Environment
Activist shares how Canadians can fight globalism through local action

From LifeSiteNews
Maggie Braun, the founder of Kicking International Council out of Local Environmental Initiatives, told LifeSiteNews that there are ‘small wins happening every day’ against globalism by pro-local Canadians.
A pro-freedom advocate told LifeSiteNews that many Canadians have already successfully stood up to the meddling of the United Nations’ globalist agenda, encouraging all citizens to know their rights under the law to protect their local communities.
During a November 20 discussion at the Rankin Culture and Recreation Centre in Pembroke, Ontario, about the ways in which the United Nations are breaking municipal laws and violating property rights in an effort to achieve their globalist goals, Maggie Braun, the founder of Kicking International Council out of Local Environmental Initiatives (KICLEI), shared just what Canadians have been doing to successfully stand up for their local communities.
“There’s small wins happening every day,” Braun told LifeSiteNews in an interview before the discussion.
“Counselors opening up and communicating with the community and our concerns and just bridging that gap and sharing and exchanging information with them and slowly watching them start to make moves to withdraw from the programs or shut down renewable energy projects that don’t make sense in their area,” she shared as an example of successful pushback.
KICLEI is an organization dedicated to empowering local governments to address the needs in their community, and not to blindly follow the direction of groups like the UN.
The group also works to ensure “every Canadian enjoys the right to privacy, property, and self-determination, while fostering respect for our cultural and regional diversity.”
According to Braun, her goal is to “advocate for local environmental stewardship programs over globally mandated climate action plans” by informing Canadians of their property rights, particularly with respect to the attempted implementation of the UN’s climate policies.
“We’ve discovered that these programs are coming in through an organization called ICLEI (Local Governments for Sustainability) and the Federation of Canadian Municipalities, who have brought certain programs down to the municipal level to drive climate action plans,” Braun explained.
Following this discovery, Braun has been working to bring awareness to the issue and persuade city and town councils to vote against UN recommendations which would undermine their citizens’ sovereignty. She revealed that her first victory was in Thorold, Ontario.
Braun explained that a group of four “saw that the environmental committee had openings,” and decided to send delegations to the meeting, start petitions and pack the council with support.
“We did four delegations in a row and by the end of it the staff recommended that they withdraw from the program,” Braun stated. “We just had to show up and do the basic work and it worked.”
“That was our first big win and now we’ve taken those strategies, developed tools that we can bring across the country” to help citizens “push back on the climate action plan.”
Earlier in November, Maggie Hope Braun told LifeSiteNews via email that the meeting will address how global agendas, “particularly UN climate initiatives,” are reshaping municipal priorities and policies across Canada.
Braun voiced concerned over local governments feeling pressured to adopt policies set by international organizations rather than responding to local priorities.
“Programs aligned with UN climate goals often come with strings attached, especially regarding federal funding, which can compel municipalities to follow UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to access resources,” she wrote. “This reliance can dilute local autonomy, making it difficult for municipalities to allocate budgets according to their own needs, as funding is often tied to specific climate-related expenditures—like electric fleets—that may not suit every community’s practical or economic realities.”
She added that these programs often introduce costly mandates, increase taxes, and, in some cases, affect privacy through the use of data-monitoring smart technologies, all of which can strain communities financially and socially.
“Canadians are beginning to feel these pressures, and many are questioning the long-term impacts on their rights, privacy, and economic well-being,” Braun stated.
Braun’s concerns are hardly unfounded as in March, the World Health Organization (WHO) issued an “urgent” call for countries around the world to sign on to their sovereignty-undermining “Pandemic Accord” by May. However, as May came around, countries were still unable to agree on the treaty, with many refusing to sign away their sovereign rights.
As a result, the treaty was not signed into law, but critics have warned that the WHO will likely continues its efforts to coerce countries to sign the document.
Similarly, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau’s “pandemic prevention and preparedness” bill is set to become law despite concerns raised by Conservative senators that it gives sweeping powers to government, particularly over agriculture.
Agriculture
The Climate Argument Against Livestock Doesn’t Add Up

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
Livestock contribute far less to emissions than activists claim, and eliminating them would weaken nutrition, resilience and food security
The war on livestock pushed by Net Zero ideologues is not environmental science; it’s a dangerous, misguided campaign that threatens global food security.
The priests of Net Zero 2050 have declared war on the cow, the pig and the chicken. From glass towers in London, Brussels and Ottawa, they argue that cutting animal protein, shrinking herds and pushing people toward lentils and lab-grown alternatives will save the climate from a steer’s burp.
This is not science. It is an urban belief that billions of people can be pushed toward a diet promoted by some policymakers who have never worked a field or heard a rooster at dawn. Eliminating or sharply reducing livestock would destabilize food systems and increase global hunger. In Canada, livestock account for about three per cent of total greenhouse gas emissions, according to Environment and Climate Change Canada.
Activists speak as if livestock suddenly appeared in the last century, belching fossil carbon into the air. In reality, the relationship between humans and the animals we raise is older than agriculture. It is part of how our species developed.
Two million years ago, early humans ate meat and marrow, mastered fire and developed larger brains. The expensive-tissue hypothesis, a theory that explains how early humans traded gut size for brain growth, is not ideology; it is basic anthropology. Animal fat and protein helped build the human brain and the societies that followed.
Domestication deepened that relationship. When humans raised cattle, sheep, pigs and chickens, we created a long partnership that shaped both species. Wolves became dogs. Aurochs, the wild ancestors of modern cattle, became domesticated animals. Junglefowl became chickens that could lay eggs reliably. These animals lived with us because it increased their chances of survival.
In return, they received protection, veterinary care and steady food during drought and winter. More than 70,000 Canadian farms raise cattle, hogs, poultry or sheep, supporting hundreds of thousands of jobs across the supply chain.
Livestock also protected people from climate extremes. When crops failed, grasslands still produced forage, and herds converted that into food. During the Little Ice Age, millions in Europe starved because grain crops collapsed. Pastoral communities, which lived from herding livestock rather than crops, survived because their herds could still graze. Removing livestock would offer little climate benefit, yet it would eliminate one of humanity’s most reliable protections against environmental shocks.
Today, a Maasai child in Kenya or northern Tanzania drinking milk from a cow grazing on dry land has a steadier food source than a vegan in a Berlin apartment relying on global shipping. Modern genetics and nutrition have pushed this relationship further. For the first time, the poorest billion people have access to complete protein and key nutrients such as iron, zinc, B12 and retinol, a form of vitamin A, that plants cannot supply without industrial processing or fortification. Canada also imports significant volumes of soy-based and other plant-protein products, making many urban vegan diets more dependent on long-distance supply chains than people assume. The war on livestock is not a war on carbon; it is a war on the most successful anti-poverty tool ever created.
And what about the animals? Remove humans tomorrow and most commercial chickens would die of exposure, merino sheep would overheat under their own wool and dairy cattle would suffer from untreated mastitis (a bacterial infection of the udder). These species are fully domesticated. Without us, they would disappear.
Net Zero 2050 is a climate target adopted by federal and provincial governments, but debates continue over whether it requires reducing livestock herds or simply improving farm practices. Net Zero advocates look at a pasture and see methane. Farmers see land producing food from nothing more than sunlight, rain and grass.
So the question is not technical. It is about how we see ourselves. Does the Net Zero vision treat humans as part of the natural world, or as a threat that must be contained by forcing diets and erasing long-standing food systems? Eliminating livestock sends the message that human presence itself is an environmental problem, not a participant in a functioning ecosystem.
The cow is not the enemy of the planet. Pasture is not a problem to fix. It is a solution our ancestors discovered long before anyone used the word “sustainable.” We abandon it at our peril and at theirs.
Dr. Joseph Fournier is a senior fellow at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy. An accomplished scientist and former energy executive, he holds graduate training in chemical physics and has written more than 100 articles on energy, environment and climate science.
Environment
Canada’s river water quality strong overall although some localized issues persist

From the Fraser Institute
By Annika Segelhorst and Elmira Aliakbari
Canada’s rivers are vital to our environment and economy. Clean freshwater is essential to support recreation, agriculture and industry, an to sustain suitable habitat for wildlife. Conversely, degraded freshwater can make it harder to maintain safe drinking water and can harm aquatic life. So, how healthy are Canada’s rivers today?
To answer that question, Environment Canada uses an index of water quality to assess freshwater quality at monitoring stations across the country. In total, scores are available for 165 monitoring stations, jointly maintained by Environment Canada and provincial authorities, from 17 in Newfoundland and Labrador, to 8 in Saskatchewan and 20 in British Columbia.
This index works like a report card for rivers, converting water test results into scores from 0 to 100. Scientists sample river water three or more times per year at fixed locations, testing indicators such as oxygen levels, nutrients and chemical levels. These measurements are then compared against national and provincial guidelines that determine the ability of a waterway to support aquatic life.
Scores are calculated based on three factors: how many guidelines are exceeded, how often they are exceeded, and by how much they are exceeded. A score of 95-100 is “excellent,” 80-94 is “good,” 65-79 is “fair,” 45-64 is “marginal” and a score below 45 is “poor.” The most recent scores are based on data from 2021 to 2023.
Among 165 river monitoring sites across the country, the average score was 76.7. Sites along four major rivers earned a perfect score: the Northeast Magaree River (Nova Scotia), the Restigouche River (New Brunswick), the South Saskatchewan River (Saskatchewan) and the Bow River (Alberta). The Bayonne River, a tributary of the St. Lawrence River near Berthierville, Quebec, scored the lowest (33.0).
Overall, between 2021 and 2023, 83.0 per cent of monitoring sites across the country recorded fair to excellent water quality. This is a strong positive signal that most of Canada’s rivers are in generally healthy environmental condition.
A total of 13.3 per cent of stations were deemed to be marginal, that is, they received a score of 45-64 on the index. Only 3.6 per cent of monitoring sites fell into the poor category, meaning that severe degradation was limited to only a few sites (6 of 165).
Monitoring sites along waterways with relatively less development in the river’s headwaters and those with lower population density tended to earn higher scores than sites with developed land uses. However, among the 11 river monitoring sites that rated “excellent,” 8 were situated in areas facing a combination of pressures from nearby human activities that can influence water quality. This indicates the resilience of Canada’s river ecosystems, even in areas facing a combination of multiple stressors from urban runoff, agriculture, and industrial activities where waterways would otherwise be expected to be the most polluted.
Poor or marginal water quality was relatively more common in monitoring sites located along the St. Lawrence River and its major tributaries and near the Great Lakes compared to other regions. Among all sites in the marginal or poor category, 50 per cent were in this area. The Great Lakes-St. Lawrence region is one of the most population-dense and extensively developed parts of Canada, supporting a mix of urban, agricultural, and industrial land uses. These pressures can introduce harmful chemical contaminants and alter nutrient balances in waterways, impairing ecosystem health.
In general, monitoring sites categorized as marginal or poor tended to be located near intensive agriculture and industrial activities. However, it’s important to reiterate that only 28 stations representing 17.0 per cent of all monitoring stations were deemed to be marginal or poor.
Provincial results vary, as shown in the figure below. Water quality scores in Newfoundland and Labrador, Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick, Saskatchewan and Alberta were, on average, 80 points or higher during the period from 2021 to 2023, indicating that water quality rarely departed from natural or desirable levels.
Rivers sites in Nova Scotia, Ontario, Manitoba and B.C. each had average scores between 74 and 78 points, suggesting occasional departures from natural or desirable levels.
Finally, Quebec’s average river water quality score was 64.5 during the 2021 to 2023 period. This score indicates that water quality departed from ideal conditions more frequently in Quebec than in other provinces, especially compared to provinces like Alberta, Saskatchewan and P.E.I. where no sites rated below “fair.”
Overall, these results highlight Canada’s success in maintaining a generally high quality of water in our rivers. Most waterways are in good shape, though some regions—especially near the Great Lakes and along the St. Lawrence River Valley—continue to face pressures from the combined effects of population growth and intensive land use.
-
 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta Next Panel calls to reform how Canada works
-

 Automotive2 days ago
Automotive2 days agoCanada’s EV gamble is starting to backfire
-

 International7 hours ago
International7 hours agoGeorgia county admits illegally certifying 315k ballots in 2020 presidential election
-
 Digital ID24 hours ago
Digital ID24 hours agoCanadian government launches trial version of digital ID for certain licenses, permits
-

 Business23 hours ago
Business23 hours agoThe “Disruptor-in-Chief” places Canada in the crosshairs
-

 Agriculture1 day ago
Agriculture1 day agoEnd Supply Management—For the Sake of Canadian Consumers
-

 Alberta6 hours ago
Alberta6 hours agoCalgary’s new city council votes to ban foreign flags at government buildings
-
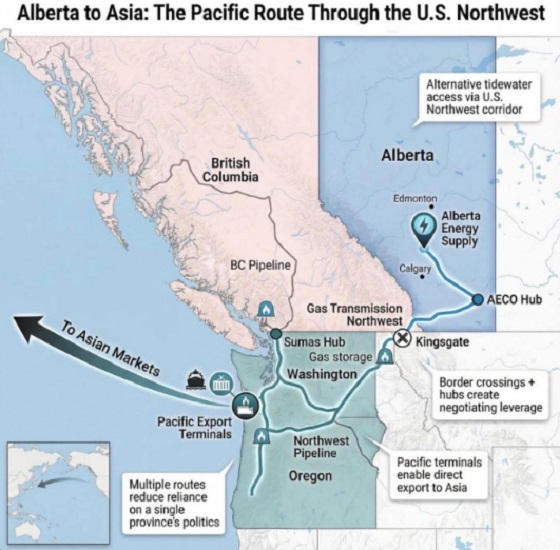
 Alberta10 hours ago
Alberta10 hours agoWhat are the odds of a pipeline through the American Pacific Northwest





