Alberta
Alberta government’s fiscal update underscores need for rainy-day account

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill
According to the Smith government’s recent fiscal update, the government’s $2.9 billion projected budget surplus has increased to a $4.6 budget surplus in 2024/25 mainly due to higher-than-expected resource revenue. But the resource boom that fuels Alberta’s fiscal fortunes could end at any moment and pile more government debt on the backs of Albertans.
Resource revenue, fuelled by commodity prices (including oil and gas), is inherently volatile. For perspective, in just the last decade, the Alberta government’s annual resource revenue has been as low as $2.8 billion (2015/16) and accounted for just 6.5 per cent of total government revenue. In contrast, according to the Smith government’s fiscal update, projected resource revenue is $20.3 billion this fiscal year and will account for more than a quarter (26.1 per cent) of total government revenue.
But here’s the problem.
Successive Alberta governments—including the Smith government—have included nearly all resource revenue in the budget. In times of relatively high resource revenue, such as we’re currently experiencing, the government typically enjoys surpluses and, flush with cash, increases spending. But when resource revenues decline, the province’s finances turn to deficits.
The last time this happened Alberta ran nearly uninterrupted deficits from 2008/09 to 2020/21 while the province’s net financial position deteriorated by nearly $95 billion. As a result, Albertans went from paying $58 per person on annual provincial government debt interest costs to nearly $600 per person.
So how can the Smith government avoid the same fate as past Alberta governments who wallowed in red ink when the boom-and-bust cycle inevitably turned to bust?
The answer is simple—save during good times to help avoid deficits during bad times. The provincial government should determine a stable amount of resource revenue to be included in the budget annually and deposit any resource revenue above that amount automatically in a rainy-day account to be withdrawn in years when resource revenue falls below that stable amount.
This wouldn’t be Alberta’s first rainy-day account. In fact, the Alberta Sustainability Fund (ASF), established in 2003, was intended to operate this way. A major problem with the ASF, however, was that it was based in statutory law, which meant the Alberta government could unilaterally change the rules governing the fund. Consequently, the stable amount was routinely increased and by 2007 nearly all resource revenue was used for annual spending. The ASF was eventually drained and eliminated entirely in 2013. This time, the government should make the fund’s rules constitutional, which would help ensure it’s sustained over time.
Put simply, funds in a resurrected ASF will provide stability in the future by mitigating the impact of cyclical declines on the budget over the long term.
In the recent fiscal update, the Alberta government continues to risk relying on relatively high resource revenue to balance the budget. To avoid deficits and truly stabilize provincial finances for the future, the Smith government should reintroduce a rainy-day account.
Tegan Hill
Director, Alberta Policy, Fraser Institute
Alberta
Made in Alberta! Province makes it easier to support local products with Buy Local program

Show your Alberta side. Buy Local. |
When the going gets tough, Albertans stick together. That’s why Alberta’s government is launching a new campaign to benefit hard-working Albertans.
Global uncertainty is threatening the livelihoods of hard-working Alberta farmers, ranchers, processors and their families. The ‘Buy Local’ campaign, recently launched by Alberta’s government, encourages consumers to eat, drink and buy local to show our unified support for the province’s agriculture and food industry.
The government’s ‘Buy Local’ campaign encourages consumers to buy products from Alberta’s hard-working farmers, ranchers and food processors that produce safe, nutritious food for Albertans, Canadians and the world.
“It’s time to let these hard-working Albertans know we have their back. Now, more than ever, we need to shop local and buy made-in-Alberta products. The next time you are grocery shopping or go out for dinner or a drink with your friends or family, support local to demonstrate your Alberta pride. We are pleased tariffs don’t impact the ag industry right now and will keep advocating for our ag industry.”
Alberta’s government supports consumer choice. We are providing tools to help folks easily identify Alberta- and Canadian-made foods and products. Choosing local products keeps Albertans’ hard-earned dollars in our province. Whether it is farm-fresh vegetables, potatoes, honey, craft beer, frozen food or our world-renowned beef, Alberta has an abundance of fresh foods produced right on our doorstep.
Quick facts
- This summer, Albertans can support local at more than 150 farmers’ markets across the province and meet the folks who make, bake and grow our food.
- In March 2023, the Alberta government launched the ‘Made in Alberta’ voluntary food and beverage labelling program to support local agriculture and food sectors.
- Through direct connections with processors, the program has created the momentum to continue expanding consumer awareness about the ‘Made in Alberta’ label to help shoppers quickly identify foods and beverages produced in our province.
- Made in Alberta product catalogue website
Related information
Alberta
Province to expand services provided by Alberta Sheriffs: New policing option for municipalities

Expanding municipal police service options |
Proposed amendments would help ensure Alberta’s evolving public safety needs are met while also giving municipalities more options for local policing.
As first announced with the introduction of the Public Safety Statutes Amendment Act, 2024, Alberta’s government is considering creating a new independent agency police service to assume the police-like duties currently performed by Alberta Sheriffs. If passed, Bill 49 would lay additional groundwork for the new police service.
Proposed amendments to the Police Act recognize the unique challenges faced by different communities and seek to empower local governments to adopt strategies that effectively respond to their specific safety concerns, enhancing overall public safety across the province.
If passed, Bill 49 would specify that the new agency would be a Crown corporation with an independent board of directors to oversee its day-to-day operations. The new agency would be operationally independent from the government, consistent with all police services in Alberta. Unlike the Alberta Sheriffs, officers in the new police service would be directly employed by the police service rather than by the government.
“With this bill, we are taking the necessary steps to address the unique public safety concerns in communities across Alberta. As we work towards creating an independent agency police service, we are providing an essential component of Alberta’s police framework for years to come. Our aim is for the new agency is to ensure that Albertans are safe in their communities and receive the best possible service when they need it most.”
Additional amendments would allow municipalities to select the new agency as their local police service once it becomes fully operational and the necessary standards, capacity and frameworks are in place. Alberta’s government is committed to ensuring the new agency works collaboratively with all police services to meet the province’s evolving public safety needs and improve law enforcement response times, particularly in rural communities. While the RCMP would remain the official provincial police service, municipalities would have a new option for their local policing needs.
Once established, the agency would strengthen Alberta’s existing policing model and complement the province’s current police services, which include the RCMP, Indigenous police services and municipal police. It would help fill gaps and ensure law enforcement resources are deployed efficiently across the province.
Related information
-
 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoCanadian student denied religious exemption for COVID jab takes tech school to court
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoNeil Young + Carney / Freedom Bros
-
 International2 days ago
International2 days agoUK Supreme Court rules ‘woman’ means biological female
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoTucker Carlson Interviews Maxime Bernier: Trump’s Tariffs, Mass Immigration, and the Oncoming Canadian Revolution
-
 Business1 day ago
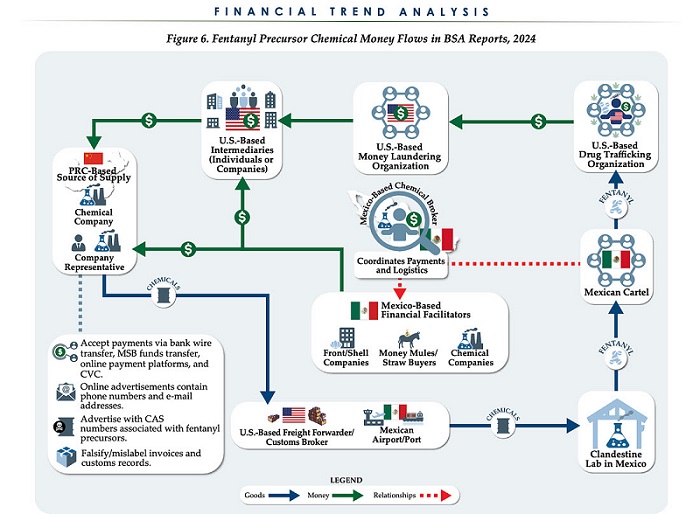
Business1 day agoChina, Mexico, Canada Flagged in $1.4 Billion Fentanyl Trade by U.S. Financial Watchdog
-

 espionage1 day ago
espionage1 day agoEx-NYPD Cop Jailed in Beijing’s Transnational Repatriation Plot, Canada Remains Soft Target
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoWHO member states agree on draft of ‘pandemic treaty’ that could be adopted in May
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDOGE Is Ending The ‘Eternal Life’ Of Government





