Canadian Energy Centre
Analyst says LNG Canada likely to start exports before year-end

Welders with JGC-Fluor following completion of the final weld on the first production train at the LNG Canada project, in Kitimat, B.C. in July 2024. Since construction began in 2018, upwards of 380 pipe welders have worked on the LNG Canada project. Photo courtesy JGC-Fluor
From the Canadian Energy Centre
By Will Gibson
Canada’s first liquefied natural gas export terminal ‘on the cusp’ of its testing phase
Momentum is building for the long-awaited start-up of Canada’s first liquefied natural gas (LNG) export project.
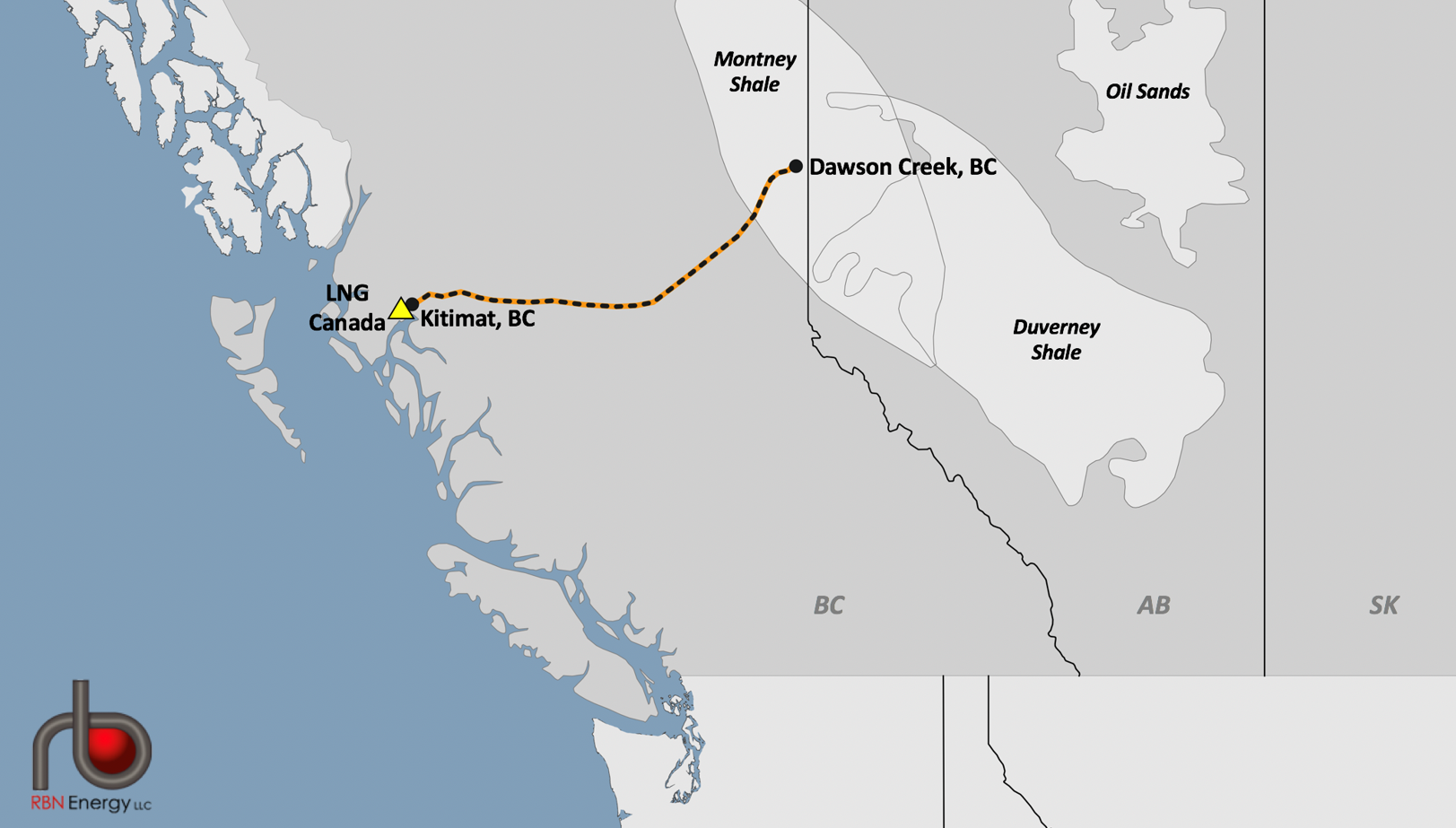
Shipments from the LNG Canada terminal at Kitimat, B.C. may now start earlier than expected, later this year rather than mid-2025, according to Martin King, Canadian energy specialist with Houston-based RBN Energy.
“LNG Canada appears to be on the cusp of its testing phase and is likely to be exporting some cargoes of LNG before the end of this year,” King wrote recently.
He made the prediction after a senior executive with Shell, the project’s lead owner, said it could deliver its first cargo earlier than previously planned, in the wake of two key milestones.
Fluor reported in July it had completed the final weld on the first production train while Petronas, which holds a 25 per cent stake in LNG Canada, announced it would add three LNG vessels to its North American fleet, doubling its size.
A longtime industry insider sees the $18 billion LNG Canada terminal as a game changer.
“This is decades in the making. Canada has been trying to get its LNG business up and running since the 1970s but it has been sidetracked for one reason or another,” says Calgary-based consultant Racim Gribaa, who has worked in the industry for more than 25 years.
“This project is perfectly placed to take advantage of an awesome opportunity given the demand for LNG worldwide is growing exponentially.”
The project, which will use the Coastal GasLink pipeline, completed in November 2023, to bring gas from northeastern British Columbia to the Kitimat terminal for processing and shipping, will have capacity to produce up to 14 million tonnes per year in its first phase.
While that’s a fraction of the 404 million tonnes of global demand in 2023, Gribaa says Asian buyers view LNG Canada as secure supplier in part due to its geography.
“The closest point to Asia is Canada’s west coast, so you have the shortest shipping route, which makes for optimal transportation costs. The traders and LNG industry see it as valuable for that reason,” says Gribaa, who previously worked in LNG trade in Qatar, one of the world’s largest exporters.
And the project is coming online at a time when worldwide demand is surging.
“The worldwide demand has effectively doubled every decade since 1990, when it was 50 MPTA. We are now closing in on 500 MPTA and that is accelerating,” Gribaa says.
“The world will need 10 LNG Canadas in 10 years and 100 more LNG Canadas in the next 30 years.”
The project has plans for a second phase that would double production to 28 million tonnes per year. Based on demand, Gribaa says “the question isn’t if it will go forward, it’s when the consortium will announce the expansion.”
World LNG demand growth will be particularly strong in Asia, where Shell’s four LNG Canada partners – Petronas (25 per cent), PetroChina (15 per cent), Mitsubishi (15 per cent) and Korea Gas Corporation (five per cent) – are headquartered.
“Each of these markets has historical demand for LNG and that demand will continue to grow in the coming decades,” he says, adding that LNG in Asia can be used for power generation and heavy industry, and to reduce air pollution from coal-fired power.
Overall, generating electricity in China with LNG from Canada rather than coal could reduce emissions by up to 62 per cent, according to a 2020 study published in the Journal for Cleaner Production.
A 2022 study by Wood Mackenzie found that growing Canada’s LNG industry could reduce net emissions in Asia by 188 million tonnes per year through 2050.
Alberta
The permanent CO2 storage site at the end of the Alberta Carbon Trunk Line is just getting started

Wells at the Clive carbon capture, utilization and storage project near Red Deer, Alta. Photo courtesy Enhance Energy
From the Canadian Energy Centre
Inside Clive, a model for reducing emissions while adding value in Alberta
It’s a bright spring day on a stretch of rolling farmland just northeast of Red Deer. It’s quiet, but for the wind rushing through the grass and the soft crunch of gravel underfoot.
The unassuming wellheads spaced widely across the landscape give little hint of the significance of what is happening underground.
In just five years, this site has locked away more than 6.5 million tonnes of CO₂ — equivalent to the annual emissions of about 1.5 million cars — stored nearly four CN Towers deep beneath the surface.
The CO₂ injection has not only reduced emissions but also breathed life into an oilfield that was heading for abandonment, generating jobs, economic activity and government revenue that would have otherwise been lost.
This is Clive, the endpoint of one of Canada’s largest carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) projects. And it’s just getting started.
Rooted in Alberta’s first oil boom
Clive’s history ties to Alberta’s first oil boom, with the field discovered in 1952 along the same geological trend as the legendary 1947 Leduc No. 1 gusher near Edmonton.
“The Clive field was discovered in the 1950s as really a follow-up to Leduc No. 1. This is, call it, Leduc No. 4,” said Chris Kupchenko, president of Enhance Energy, which now operates the Clive field.
Over the last 70 years Clive has produced about 70 million barrels of the site’s 130 million barrels of original oil in place, leaving enough energy behind to fuel six million gasoline-powered vehicles for one year.
“By the late 1990s and early 2000s, production had gone almost to zero,” said Candice Paton, Enhance’s vice-president of corporate affairs.
“There was resource left in the reservoir, but it would have been uneconomic to recover it.”
Gearing up for CO2
Calgary-based Enhance bought Clive in 2013 and kept it running despite high operating costs because of a major CO2 opportunity the company was developing on the horizon.
In 2008, Enhance and North West Redwater Partnership had launched development of the Alberta Carbon Trunk Line (ACTL), one of the world’s largest CO2 transportation systems.
Wolf Midstream joined the project in 2018 as the pipeline’s owner and operator.
Completed in 2020, the groundbreaking $1.2 billion project — supported by the governments of Canada and Alberta — connects carbon captured at industrial sites near Edmonton to the Clive facility.
“With CO2 we’re able to revitalize some of these fields, continue to produce some of the resource that was left behind and permanently store CO2 emissions,” Paton said.
An oversized pipeline on purpose
Each year, about 1.6 million tonnes of CO2 captured at the NWR Sturgeon Refinery and Nutrien Redwater fertilizer facility near Fort Saskatchewan travels down the trunk line to Clive.
In a unique twist, that is only about 10 per cent of the pipeline’s available space. The project partners intentionally built it with room to grow.
“We have a lot of excess capacity. The vision behind the pipe was, let’s remove barriers for the future,” Kupchenko said.
The Alberta government-supported goal was to expand CCS in the province, said James Fann, CEO of the Regina-based International CCS Knowledge Centre.
“They did it on purpose. The size of the infrastructure project creates the opportunity for other emitters to build capture projects along the way,” he said.

CO2 captured at the Sturgeon Refinery near Edmonton is transported by the Alberta Carbon Trunk Line to the Clive project. Photo courtesy North West Redwater Partnership
Extending the value of aging assets
Building more CCUS projects like Clive that incorporate enhanced oil recovery (EOR) is a model for extending the economic value of aging oil and gas fields in Alberta, Kupchenko said.
“EOR can be thought of as redeveloping real estate,” he said.
“Take an inner-city lot with a 700-square-foot house on it. The bad thing is there’s a 100-year-old house that has to be torn down. But the great thing is there’s a road to it. There’s power to it, there’s a sewer connection, there’s water, there’s all the things.
“That’s what this is. We’re redeveloping a field that was discovered 70 years ago and has at least 30 more years of life.”
The 180 existing wellbores are also all assets, Kupchenko said.
“They may not all be producing oil or injecting CO2, but every one of them is used. They are our eyes into the reservoir.”

CO2 injection well at the Clive carbon capture, utilization and storage project. Photo for the Canadian Energy Centre
Alberta’s ‘beautiful’ CCUS geology
The existing wells are an important part of measurement, monitoring and verification (MMV) at Clive.
The Alberta Energy Regulator requires CCUS projects to implement a comprehensive MMV program to assess storage performance and demonstrate the long-term safety and security of CO₂.
Katherine Romanak, a subsurface CCUS specialist at the University of Texas at Austin, said that her nearly 20 years of global research indicate the process is safe.
“There’s never been a leak of CO2 from a storage site,” she said.
Alberta’s geology is particularly suitable for CCUS, with permanent storage potential estimated at more than 100 billion tonnes.
“The geology is beautiful,” Romanak said.
“It’s the thickest reservoir rocks you’ve ever seen. It’s really good injectivity, porosity and permeability, and the confining layers are crazy thick.”
CO2-EOR gaining prominence
The extra capacity on the ACTL pipeline offers a key opportunity to capitalize on storage potential while addressing aging oil and gas fields, according to the Alberta government’s Mature Asset Strategy, released earlier this year.
The report says expanding CCUS to EOR could attract investment, cut emissions and encourage producers to reinvest in existing properties — instead of abandoning them.
However, this opportunity is limited by federal policy.
Ottawa’s CCUS Investment Tax Credit, which became available in June 2024, does not apply to EOR projects.
“Often people will equate EOR with a project that doesn’t store CO2 permanently,” Kupchenko said.
“We like to always make sure that people understand that every ton of CO2 that enters this project is permanently sequestered. And we take great effort into storing that CO2.”
The International Energy Forum — representing energy ministers from nearly 70 countries including Canada, the U.S., China, India, Norway, and Saudi Arabia — says CO₂-based EOR is gaining prominence as a carbon sequestration tool.
The technology can “transform a traditional oil recovery method into a key pillar of energy security and climate strategy,” according to a June 2025 IEF report.
Tapping into more opportunity
In Central Alberta, Enhance Energy is advancing a new permanent CO2 storage project called Origins that is designed to revitalize additional aging oil and gas fields while reducing emissions, using the ACTL pipeline.
“Origins is a hub that’s going to enable larger scale EOR development,” Kupchenko said.
“There’s at least 10 times more oil in place in this area.”
Meanwhile, Wolf Midstream is extending the pipeline further into the Edmonton region to transport more CO2 captured from additional industrial facilities.
Canadian Energy Centre
Cross-Canada economic benefits of the proposed Northern Gateway Pipeline project

From the Canadian Energy Centre
Billions in government revenue and thousands of jobs across provinces
Announced in 2006, the Northern Gateway project would have built twin pipelines between Bruderheim, Alta. and a marine terminal at Kitimat, B.C.
One pipeline would export 525,000 barrels per day of heavy oil from Alberta to tidewater markets. The other would import 193,000 barrels per day of condensate to Alberta to dilute heavy oil for pipeline transportation.
The project would have generated significant economic benefits across Canada.

The following projections are drawn from the report Public Interest Benefits of the Northern Gateway Project (Wright Mansell Research Ltd., July 2012), which was submitted as reply evidence during the regulatory process.
Financial figures have been adjusted to 2025 dollars using the Bank of Canada’s Inflation Calculator, with $1.00 in 2012 equivalent to $1.34 in 2025.
Total Government Revenue by Region
Between 2019 and 2048, a period encompassing both construction and operations, the Northern Gateway project was projected to generate the following total government revenues by region (direct, indirect and induced):

British Columbia
- Provincial government revenue: $11.5 billion
- Federal government revenue: $8.9 billion
- Total: $20.4 billion
Alberta
- Provincial government revenue: $49.4 billion
- Federal government revenue: $41.5 billion
- Total: $90.9 billion
Ontario
- Provincial government revenue: $1.7 billion
- Federal government revenue: $2.7 billion
- Total: $4.4 billion
Quebec
- Provincial government revenue: $746 million
- Federal government revenue: $541 million
- Total: $1.29 billion
Saskatchewan
- Provincial government revenue: $6.9 billion
- Federal government revenue: $4.4 billion
- Total: $11.3 billion
Other
- Provincial government revenue: $1.9 billion
- Federal government revenue: $1.4 billion
- Total: $3.3 billion
Canada
- Provincial government revenue: $72.1 billion
- Federal government revenue: $59.4 billion
- Total: $131.7 billion
Annual Government Revenue by Region
Over the period 2019 and 2048, the Northern Gateway project was projected to generate the following annual government revenues by region (direct, indirect and induced):

British Columbia
- Provincial government revenue: $340 million
- Federal government revenue: $261 million
- Total: $601 million per year
Alberta
- Provincial government revenue: $1.5 billion
- Federal government revenue: $1.2 billion
- Total: $2.7 billion per year
Ontario
- Provincial government revenue: $51 million
- Federal government revenue: $79 million
- Total: $130 million per year
Quebec
- Provincial government revenue: $21 million
- Federal government revenue: $16 million
- Total: $37 million per year
Saskatchewan
- Provincial government revenue: $204 million
- Federal government revenue: $129 million
- Total: $333 million per year
Other
- Provincial government revenue: $58 million
- Federal government revenue: $40 million
- Total: $98 million per year
Canada
- Provincial government revenue: $2.1 billion
- Federal government revenue: $1.7 billion
- Total: $3.8 billion per year
Employment by Region
Over the period 2019 to 2048, the Northern Gateway Pipeline was projected to generate the following direct, indirect and induced full-time equivalent (FTE) jobs by region:

British Columbia
- Annual average: 7,736
- Total over the period: 224,344
Alberta
- Annual average: 11,798
- Total over the period: 342,142
Ontario
- Annual average: 3,061
- Total over the period: 88,769
Quebec
- Annual average: 1,003
- Total over the period: 29,087
Saskatchewan
- Annual average: 2,127
- Total over the period: 61,683
Other
- Annual average: 953
- Total over the period: 27,637
Canada
- Annual average: 26,678
- Total over the period: 773,662
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoWhat Connor Should Say To Oilers: It’s Not You. It’s Me.
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoThe Passage of Bill C-5 Leaves the Conventional Energy Sector With as Many Questions as Answers
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoFederal fiscal anchor gives appearance of prudence, fails to back it up
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCanada should already be an economic superpower. Why is Canada not doing better?
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta poll shows strong resistance to pornographic material in school libraries
-

 Crime1 day ago
Crime1 day agoFlorida rescues 60 missing kids in nation’s largest-ever operation
-

 Banks1 day ago
Banks1 day agoScrapping net-zero commitments step in right direction for Canadian Pension Plan
-

 Business11 hours ago
Business11 hours agoWhile China Hacks Canada, B.C. Sends Them a Billion-Dollar Ship Building Contract