Brownstone Institute
The New Enthusiasm for Slaughter

From the Brownstone Institute
By
What War Means
My mother once told me how my father still woke up screaming in the night years after I was born, decades after the Second World War (WWII) ended. I had not known – probably like most children of those who fought. For him, it was visions of his friends going down in burning aircraft – other bombers of his squadron off north Australia – and to be helpless, watching, as they burnt and fell. Few born after that war could really appreciate what their fathers, and mothers, went through.
Early in the movie Saving Private Ryan, there is an extended D-Day scene of the front doors of the landing craft opening on the Normandy beaches, and all those inside being torn apart by bullets. It happens to one landing craft after another. Bankers, teachers, students, and farmers being ripped in pieces and their guts spilling out whilst they, still alive, call for help that cannot come. That is what happens when a machine gun opens up through the open door of a landing craft, or an armored personnel carrier, of a group sent to secure a tree line.
It is what a lot of politicians are calling for now.
People with shares in the arms industry become a little richer every time one of those shells is fired and has to be replaced. They gain financially, and often politically, from bodies being ripped open. This is what we call war. It is increasingly popular as a political strategy, though generally for others and the children of others.
Of course, the effects of war go beyond the dismembering and lonely death of many of those fighting. Massacres of civilians and rape of women can become common, as brutality enables humans to be seen as unwanted objects. If all this sounds abstract, apply it to your loved ones and think what that would mean.
I believe there can be just wars, and this is not a discussion about the evil of war, or who is right or wrong in current wars. Just a recognition that war is something worth avoiding, despite its apparent popularity amongst many leaders and our media.
The EU Reverses Its Focus
When the Brexit vote determined that Britain would leave the European Union (EU), I, like many, despaired. We should learn from history, and the EU’s existence had coincided with the longest period of peace between Western European States in well over 2,000 years.
Leaving the EU seemed to be risking this success. Surely, it is better to work together, to talk and cooperate with old enemies, in a constructive way? The media, and the political left, center, and much of the right seemed at that time, all of nine years ago, to agree. Or so the story went.
We now face a new reality as the EU leadership scrambles to justify continuing a war. Not only continuing, but they had been staunchly refusing to even countenance discussion on ending the killing. It has taken a new regime from across the ocean, a subject of European mockery, to do that.
In Europe, and in parts of American politics, something is going on that is very different from the question of whether current wars are just or unjust. It is an apparent belief that advocacy for continued war is virtuous. Talking to leaders of an opposing country in a war that is killing Europeans by the tens of thousands has been seen as traitorous. Those proposing to view the issues from both sides are somehow “far right.”
The EU, once intended as an instrument to end war, now has a European rearmament strategy. The irony seems lost on both its leaders and its media. Arguments such as “peace through strength” are pathetic when accompanied by censorship, propaganda, and a refusal to talk.
As US Vice-President JD Vance recently asked European leaders, what values are they actually defending?
Europe’s Need for Outside Help
A lack of experience of war does not seem sufficient to explain the current enthusiasm to continue them. Architects of WWII in Europe had certainly experienced the carnage of the First World War. Apart from the financial incentives that human slaughter can bring, there are also political ideologies that enable the mass death of others to be turned into an abstract and even positive idea.
Those dying must be seen to be from a different class, of different intelligence, or otherwise justifiable fodder to feed the cause of the Rules-Based Order or whatever other slogan can distinguish an ‘us’ from a ‘them’…While the current incarnation seems more of a class thing than a geographical or nationalistic one, European history is ripe with variations of both.
Europe appears to be back where it used to be, the aristocracy burning the serfs when not visiting each other’s clubs. Shallow thinking has the day, and the media have adapted themselves accordingly. Democracy means ensuring that only the right people get into power.
Dismembered European corpses and terrorized children are just part of maintaining this ideological purity. War is acceptable once more. Let’s hope such leaders and ideologies can be sidelined by those beyond Europe who are willing to give peace a chance.
There is no virtue in the promotion of mass death. Europe, with its leadership, will benefit from outside help and basic education. It would benefit even further from leadership that values the lives of its people.
Brownstone Institute
The Unmasking of Vaccine Science
From the Brownstone Institute
By
I recently purchased Aaron Siri’s new book Vaccines, Amen. As I flipped though the pages, I noticed a section devoted to his now-famous deposition of Dr Stanley Plotkin, the “godfather” of vaccines.
I’d seen viral clips circulating on social media, but I had never taken the time to read the full transcript — until now.
Siri’s interrogation was methodical and unflinching…a masterclass in extracting uncomfortable truths.
A Legal Showdown
In January 2018, Dr Stanley Plotkin, a towering figure in immunology and co-developer of the rubella vaccine, was deposed under oath in Pennsylvania by attorney Aaron Siri.
The case stemmed from a custody dispute in Michigan, where divorced parents disagreed over whether their daughter should be vaccinated. Plotkin had agreed to testify in support of vaccination on behalf of the father.
What followed over the next nine hours, captured in a 400-page transcript, was extraordinary.
Plotkin’s testimony revealed ethical blind spots, scientific hubris, and a troubling indifference to vaccine safety data.
He mocked religious objectors, defended experiments on mentally disabled children, and dismissed glaring weaknesses in vaccine surveillance systems.
A System Built on Conflicts
From the outset, Plotkin admitted to a web of industry entanglements.
He confirmed receiving payments from Merck, Sanofi, GSK, Pfizer, and several biotech firms. These were not occasional consultancies but long-standing financial relationships with the very manufacturers of the vaccines he promoted.
Plotkin appeared taken aback when Siri questioned his financial windfall from royalties on products like RotaTeq, and expressed surprise at the “tone” of the deposition.
Siri pressed on: “You didn’t anticipate that your financial dealings with those companies would be relevant?”
Plotkin replied: “I guess, no, I did not perceive that that was relevant to my opinion as to whether a child should receive vaccines.”
The man entrusted with shaping national vaccine policy had a direct financial stake in its expansion, yet he brushed it aside as irrelevant.
Contempt for Religious Dissent
Siri questioned Plotkin on his past statements, including one in which he described vaccine critics as “religious zealots who believe that the will of God includes death and disease.”
Siri asked whether he stood by that statement. Plotkin replied emphatically, “I absolutely do.”
Plotkin was not interested in ethical pluralism or accommodating divergent moral frameworks. For him, public health was a war, and religious objectors were the enemy.
He also admitted to using human foetal cells in vaccine production — specifically WI-38, a cell line derived from an aborted foetus at three months’ gestation.
Siri asked if Plotkin had authored papers involving dozens of abortions for tissue collection. Plotkin shrugged: “I don’t remember the exact number…but quite a few.”
Plotkin regarded this as a scientific necessity, though for many people — including Catholics and Orthodox Jews — it remains a profound moral concern.
Rather than acknowledging such sensitivities, Plotkin dismissed them outright, rejecting the idea that faith-based values should influence public health policy.
That kind of absolutism, where scientific aims override moral boundaries, has since drawn criticism from ethicists and public health leaders alike.
As NIH director Jay Bhattacharya later observed during his 2025 Senate confirmation hearing, such absolutism erodes trust.
“In public health, we need to make sure the products of science are ethically acceptable to everybody,” he said. “Having alternatives that are not ethically conflicted with foetal cell lines is not just an ethical issue — it’s a public health issue.”
Safety Assumed, Not Proven
When the discussion turned to safety, Siri asked, “Are you aware of any study that compares vaccinated children to completely unvaccinated children?”
Plotkin replied that he was “not aware of well-controlled studies.”
Asked why no placebo-controlled trials had been conducted on routine childhood vaccines such as hepatitis B, Plotkin said such trials would be “ethically difficult.”
That rationale, Siri noted, creates a scientific blind spot. If trials are deemed too unethical to conduct, then gold-standard safety data — the kind required for other pharmaceuticals — simply do not exist for the full childhood vaccine schedule.
Siri pointed to one example: Merck’s hepatitis B vaccine, administered to newborns. The company had only monitored participants for adverse events for five days after injection.
Plotkin didn’t dispute it. “Five days is certainly short for follow-up,” he admitted, but claimed that “most serious events” would occur within that time frame.
Siri challenged the idea that such a narrow window could capture meaningful safety data — especially when autoimmune or neurodevelopmental effects could take weeks or months to emerge.
Siri pushed on. He asked Plotkin if the DTaP and Tdap vaccines — for diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis — could cause autism.
“I feel confident they do not,” Plotkin replied.
But when shown the Institute of Medicine’s 2011 report, which found the evidence “inadequate to accept or reject” a causal link between DTaP and autism, Plotkin countered, “Yes, but the point is that there were no studies showing that it does cause autism.”
In that moment, Plotkin embraced a fallacy: treating the absence of evidence as evidence of absence.
“You’re making assumptions, Dr Plotkin,” Siri challenged. “It would be a bit premature to make the unequivocal, sweeping statement that vaccines do not cause autism, correct?”
Plotkin relented. “As a scientist, I would say that I do not have evidence one way or the other.”
The MMR
The deposition also exposed the fragile foundations of the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
When Siri asked for evidence of randomised, placebo-controlled trials conducted before MMR’s licensing, Plotkin pushed back: “To say that it hasn’t been tested is absolute nonsense,” he said, claiming it had been studied “extensively.”
Pressed to cite a specific trial, Plotkin couldn’t name one. Instead, he gestured to his own 1,800-page textbook: “You can find them in this book, if you wish.”
Siri replied that he wanted an actual peer-reviewed study, not a reference to Plotkin’s own book. “So you’re not willing to provide them?” he asked. “You want us to just take your word for it?”
Plotkin became visibly frustrated.
Eventually, he conceded there wasn’t a single randomised, placebo-controlled trial. “I don’t remember there being a control group for the studies, I’m recalling,” he said.
The exchange foreshadowed a broader shift in public discourse, highlighting long-standing concerns that some combination vaccines were effectively grandfathered into the schedule without adequate safety testing.
In September this year, President Trump called for the MMR vaccine to be broken up into three separate injections.
The proposal echoed a view that Andrew Wakefield had voiced decades earlier — namely, that combining all three viruses into a single shot might pose greater risk than spacing them out.
Wakefield was vilified and struck from the medical register. But now, that same question — once branded as dangerous misinformation — is set to be re-examined by the CDC’s new vaccine advisory committee, chaired by Martin Kulldorff.
The Aluminium Adjuvant Blind Spot
Siri next turned to aluminium adjuvants — the immune-activating agents used in many childhood vaccines.
When asked whether studies had compared animals injected with aluminium to those given saline, Plotkin conceded that research on their safety was limited.
Siri pressed further, asking if aluminium injected into the body could travel to the brain. Plotkin replied, “I have not seen such studies, no, or not read such studies.”
When presented with a series of papers showing that aluminium can migrate to the brain, Plotkin admitted he had not studied the issue himself, acknowledging that there were experiments “suggesting that that is possible.”
Asked whether aluminium might disrupt neurological development in children, Plotkin stated, “I’m not aware that there is evidence that aluminum disrupts the developmental processes in susceptible children.”
Taken together, these exchanges revealed a striking gap in the evidence base.
Compounds such as aluminium hydroxide and aluminium phosphate have been injected into babies for decades, yet no rigorous studies have ever evaluated their neurotoxicity against an inert placebo.
This issue returned to the spotlight in September 2025, when President Trump pledged to remove aluminium from vaccines, and world-leading researcher Dr Christopher Exley renewed calls for its complete reassessment.
A Broken Safety Net
Siri then turned to the reliability of the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) — the primary mechanism for collecting reports of vaccine-related injuries in the United States.
Did Plotkin believe most adverse events were captured in this database?
“I think…probably most are reported,” he replied.
But Siri showed him a government-commissioned study by Harvard Pilgrim, which found that fewer than 1% of vaccine adverse events are reported to VAERS.
“Yes,” Plotkin said, backtracking. “I don’t really put much faith into the VAERS system…”
Yet this is the same database officials routinely cite to claim that “vaccines are safe.”
Ironically, Plotkin himself recently co-authored a provocative editorial in the New England Journal of Medicine, conceding that vaccine safety monitoring remains grossly “inadequate.”
Experimenting on the Vulnerable
Perhaps the most chilling part of the deposition concerned Plotkin’s history of human experimentation.
“Have you ever used orphans to study an experimental vaccine?” Siri asked.
“Yes,” Plotkin replied.
“Have you ever used the mentally handicapped to study an experimental vaccine?” Siri asked.
“I don’t recollect…I wouldn’t deny that I may have done so,” Plotkin replied.
Siri cited a study conducted by Plotkin in which he had administered experimental rubella vaccines to institutionalised children who were “mentally retarded.”
Plotkin stated flippantly, “Okay well, in that case…that’s what I did.”
There was no apology, no sign of ethical reflection — just matter-of-fact acceptance.
Siri wasn’t done.
He asked if Plotkin had argued that it was better to test on those “who are human in form but not in social potential” rather than on healthy children.
Plotkin admitted to writing it.
Siri established that Plotkin had also conducted vaccine research on the babies of imprisoned mothers, and on colonised African populations.
Plotkin appeared to suggest that the scientific value of such studies outweighed the ethical lapses—an attitude that many would interpret as the classic ‘ends justify the means’ rationale.
But that logic fails the most basic test of informed consent. Siri asked whether consent had been obtained in these cases.
“I don’t remember…but I assume it was,” Plotkin said.
Assume?
This was post-Nuremberg research. And the leading vaccine developer in America couldn’t say for sure whether he had properly informed the people he experimented on.
In any other field of medicine, such lapses would be disqualifying.
A Casual Dismissal of Parental Rights
Plotkin’s indifference to experimenting on disabled children didn’t stop there.
Siri asked whether someone who declined a vaccine due to concerns about missing safety data should be labelled “anti-vax.”
Plotkin replied, “If they refused to be vaccinated themselves or refused to have their children vaccinated, I would call them an anti-vaccination person, yes.”
Plotkin was less concerned about adults making that choice for themselves, but he had no tolerance for parents making those choices for their own children.
“The situation for children is quite different,” said Plotkin, “because one is making a decision for somebody else and also making a decision that has important implications for public health.”
In Plotkin’s view, the state held greater authority than parents over a child’s medical decisions — even when the science was uncertain.
The Enabling of Figures Like Plotkin
The Plotkin deposition stands as a case study in how conflicts of interest, ideology, and deference to authority have corroded the scientific foundations of public health.
Plotkin is no fringe figure. He is celebrated, honoured, and revered. Yet he promotes vaccines that have never undergone true placebo-controlled testing, shrugs off the failures of post-market surveillance, and admits to experimenting on vulnerable populations.
This is not conjecture or conspiracy — it is sworn testimony from the man who helped build the modern vaccine program.
Now, as Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy, Jr. reopens long-dismissed questions about aluminium adjuvants and the absence of long-term safety studies, Plotkin’s once-untouchable legacy is beginning to fray.
Republished from the author’s Substack
Brownstone Institute
Bizarre Decisions about Nicotine Pouches Lead to the Wrong Products on Shelves

From the Brownstone Institute
A walk through a dozen convenience stores in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, says a lot about how US nicotine policy actually works. Only about one in eight nicotine-pouch products for sale is legal. The rest are unauthorized—but they’re not all the same. Some are brightly branded, with uncertain ingredients, not approved by any Western regulator, and clearly aimed at impulse buyers. Others—like Sweden’s NOAT—are the opposite: muted, well-made, adult-oriented, and already approved for sale in Europe.
Yet in the United States, NOAT has been told to stop selling. In September 2025, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued the company a warning letter for offering nicotine pouches without marketing authorization. That might make sense if the products were dangerous, but they appear to be among the safest on the market: mild flavors, low nicotine levels, and recyclable paper packaging. In Europe, regulators consider them acceptable. In America, they’re banned. The decision looks, at best, strange—and possibly arbitrary.
What the Market Shows
My October 2025 audit was straightforward. I visited twelve stores and recorded every distinct pouch product visible for sale at the counter. If the item matched one of the twenty ZYN products that the FDA authorized in January, it was counted as legal. Everything else was counted as illegal.
Two of the stores told me they had recently received FDA letters and had already removed most illegal stock. The other ten stores were still dominated by unauthorized products—more than 93 percent of what was on display. Across all twelve locations, about 12 percent of products were legal ZYN, and about 88 percent were not.
The illegal share wasn’t uniform. Many of the unauthorized products were clearly high-nicotine imports with flashy names like Loop, Velo, and Zimo. These products may be fine, but some are probably high in contaminants, and a few often with very high nicotine levels. Others were subdued, plainly meant for adult users. NOAT was a good example of that second group: simple packaging, oat-based filler, restrained flavoring, and branding that makes no effort to look “cool.” It’s the kind of product any regulator serious about harm reduction would welcome.
Enforcement Works
To the FDA’s credit, enforcement does make a difference. The two stores that received official letters quickly pulled their illegal stock. That mirrors the agency’s broader efforts this year: new import alerts to detain unauthorized tobacco products at the border (see also Import Alert 98-06), and hundreds of warning letters to retailers, importers, and distributors.
But effective enforcement can’t solve a supply problem. The list of legal nicotine-pouch products is still extremely short—only a narrow range of ZYN items. Adults who want more variety, or stores that want to meet that demand, inevitably turn to gray-market suppliers. The more limited the legal catalog, the more the illegal market thrives.
Why the NOAT Decision Appears Bizarre
The FDA’s own actions make the situation hard to explain. In January 2025, it authorized twenty ZYN products after finding that they contained far fewer harmful chemicals than cigarettes and could help adult smokers switch. That was progress. But nine months later, the FDA has approved nothing else—while sending a warning letter to NOAT, arguably the least youth-oriented pouch line in the world.
The outcome is bad for legal sellers and public health. ZYN is legal; a handful of clearly risky, high-nicotine imports continue to circulate; and a mild, adult-market brand that meets European safety and labeling rules is banned. Officially, NOAT’s problem is procedural—it lacks a marketing order. But in practical terms, the FDA is punishing the very design choices it claims to value: simplicity, low appeal to minors, and clean ingredients.
This approach also ignores the differences in actual risk. Studies consistently show that nicotine pouches have far fewer toxins than cigarettes and far less variability than many vapes. The biggest pouch concerns are uneven nicotine levels and occasional traces of tobacco-specific nitrosamines, depending on manufacturing quality. The serious contamination issues—heavy metals and inconsistent dosage—belong mostly to disposable vapes, particularly the flood of unregulated imports from China. Treating all “unauthorized” products as equally bad blurs those distinctions and undermines proportional enforcement.
A Better Balance: Enforce Upstream, Widen the Legal Path
My small Montgomery County survey suggests a simple formula for improvement.
First, keep enforcement targeted and focused on suppliers, not just clerks. Warning letters clearly change behavior at the store level, but the biggest impact will come from auditing distributors and importers, and stopping bad shipments before they reach retail shelves.
Second, make compliance easy. A single-page list of authorized nicotine-pouch products—currently the twenty approved ZYN items—should be posted in every store and attached to distributor invoices. Point-of-sale systems can block barcodes for anything not on the list, and retailers could affirm, once a year, that they stock only approved items.
Third, widen the legal lane. The FDA launched a pilot program in September 2025 to speed review of new pouch applications. That program should spell out exactly what evidence is needed—chemical data, toxicology, nicotine release rates, and behavioral studies—and make timely decisions. If products like NOAT meet those standards, they should be authorized quickly. Legal competition among adult-oriented brands will crowd out the sketchy imports far faster than enforcement alone.
The Bottom Line
Enforcement matters, and the data show it works—where it happens. But the legal market is too narrow to protect consumers or encourage innovation. The current regime leaves a few ZYN products as lonely legal islands in a sea of gray-market pouches that range from sensible to reckless.
The FDA’s treatment of NOAT stands out as a case study in inconsistency: a quiet, adult-focused brand approved in Europe yet effectively banned in the US, while flashier and riskier options continue to slip through. That’s not a public-health victory; it’s a missed opportunity.
If the goal is to help adult smokers move to lower-risk products while keeping youth use low, the path forward is clear: enforce smartly, make compliance easy, and give good products a fair shot. Right now, we’re doing the first part well—but failing at the second and third. It’s time to fix that.
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin3 hours ago
Bruce Dowbiggin3 hours agoWayne Gretzky’s Terrible, Awful Week.. And Soccer/ Football.
-

 espionage6 hours ago
espionage6 hours agoWestern Campuses Help Build China’s Digital Dragnet With U.S. Tax Funds, Study Warns
-

 Agriculture2 hours ago
Agriculture2 hours agoCanada’s air quality among the best in the world
-

 Business4 hours ago
Business4 hours agoCanada invests $34 million in Chinese drones now considered to be ‘high security risks’
-

 Economy5 hours ago
Economy5 hours agoAffordable housing out of reach everywhere in Canada
-
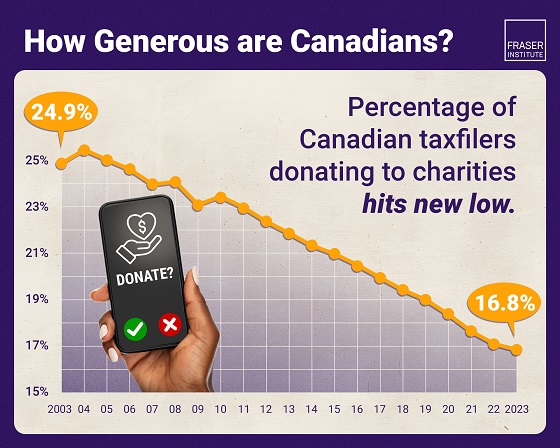
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoAlbertans give most on average but Canadian generosity hits lowest point in 20 years
-

 Fraser Institute1 day ago
Fraser Institute1 day agoClaims about ‘unmarked graves’ don’t withstand scrutiny
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoCarney Hears A Who: Here Comes The Grinch







