Censorship Industrial Complex
Australia passes digital ID bill, raising fears of government surveillance without accountability

From LifeSiteNews
By David James
Critics argue the legislation, enacted under the guise of increased security, ramps up government surveillance and control, with no accountability mechanisms for public sector misuse.
The Australian Parliament has passed the Digital ID Bill 2024 and Digital ID (Transitional and Consequential Provisions) Bill 2024 which, it claims, will provide “certainty” for the expansion of the existing Australian government digital ID system.
The move is being presented as a way to improve “privacy and security” for people when interacting online by “verifying” users’ identities. The government claims that the legislation will reduce fraud and other malpractice by private actors, but the bill says nothing about the public actors, the government. The implication is that that the public sector will never do anything wrong with its increased powers, raising the suspicion that it is yet another move by state and federal governments to increase surveillance and control over the lives of citizens.
Australia is a paternalistic society and there is no mechanism to hold the executive branch of government accountable – indeed the possibility is rarely raised. There is thus nothing to stop more intrusions into people’s privacy by the government.
Commenting on the passing of the bill, Queensland Senator Malcolm Roberts from the One Nation Party said that, while the voluntary system has been presented as a measure for security and convenience it could lead to significant privacy breaches, cyber-attacks, and government overreach. He described it as a potential attack on Australians’ “freedom, privacy, and way of life,” especially if it eventually becomes mandatory.
Roberts pointed to the Digital ID bill, the Online Safety Act, the Identity Services Verification Act, and the Misinformation and Disinformation Bill as elements of what looks like a coordinated plan by the federal government “to identify, punish and imprison anyone who resists this slide back into serfdom.” In the initial inquiry into the Digital ID bill, he said, the Human Rights Commission “drew attention to the lack of protection of privacy and human rights in the bill,” but it was ignored. Roberts added that the bill is very similar to legislation being implemented in other Western nations.
A significant proportion of the Australian population has concluded that politicians and the public sector cannot be trusted and that they fail to scrutinize their own actions. As if to underline this unaccountability, the Digital ID bill was passed using “tricks used to stifle debate and public discussion,” according to former federal senator Craig Kelly. He said on X (formerly Twitter) that the way the bill was passed was “contrary to precedent, the spirit of the Constitution and [the] Westminster tradition.”
“Labor introduced the Digital ID in the Senate (the House of review) instead of the House of Representatives,” Kelly wrote. “Then they guillotined debate in the Senate. And in House of Representatives, Labor shifted debate to the Federation Chamber where the Liberals put up token resistance with only one Liberal MP and two National MP’s bothering to speak on the Bill – and they didn’t even try any amendments to protect privacy or to try and safeguard against it being made compulsory.”
🔥🔥🔥BREAKING 😥😥😥
At 4.50pm this afternoon, and with only token opposition from the Liberals & Nationals the Digital ID Bill was passed by the Parliament.
A sad day for Australia, as the nation marches further down the road towards a totalitarian society.
And never… pic.twitter.com/GjVtIxwK0t
— Craig Kelly (@CraigKellyPHON) May 16, 2024
The aggressive government actions during the COVID crisis have shown just how abusive Australian politicians and the public sector can be, and how few ways there are for citizens to protect themselves. The restrictions on free speech, free movement, and freedom of thought were extreme.
The government mendacity continues – at a time when federal laws against “disinformation and misinformation” are being debated. There is constant propaganda in government-funded media outlets about what an effective job was done against the “pandemic” by pursuing lockdowns and mass vaccination. It is false; there was no pandemic. The Australian Bureau of Statistics found that 2020 and 2021 had the lowest number of deaths from respiratory diseases since records have been kept.
The federal government, in a statement, is giving the impression that the move is merely a way to protect vulnerable Australians, to give certainty for providers and services, and to provide transparency in order “to build public trust.” But what is not said is more important than what is said. There is no mechanism for Australians to redress wrongs committed by the government.
What should happen is something that has never existed in Australia: the establishment of a way for Australians to hold the public sector accountable and stop their governments becoming a menace, as occurred during the “pandemic.” Unless public servants are at risk of being penalized, or at least of having their actions constrained, there is a strong likelihood that fears about the Digital ID Bill will ultimately be realized.
Censorship Industrial Complex
Former residential school student refutes ‘genocide’ claims, recalls positive experience

From LifeSiteNews
An Indigenous whistleblower condemned the media-driven narrative about ‘mass’ graves at residential schools that led to church burnings across Canada.
An Indigenous whistleblower shared his positive experience at a Residential school, debunking the claim that the schools abused and murdered their students.
In an April 5 interview with Rebel News reporter Drea Humphrey, a Kamloops Band member and former Kamloops Indian Residential School student revealed that there was no”genocide” at the schools and many students benefited from the institution.
“A lot of the students were happy to be there,” the Band member, whose identity was kept anonymous, said. “They were away from abusive families, dysfunctional families, alcoholism. So, they were happy to be there.”
The former student revealed that he was treated well during his time at the residential schools in the 1970s. He also described the priests and nuns who ran the school as good people, referring to Father Noonan, the principal at the time, as “a real nice guy.”
Residential schools, while run by both the Catholic Church and other Christian churches, were mandated and set up by the federal government and ran from the late 19th century until the last school closed in 1996.
While some children did tragically die at the once-mandatory boarding schools, evidence has revealed that many of the children passed away as a result of unsanitary conditions due to underfunding by the federal government, not the Catholic Church.
As a consequence, since 2021, when the mainstream media ran with inflammatory and dubious claims that hundreds of children were buried and disregarded by Catholic priests and nuns who ran some of the schools, over 100 churches have been burned or vandalized across Canada in seeming retribution.
However, to date, there have been no mass graves discovered at any residential schools across Canada.
The Band member revealed that the Kamloops Band knows they “made a mistake” in labeling the ground anomalies as “unmarked graves.”
In fact, according to the Band member, in the 1990s, the Band used the supposed location of the 215 child graves for their new Powwow Arbour and Heritage Park. The project was only allowed to continue after studies concluded that there were no artifacts or archaeological remains at the site.
Therefore, if there were mass graves at that location, they would have been discovered in the 1990s, not in 2021.
The Band member revealed that he does not believe a “genocide” took place at residential schools, while condemning the church burnings across Canada.
“When I was growing up religion and church meant community and family,” he explained. “It seems like the Liberals want to destroy family so the way to do that is to attack religion.”
“Attacking religion was a good excuse to burn the churches,” he said.
Regardless of his testimony and the lack of evidence to support the claim, mainstream media outlets perpetuate the “mass graves” narrative and even threaten to punish those who oppose it. In November, CBC subtly suggested that “residential school denialism” should be criminalized.
Censorship Industrial Complex
Scott Atlas: COVID lockdowns, censorship have left a ‘permanent black mark on America’

From LifeSiteNews
Editor’s note: The following text is taken from a speech delivered by radiologist and political commentator Scott Atlas to the Independent Medical Alliance conference in Atlanta, Georgia, on April 5, 2025. Transcription provided by Dr. Robert Malone.
ATLANTA (Robert Malone) — First, thank you to the organizers, and to my many friends and supporters here. It’s great to be here – surrounded by people who believe in personal freedom!
At the recent international Alliance for Responsible Citizenship (ARC) forum in London, I was invited to address the question, “Can Institutions be Reformed?” Begun with Jordan Peterson, ARC joins voices from all over the world to discuss how to refresh the institutions and best values of Western heritage, values that provided the world with history’s most successful societies, particularly the commitment to freedom.
I asked that audience to first consider:
Why, at this moment in history, are we finally focusing on how institutions should be reformed, or if institutions can even be reformed?
After all, for decades we have been aware that our institutions were failing – editorialized, dishonest journalism; wasteful, corrupt government; and agenda-driven schools and universities increasingly unbalanced toward the left, with many conservative faculty and students often self-censoring, afraid to offer unpopular views.
The answer? It is COVID, the pandemic mismanagement specifically – the most tragic breakdown of leadership and ethics that free societies have seen in our lifetimes.
COVID fully exposed the massive, across-the-board, institutional failure – including the shocking reality of overt censorship in our country, the loss of freedoms and the frank violation of human rights – in this country, one explicitly founded on a commitment to freedom.
Yet, oddly, the pandemic remained invisible at the ARC conference, unmentioned by dozens of speakers addressing freedom. It was the elephant in the room – just as explaining the truth about lockdowns, the pseudoscience mandates on masks and social distancing, closing churches and businesses, prohibiting visits to elderly parents in nursing homes while they die – all are missing from post-election discussions today in the United States, including, notably, any of the very public statements and proclamations from the new administration about health care today.
Today, in the wake of COVID, we are left with an undeniable crisis in health. Trust in health guidance has plummeted more rapidly since 2019 than any other government institution, with almost two-thirds now rating the FDA and the CDC as “only fair or poor.”
Half of America no longer has much confidence in science itself. Trust in our doctors and hospitals dropped from 71 percent in 2019 to 40 percent in 2024. The loss of trust is part of the disgraceful legacy of those who held power, who were relied upon to use critical thinking and an ethical compass on behalf of the public, who were handed the precious gift of automatic credibility and almost blind trust.
To understand how to move forward to restore trust, it’s important to first acknowledge basic facts about the pandemic, and keep repeating them, because truth serves as the starting point of all rational discussion. And we must live in a society where facts are acknowledged.
Remember – lockdowns were not caused by the virus. Human beings decided to impose lockdowns.
Indeed, lockdowns were widely instituted, they failed to stop the dying, and they failed to stop the spread – that’s the data: Bjornskov, 2021; Bendavid, 2021; Agarwal, 2021; Herby, 2022; Kerpen, 2023; Ioannidis, 2024; Atlas, 2024.
Lockdowners ignored Henderson’s classic review 15 years earlier showing lockdowns were both ineffective and extremely harmful. They rejected the alternative, targeted protection, first recommended on national media in March 2020 independently by Ioannidis, by Katz, and by me (Atlas) – and then repeatedly for months – based on data already known back then, in spring of 2020. It was not learned 7 months later in 2020, when the Great Barrington Declaration reiterated it, or in 2021, or 2022, or more recently.
And the Birx-Fauci lockdowns directly inflicted massive damage on children and literally killed millions, especially, sinfully, the poor. “The U.S. alone would have had 1.6 million fewer deaths (through July 2023) if it had the performance of Sweden,” according to a review of 34 countries. Bianchi calculates that over the next 15-20 years, the unemployment alone will cause another million additional American deaths – from the economic shutdown, not the virus.
Beyond a reckless disregard for foreseeable death from their policies, America’s leaders imposed sinful harms and long-lasting damage on our children, the totality of which may not be realized for decades. Mandatory school closings, forced isolation of teens and college students, and required injections of healthy children with experimental drugs attempting to shield adults will be a permanent black mark on America.
It is also worth remembering that this was a health policy problem.
While credentials are not the sole determinant of expertise, I was the only health policy scholar on the White House Task Force and advising the president. Virology is not health policy; epidemiology is not health policy. And while physicians are important in contributing, they are not inherently expert in health policy. Those are only pieces of a larger, more complex puzzle. The stunning fact is – I was the only medical expert there focused on stopping both the death and destruction from the virus and the death and destruction from the policy itself.
As Hannah Arendt observed in “Eichmann in Jerusalem”:
What has come to light is neither nihilism nor cynicism, as one might have expected, but a quite extraordinary confusion over elementary questions of morality.
More than massive incompetence, more than a fundamental lack of critical thinking, we saw the disappearance of society’s moral compass, so pervasive that we have rightfully lost trust in our institutions, leaders, and fellow citizens, trust that is essential to the function of any free and diverse society.
Why did free people accept these draconian, unprecedented, and illogical lockdowns?
This is the question. And the answer reveals the reason for today’s silence on the pandemic.
Clearly, censorship and propaganda are key parts of the explanation, tools of control that convinced the public of two fallacies – that a consensus of experts on lockdowns existed, and dissenters to that false consensus were highly dangerous.
Censorship first was done by the media companies themselves – when it counted most:
- In 2020, before the Biden administration, when school closures and lockdowns were being implemented;
- May 2020, YouTube bragged about its “aggressive policies against misinformation”;
- August 2020, Facebook shamelessly admitted to the Washington Post it had already taken down 7 million posts on the pandemic;
- My interviews as advisor to the president were pulled down by YouTube on September 11, 2020, by Twitter blocking me on October 18, 2020.
You might think the public – in a free society – should know what the advisor to the president was saying?
And what was the response to truth at America’s universities, our centers for the free exchange of ideas, including Stanford, my employer?
Censorship: character assassination, intimidation, and to me, formal censure.
Why is censorship used? To shut someone up, yes; but more importantly, to deceive the public – to stop others from hearing, to convince a naïve public there is a “consensus on truth.”
Truth is not a team sport.
Truth is not determined by consensus, or by numbers of people who agree, or by titles. It is discovered by debate, proven by critical analysis of evidence. Arguments are won by data and logic, not by personal attack or censoring others.
I am proud to be an outlier – happily proven right when the inliers are so wrong – but Cancel Culture is effective because it stops others from speaking. I received hundreds of emails from doctors and scientists all over the country, including from Stanford, from other professors, and from inside the NIH, saying, “Keep talking, Scott, you’re 100 percent right, but we’re afraid for our families and our jobs.”
And indeed, no one at Stanford Medical School – not a single faculty member there – spoke publicly against their attack on me. Only Martin Kulldorff, then a Harvard epidemiologist, wrote in and publicly challenged the 98 signatories at Stanford to debate on whether I was correct or not (none accepted that challenge!).
But that alone doesn’t explain today’s silence about that extraordinary collapse. It is not simply “issue fatigue.”
It is also that so many smart people, including many claiming to support the new “disruptors,” bought into the irrational measures when it counted most, when our kids and particularly the poor were being destroyed in 2020, uncomfortable to discuss and admit, but far more fundamental than the Sars2 origin, or Fauci, or the vaccine. That acquiescence, that silence, that cowardice, and that failure to grasp reality are inconvenient truths that no one wants to admit.
Today, disruption is sorely needed, and many are basking in the resounding victory of history’s most disruptive politician, President Donald J. Trump.
As promised, his new administration is moving quickly, disrupting on several fronts: national security, energy, trade, justice, immigration, and perhaps most importantly with Elon Musk’s effort to eliminate government waste and fraud, and protect our money. After all, the government has no money – it’s all our money, taxpayers’ money!
In health care, important changes in the status quo have also begun, first with Elon Musk’s much needed DOGE, streamlining tens of thousands of Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) bureaucrats while exposing massive fraud and waste in programs like Medicaid.
And Secretary of HHS Bobby Kennedy has also provoked an important, new national dialogue with his “Make America Healthy Again” mantra focused on wholesome foods to achieve the goal everyone readily supports – good health for themselves and their children. And no doubt, ensuring safety of all drugs and eliminating corruption in pharma and the food industry are also crucial to health. I am a strong supporter of those ideas.
We also have two excellent appointments in health – my friends and colleagues, Marty Makary to FDA and Jay Bhattacharya to NIH. Both Marty and Jay are highly knowledgeable, have top training and expertise, and are committed to critical thinking, to legitimate science, and most importantly to free scientific debate.
But I am concerned that most are simultaneously eager to “turn the page” on the human rights violations, the censorship, the true “constitutional crisis” – no setting the record straight, no official recognition of facts, no accountability? The ultimate disruptor won, and his disruptor appointees will now be in charge – so all is well?
Silently turning the page on modern history’s most egregious societal failure would be extraordinarily harmful. Failure to issue official statements of truth by the new government health agency leaders about the pandemic management would prevent closure for the millions who lost loved ones and whose children suffered such harms. And it would completely eliminate all accountability. Remember, only public accountability will prevent recurrence, and accountability is necessary to restore trust in institutions, leadership, and among fellow citizens.
My second concern: the era of trusting experts based solely on credentials must be over. But will that backlash against the failed “expert class” usher in a different wave of false belief? We cannot forget that legitimate expertise is still legitimate; that known, solid medical science is still valid; that unfounded theories based on simple correlations are not scientifically sound.
And we do not want to inadvertently replicate the cancel culture that harmed so many, with another wave of demonizing anyone who doesn’t 100 percent support the new narratives. It’s already begun – that if you disagree with any of the incoming opinions, then you must be “bought by pharma!” Blind support is just as bad as blind opposition; critical thinking must prevail.
What reforms are needed now?
- The first step to restore trust is formal, official statements of truth on the COVID lockdowns, masks, and other pseudoscience mandates from new HHS, NIH, FDA, CDC, CMS leaders.
- We need to forbid – by law – all shutdowns and reset that the CDC and other health agencies are (only) advisory. They recommend; they give information – they don’t set laws. They don’t have the power to set mandates. And if our guaranteed freedoms are not always valid, especially during crises, then they are not guaranteed at all.
- We need to add term limits (5 years?) to all mid- and top-level health agency positions. We cannot continue the perverse incentives of career bureaucrats accruing personal power, like Anthony Fauci and Deborah Birx with their 30-plus years in government.
- All new heads of HHS, FDA, NIH, CDC, and CMS should be prohibited from post-government company board positions in health sectors they regulate for ~5 years. It’s unethical, an overt conflict-of-interest. Why hasn’t that been announced?
- We need to forbid drug royalty sharing by employees of the NIH, the FDA, and the CDC. $325 million of royalties were shared with pharma by those people over the 10 years prior to the pandemic. That’s a shocking conflict of interest.
- We should forbid all mandates forcing people to take drugs. First, the essence of all ethical medical practice is informed consent. And what kind of a “free country” requires you to inject a drug into your child or yourself? No – that’s antithetical to freedom. In public health, you give the information… you shouldn’t need to force anything legitimate, but you do need to prove the case.
- We need to require the immediate posting of discussions in all FDA, CDC, and NIH meetings. They work for us. What are they saying? We should know in real-time.
- We need accountability for all government funding. We have 15+ universities getting >$500M/year from NIH alone. The essence of research is free debate. If they’re thwarting that with intimidation, like faculty censures, why would they be entitled to U.S. taxpayers’ money?
More broadly, I and others are working on policies to ensure the free exchange of ideas – the essence of all legitimate science, the basis for the mission of education.
Ideological gatekeeping in public discourse has no place in free societies, especially in science and health.
Here’s the point – the solution to misinformation is more information. No one should be trusted to be the arbiter of truth.
Ultimately, most solutions come from individuals, and ultimately, it is individuals, not institutions, who will save freedom.
I fear we still have a disastrous void in courage in our society today.
To quote CS Lewis, “Courage is not simply one of the virtues, but the form of every virtue at the testing point.”
We cannot have a peaceful, free society if it’s filled with people who lack the courage to speak and act with certainty on Hannah Arendt’s “elementary questions of morality.”
Finally, to the young people here, never forget what GK Chesterton said:
Right is right, even if nobody does it. Wrong is wrong, even if everybody is wrong about it.
Reprinted with permission from Robert Malone.
-

 Also Interesting2 days ago
Also Interesting2 days agoMortgage Mayhem: How Rising Interest Rates Are Squeezing Alberta Homeowners
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta takes big step towards shorter wait times and higher quality health care
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoStocks soar after Trump suspends tariffs
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoBiden Admin concealed report on earliest COVID cases from 2019
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump raises China tariffs to 125%, announces 90-day pause for countries who’ve reached out to negotiate
-
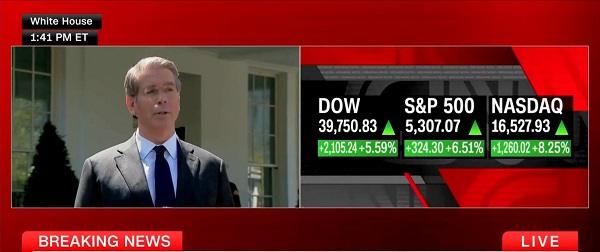
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoScott Bessent Says Trump’s Goal Was Always To Get Trading Partners To Table After Major Pause Announcement
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoResearchers Link China’s Intelligence and Elite Influence Arms to B.C. Government, Liberal Party, and Trudeau-Appointed Senator
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoTrump signs four executive orders promoting coal industry




