefied natural gas export terminal ‘on the cusp’ of its testing phase
Momentum is building for the long-awaited start-up of Canada’s first liquefied natural gas (LNG) export project.
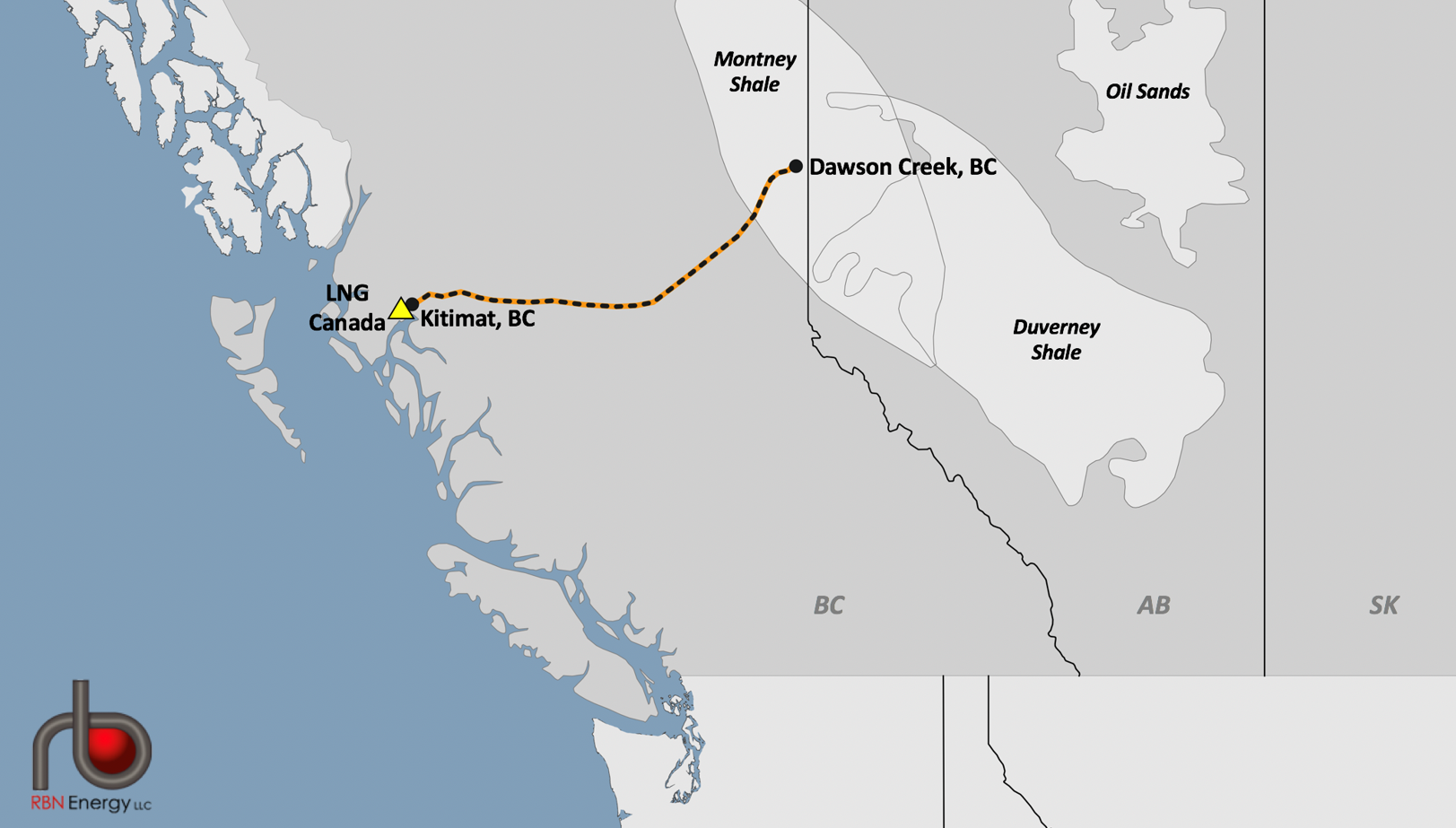
Shipments from the LNG Canada terminal at Kitimat, B.C. may now start earlier than expected, later this year rather than mid-2025, according to Martin King, Canadian energy specialist with Houston-based RBN Energy.
“LNG Canada appears to be on the cusp of its testing phase and is likely to be exporting some cargoes of LNG before the end of this year,” King wrote recently.
He made the prediction after a senior executive with Shell, the project’s lead owner, said it could deliver its first cargo earlier than previously planned, in the wake of two key milestones.
Fluor reported in July it had completed the final weld on the first production train while Petronas, which holds a 25 per cent stake in LNG Canada, announced it would add three LNG vessels to its North American fleet, doubling its size.
A longtime industry insider sees the $18 billion LNG Canada terminal as a game changer.
“This is decades in the making. Canada has been trying to get its LNG business up and running since the 1970s but it has been sidetracked for one reason or another,” says Calgary-based consultant Racim Gribaa, who has worked in the industry for more than 25 years.
“This project is perfectly placed to take advantage of an awesome opportunity given the demand for LNG worldwide is growing exponentially.”
The project, which will use the Coastal GasLink pipeline, completed in November 2023, to bring gas from northeastern British Columbia to the Kitimat terminal for processing and shipping, will have capacity to produce up to 14 million tonnes per year in its first phase.
While that’s a fraction of the 404 million tonnes of global demand in 2023, Gribaa says Asian buyers view LNG Canada as secure supplier in part due to its geography.
“The closest point to Asia is Canada’s west coast, so you have the shortest shipping route, which makes for optimal transportation costs. The traders and LNG industry see it as valuable for that reason,” says Gribaa, who previously worked in LNG trade in Qatar, one of the world’s largest exporters.
And the project is coming online at a time when worldwide demand is surging.
“The worldwide demand has effectively doubled every decade since 1990, when it was 50 MPTA. We are now closing in on 500 MPTA and that is accelerating,” Gribaa says.
“The world will need 10 LNG Canadas in 10 years and 100 more LNG Canadas in the next 30 years.”
The project has plans for a second phase that would double production to 28 million tonnes per year. Based on demand, Gribaa says “the question isn’t if it will go forward, it’s when the consortium will announce the expansion.”
World LNG demand growth will be particularly strong in Asia, where Shell’s four LNG Canada partners – Petronas (25 per cent), PetroChina (15 per cent), Mitsubishi (15 per cent) and Korea Gas Corporation (five per cent) – are headquartered.
“Each of these markets has historical demand for LNG and that demand will continue to grow in the coming decades,” he says, adding that LNG in Asia can be used for power generation and heavy industry, and to reduce air pollution from coal-fired power.
Overall, generating electricity in China with LNG from Canada rather than coal could reduce emissions by up to 62 per cent, according to a 2020 study published in the Journal for Cleaner Production.
A 2022 study by Wood Mackenzie found that growing Canada’s LNG industry could reduce net emissions in Asia by 188 million tonnes per year through 2050.
Canadian Energy Centre
Alberta oil sands legacy tailings down 40 per cent since 2015

Wapisiw Lookout, reclaimed site of the oil sands industry’s first tailings pond, which started in 1967. The area was restored to a solid surface in 2010 and now functions as a 220-acre watershed. Photo courtesy Suncor Energy
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By CEC Research
Mines demonstrate significant strides through technological innovation
Tailings are a byproduct of mining operations around the world.
In Alberta’s oil sands, tailings are a fluid mixture of water, sand, silt, clay and residual bitumen generated during the extraction process.
Engineered basins or “tailings ponds” store the material and help oil sands mining projects recycle water, reducing the amount withdrawn from the Athabasca River.
In 2023, 79 per cent of the water used for oil sands mining was recycled, according to the latest data from the Alberta Energy Regulator (AER).
Decades of operations, rising production and federal regulations prohibiting the release of process-affected water have contributed to a significant accumulation of oil sands fluid tailings.
The Mining Association of Canada describes that:
“Like many other industrial processes, the oil sands mining process requires water.
However, while many other types of mines in Canada like copper, nickel, gold, iron ore and diamond mines are allowed to release water (effluent) to an aquatic environment provided that it meets stringent regulatory requirements, there are no such regulations for oil sands mines.
Instead, these mines have had to retain most of the water used in their processes, and significant amounts of accumulated precipitation, since the mines began operating.”
Despite this ongoing challenge, oil sands mining operators have made significant strides in reducing fluid tailings through technological innovation.
This is demonstrated by reductions in “legacy fluid tailings” since 2015.
Legacy Fluid Tailings vs. New Fluid Tailings
As part of implementing the Tailings Management Framework introduced in March 2015, the AER released Directive 085: Fluid Tailings Management for Oil Sands Mining Projects in July 2016.
Directive 085 introduced new criteria for the measurement and closure of “legacy fluid tailings” separate from those applied to “new fluid tailings.”
Legacy fluid tailings are defined as those deposited in storage before January 1, 2015, while new fluid tailings are those deposited in storage after January 1, 2015.
The new rules specified that new fluid tailings must be ready to reclaim ten years after the end of a mine’s life, while legacy fluid tailings must be ready to reclaim by the end of a mine’s life.
Total Oil Sands Legacy Fluid Tailings
Alberta’s oil sands mining sector decreased total legacy fluid tailings by approximately 40 per cent between 2015 and 2024, according to the latest company reporting to the AER.
Total legacy fluid tailings in 2024 were approximately 623 million cubic metres, down from about one billion cubic metres in 2015.
The reductions are led by the sector’s longest-running projects: Suncor Energy’s Base Mine (opened in 1967), Syncrude’s Mildred Lake Mine (opened in 1978), and Syncrude’s Aurora North Mine (opened in 2001). All are now operated by Suncor Energy.
The Horizon Mine, operated by Canadian Natural Resources (opened in 2009) also reports a significant reduction in legacy fluid tailings.
The Muskeg River Mine (opened in 2002) and Jackpine Mine (opened in 2010) had modest changes in legacy fluid tailings over the period. Both are now operated by Canadian Natural Resources.
Imperial Oil’s Kearl Mine (opened in 2013) and Suncor Energy’s Fort Hills Mine (opened in 2018) have no reported legacy fluid tailings.
Suncor Energy Base Mine
Between 2015 and 2024, Suncor Energy’s Base Mine reduced legacy fluid tailings by approximately 98 per cent, from 293 million cubic metres to 6 million cubic metres.
Syncrude Mildred Lake Mine
Between 2015 and 2024, Syncrude’s Mildred Lake Mine reduced legacy fluid tailings by approximately 15 per cent, from 457 million cubic metres to 389 million cubic metres.
Syncrude Aurora North Mine
Between 2015 and 2024, Syncrude’s Aurora North Mine reduced legacy fluid tailings by approximately 25 per cent, from 102 million cubic metres to 77 million cubic metres.
Canadian Natural Resources Horizon Mine
Between 2015 and 2024, Canadian Natural Resources’ Horizon Mine reduced legacy fluid tailings by approximately 36 per cent, from 66 million cubic metres to 42 million cubic metres.
Total Oil Sands Fluid Tailings
Reducing legacy fluid tailings has helped slow the overall growth of fluid tailings across the oil sands sector.
Without efforts to reduce legacy fluid tailings, the total oil sands fluid tailings footprint today would be approximately 1.6 billion cubic metres.
The current fluid tailings volume stands at approximately 1.2 billion cubic metres, up from roughly 1.1 billion in 2015.
The unaltered reproduction of this content is free of charge with attribution to the Canadian Energy Centre.
Business
Why it’s time to repeal the oil tanker ban on B.C.’s north coast

The Port of Prince Rupert on the north coast of British Columbia. Photo courtesy Prince Rupert Port Authority
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
Moratorium does little to improve marine safety while sending the wrong message to energy investors
In 2019, Martha Hall Findlay, then-CEO of the Canada West Foundation, penned a strongly worded op-ed in the Globe and Mail calling the federal ban of oil tankers on B.C.’s northern coast “un-Canadian.”
Six years later, her opinion hasn’t changed.
“It was bad legislation and the government should get rid of it,” said Hall Findlay, now director of the University of Calgary’s School of Public Policy.
The moratorium, known as Bill C-48, banned vessels carrying more than 12,500 tonnes of oil from accessing northern B.C. ports.
Targeting products from one sector in one area does little to achieve the goal of overall improved marine transport safety, she said.
“There are risks associated with any kind of transportation with any goods, and not all of them are with oil tankers. All that singling out one part of one coast did was prevent more oil and gas from being produced that could be shipped off that coast,” she said.
Hall Findlay is a former Liberal MP who served as Suncor Energy’s chief sustainability officer before taking on her role at the University of Calgary.
She sees an opportunity to remove the tanker moratorium in light of changing attitudes about resource development across Canada and a new federal government that has publicly committed to delivering nation-building energy projects.
“There’s a greater recognition in large portions of the public across the country, not just Alberta and Saskatchewan, that Canada is too dependent on the United States as the only customer for our energy products,” she said.
“There are better alternatives to C-48, such as setting aside what are called Particularly Sensitive Sea Areas, which have been established in areas such as the Great Barrier Reef and the Galapagos Islands.”
The Business Council of British Columbia, which represents more than 200 companies, post-secondary institutions and industry associations, echoes Hall Findlay’s call for the tanker ban to be repealed.
“Comparable shipments face no such restrictions on the East Coast,” said Denise Mullen, the council’s director of environment, sustainability and Indigenous relations.
“This unfair treatment reinforces Canada’s over-reliance on the U.S. market, where Canadian oil is sold at a discount, by restricting access to Asia-Pacific markets.
“This results in billions in lost government revenues and reduced private investment at a time when our economy can least afford it.”
The ban on tanker traffic specifically in northern B.C. doesn’t make sense given Canada already has strong marine safety regulations in place, Mullen said.
Notably, completion of the Trans Mountain Pipeline expansion in 2024 also doubled marine spill response capacity on Canada’s West Coast. A $170 million investment added new equipment, personnel and response bases in the Salish Sea.
“The [C-48] moratorium adds little real protection while sending a damaging message to global investors,” she said.
“This undermines the confidence needed for long-term investment in critical trade-enabling infrastructure.”
Indigenous Resource Network executive director John Desjarlais senses there’s an openness to revisiting the issue for Indigenous communities.
“Sentiment has changed and evolved in the past six years,” he said.
“There are still concerns and trust that needs to be built. But there’s also a recognition that in addition to environmental impacts, [there are] consequences of not doing it in terms of an economic impact as well as the cascading socio-economic impacts.”
The ban effectively killed the proposed $16-billion Eagle Spirit project, an Indigenous-led pipeline that would have shipped oil from northern Alberta to a tidewater export terminal at Prince Rupert, B.C.
“When you have Indigenous participants who want to advance these projects, the moratorium needs to be revisited,” Desjarlais said.
He notes that in the six years since the tanker ban went into effect, there are growing partnerships between B.C. First Nations and the energy industry, including the Haisla Nation’s Cedar LNG project and the Nisga’a Nation’s Ksi Lisims LNG project.
This has deepened the trust that projects can mitigate risks while providing economic reconciliation and benefits to communities, Dejarlais said.
“Industry has come leaps and bounds in terms of working with First Nations,” he said.
“They are treating the rights of the communities they work with appropriately in terms of project risk and returns.”
Hall Findlay is cautiously optimistic that the tanker ban will be replaced by more appropriate legislation.
“I’m hoping that we see the revival of a federal government that brings pragmatism to governing the country,” she said.
“Repealing C-48 would be a sign of that happening.”
-

 MAiD2 days ago
MAiD2 days agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is already killing the disabled. It’s about to get worse
-

 Daily Caller15 hours ago
Daily Caller15 hours agoUSAID Quietly Sent Thousands Of Viruses To Chinese Military-Linked Biolab
-

 Alberta12 hours ago
Alberta12 hours ago‘Far too serious for such uninformed, careless journalism’: Complaint filed against Globe and Mail article challenging Alberta’s gender surgery law
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex23 hours ago
Censorship Industrial Complex23 hours agoCanadian pro-freedom group sounds alarm over Liberal plans to revive internet censorship bill
-

 Fraser Institute1 day ago
Fraser Institute1 day agoBefore Trudeau average annual immigration was 617,800. Under Trudeau number skyrocketted to 1.4 million from 2016 to 2024
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoChicago suburb purchases childhood home of Pope Leo XIV
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days ago‘I Know How These People Operate’: Fmr CIA Officer Calls BS On FBI’s New Epstein Intel
-

 Economy1 day ago
Economy1 day agoThe stars are aligning for a new pipeline to the West Coast