Business
Comparing four federal finance ministers in moments of crisis

From the Fraser Institute
By Grady Munro, Milagros Palacios and Jason Clemens
The sudden resignation of federal finance minister (and deputy prime minister) Chrystia Freeland, hours before the government was scheduled to release its fall economic update has thrown an already badly underperforming government into crisis. In her letter of resignation, Freeland criticized the government, and indirectly the prime minister, for “costly political gimmicks” and irresponsible handling of the country’s finances and economy during a period of great uncertainty.
But while Freeland’s criticism of recent poorly-designed federal policies is valid, her resignation, in some ways, tries to reshape her history into that of a more responsible finance minister. That is, however, ultimately an empirical question. If we contrast the performance of the last four long-serving (more than three years) federal finance ministers—Paul Martin (Liberal), Jim Flaherty (Conservative), Bill Morneau (Liberal) and Freeland (Liberal)—it’s clear that neither Freeland nor her predecessor (Morneau) were successful finance ministers in terms of imposing fiscal discipline or overseeing a strong Canadian economy.
Let’s first consider the most basic measure of economic performance, growth in per-person gross domestic product (GDP), adjusted for inflation. This is a broad measure of living standards that gauges the value of all goods and services produced in the economy adjusted for the population and inflation. The chart below shows the average annual growth in inflation-adjusted per-person GDP over the course of each finance minister’s term. (Adjustments are made to reflect the effects of temporary recessions or unique aspects of each minister’s tenure to make it easier to compare the performances of each finance minister.)

Sources: Statistics Canada Table 17-10-0005-01, Table 36-10-0222-01; 2024 Fall Economic Statement
By far Paul Martin oversaw the strongest growth in per-person GDP, with an average annual increase of 2.4 per cent. Over his entire tenure spanning a decade, living standards rose more than 25 per cent.
The average annual increase in per-person GDP under Flaherty was 0.6 per cent, although that includes the financial recession of 2008-09. If we adjust the data for the recession, average annual growth in per-person GDP was 1.4 per cent, still below Martin but more than double the rate if the effects of the recession are included.
During Bill Morneau’s term, average annual growth in per-person GDP was -0.5 per cent, although this includes the effects of the COVID recession. If we adjust to exclude 2020, Morneau averaged a 0.7 per cent annual increase—half the adjusted average annual growth rate under Flaherty.
Finally, Chrystia Freeland averaged annual growth in per-person GDP of -0.3 per cent during her tenure. And while the first 18 or so months of her time as finance minister, from the summer of 2020 through 2021, were affected by the COVID recession and the subsequent rebound, the average annual rate of per-person GDP growth was -0.2 per cent during her final three years. Consequently, at the time of her resignation from cabinet in 2024, Canadian living standards are projected to be 1.8 per cent lower than they were in 2019.
Let’s now consider some basic fiscal measures.
Martin is by far the strongest performing finance minister across almost every metric. Faced with a looming fiscal crisis brought about by decades of deficits and debt accumulation, he reduced spending both in nominal terms and as a share of the economy. For example, after adjusting for inflation, per-person spending on federal programs dropped by 5.9 per cent during his tenure as finance minister (see chart below). As a result, the federal government balanced the budget and lowered the national debt, ultimately freeing up resources via lower interest costs for personal and business tax relief that made the country more competitive and improved incentives for entrepreneurs, businessowners, investors and workers.

*Note: Freeland’s term began in 2020, but given the influence of COVID, 2019 is utilized as the baseline for the overall change in spending. Sources: Statistics Canada Table 17-10-0005-01, Table 36-10-0130-01; Fiscal Reference Tables 2024; 2024 Fall Economic Statement
Flaherty’s record as finance minister is mixed, in part due to the recession of 2008-09. Per-person program spending (inflation adjusted) increased by 11.6 per cent, and there was a slight (0.6 percentage point) increase in spending as a share of the economy. Debt also increased as a share of the economy, although again, much of the borrowing during Flaherty’s tenure was linked with the 2008-09 recession. Flaherty did implement tax relief, including extending the business income tax cuts started under Martin, which made Canada more competitive in attracting investment and fostering entrepreneurship.
Both Morneau and Freeland recorded much worse financial performances than Flaherty and Martin. Morneau increased per-person spending on programs (inflation adjusted) by 37.1 per cent after removing 2020 COVID-related expenditures. Even if a more generous assessment is used, specifically comparing spending in 2019 (prior to the effects of the pandemic and recession) per-person spending still increased by 18.1 per cent compared to the beginning of his tenure.
In his five years, Morneau oversaw an increase in total federal debt of more than $575 billion, some of which was linked with COVID spending in 2020. However, as multiple analyses have concluded, the Trudeau government spent more and accumulated more debt during COVID than most comparable industrialized countries, with little or nothing to show for it in terms of economic growth or better health performance. Simply put, had Morneau exercised more restraint, Canada would have accumulated less debt and likely performed better economically.
Freeland’s tenure as finance minister is the shortest of the four ministers examined. It’s nonetheless equally as unimpressive as that of her Trudeau government predecessor (Morneau). If we use baseline spending from 2019 to adjust for the spike in spending in 2020 when she was appointed finance minister, per-person spending on programs by the federal government (inflation adjusted) during Freeland’s term increased by 4.1 per cent. Total federal debt is expected to increase from $1.68 trillion when Freeland took over to an estimated $2.2 trillion this year, despite the absence of a recession or any other event that would impair federal finances since the end of COVID in 2021. For some perspective, the $470.8 billion in debt accumulated under Freeland is more than double the $220.3 billion accumulated under Morneau prior to COVID. And there’s an immediate cost to that debt in the form of $53.7 billion in expected federal debt interest costs this year. These are taxpayer resources unavailable for actual services such as health care.
Freeland’s resignation from cabinet sent shock waves throughout the country, perhaps relieving her of responsibility for the Trudeau government’s latest poorly-designed fiscal policies. However, cabinet ministers bear responsibility for the performance of their ministries—meaning Freeland must be held accountable for her previous budgets and the fiscal and economic performance of the government during her tenure. Compared to previous long-serving finances ministers, it’s clear that Chrystia Freeland, and her Trudeau predecessor Bill Morneau, failed to shepherd a strong economy or maintain responsible and prudent finances.
Automotive
Trump warns U.S. automakers: Do not raise prices in response to tariffs

 MxM News
MxM News
Quick Hit:
Former President Donald Trump warned automakers not to raise car prices in response to newly imposed tariffs, arguing that the move would ultimately benefit the industry by strengthening American manufacturing. However, automakers are signaling that price increases may be unavoidable.
Key Details:
- Trump told auto executives on a recent call that his administration would look unfavorably on price hikes due to tariffs.
- A 25% tariff on imported vehicles and parts is set to take effect on April 2, likely driving up costs for U.S. automakers.
- Industry analysts predict vehicle prices could rise 11% to 12% in response, despite Trump’s insistence that tariffs will benefit American manufacturing.
Diving Deeper:
In a conference call with leading automakers earlier this month, former President Donald Trump issued a stern warning: do not use his new tariffs as an excuse to raise car prices. While Trump presented the tariffs as a boon for American manufacturing, industry leaders remain unconvinced, arguing that the financial burden will inevitably lead to higher costs for consumers.
Trump’s administration is pressing ahead with a 25% tariff on all imported vehicles and parts, set to take effect on April 2. The move is aimed at reshaping trade dynamics in the auto industry, encouraging domestic manufacturing, and reversing what Trump calls the damaging effects of President Joe Biden’s electric vehicle mandates. Despite this, automakers say that rising costs on foreign parts—which many depend on—will leave them little choice but to pass expenses onto consumers.
“You’re going to see prices going down, but going to go down specifically because they’re going to buy what we’re doing, incentivizing companies to—and even countries—companies to come into America,” Trump stated at a recent event, reinforcing his stance that the tariffs will ultimately lower costs in the long run.
However, industry insiders are pushing back, warning that a rapid shift to domestic production is unrealistic. “Tariffs, at any level, cannot be offset or absorbed,” said Ray Scott, CEO of Lear, a major automotive parts supplier. His concern reflects broader anxieties within the industry, as automakers calculate the financial strain of the tariffs. Analysts at Morgan Stanley estimate that vehicle prices could increase between 11% and 12% in the coming months as the new tariffs take effect.
Automakers have been bracing for the fallout. Detroit’s major manufacturers and industry suppliers have voiced their concerns, emphasizing that transitioning supply chains and manufacturing operations back to the U.S. will take years. Meanwhile, auto retailers have stocked up on inventory, temporarily shielding consumers from price hikes. But once that supply runs low—likely by May—the full impact of the tariffs could hit.
Within the Trump administration, inflation remains a pressing concern, though Trump himself rarely discusses it publicly. His economic team is aware of the potential for tariffs to drive up costs, yet the administration’s stance remains firm: automakers must adapt without raising prices. It remains unclear, however, what actions Trump might take should automakers defy his warning.
The auto industry isn’t alone in its concerns. Executives across multiple sectors, from oil and gas to food manufacturing, have been lobbying against major tariffs, arguing that they will inevitably result in higher prices for American consumers. While Trump has largely dismissed these warnings, some analysts suggest that public dissatisfaction with rising costs played a key role in shaping the outcome of the 2024 election.
With the tariffs set to take effect in just weeks, automakers are left grappling with a difficult reality: absorb billions in new costs or risk the ire of a White House determined to remake America’s trade policies.
Business
Labor Department cancels “America Last” spending spree spanning five continents

 MxM News
MxM News
Quick Hit:
The U.S. Department of Labor has scrapped nearly $600 million in foreign aid grants, including $10 million aimed at promoting “gender equity in the Mexican workplace.”
Key Details:
-
Labor Secretary Lori Chavez-DeRemer and Deputy Secretary Keith Sonderling were credited with delivering $237 million in savings through the latest round of canceled programs.
-
Among the defunded initiatives: $12.2 million for “worker empowerment” efforts in South America, $6.25 million to improve labor rights in Central American agriculture, and $5 million to promote women’s workplace participation in West Africa.
-
The Department of Government Efficiency described the cuts as necessary to realign U.S. labor policy with national interests and applauded the elimination of all 69 international grants managed by the Bureau of International Labor Affairs.
Diving Deeper:
The U.S. Department of Labor on Wednesday canceled $577 million in foreign aid grants, including a controversial $10 million program aimed at promoting “gender equity in the Mexican workplace,” according to documents obtained by The Washington Post. The sweeping decision to terminate all 69 active international labor grants comes as part of a larger restructuring effort led by John Clark, a senior DOL official appointed during the Trump administration.
Clark directed the department’s Bureau of International Labor Affairs (ILAB) to shut down its entire grant portfolio, citing a “lack of alignment with agency priorities and national interest.” The memo explaining the cancellations was first reported by The Washington Post and highlights a broader shift in federal labor policy toward domestic-focused initiatives.
Among the eliminated grants were high-dollar projects that had drawn criticism from watchdog groups for years. These included $12.2 million designated for “worker empowerment in South America,” $6.25 million targeting labor conditions in Honduras, Guatemala, and El Salvador, and $5 million to elevate women’s workplace participation in West Africa. Other defunded programs involved $4.3 million to support foreign migrant workers in Malaysia, $3 million to improve social protections for internal migrants in Bangladesh, and $3 million to promote “safe and inclusive work environments” in Lesotho.
The Department of Government Efficiency, also involved in the review, labeled the grants as “America Last” initiatives, and pointed to the lack of measurable outcomes and limited benefits to American workers. The agency commended the leadership of Labor Secretary Lori Chavez-DeRemer and Deputy Secretary Keith Sonderling for securing $237 million in savings during this round alone.
The cuts mark the second major cost-saving move under Chavez-DeRemer’s leadership in as many weeks. Just days earlier, she canceled an additional $33 million in funding, including a $1.5 million grant focused on increasing transparency in Uzbekistan’s cotton sector. Chavez-DeRemer, a former Republican congresswoman from Oregon, was confirmed as Labor Secretary on March 11th by a bipartisan Senate vote of 67-32.
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta Institute urging Premier Smith to follow Saskatchewan and drop Industrial Carbon Tax
-

 Addictions2 days ago
Addictions2 days agoShould fentanyl dealers face manslaughter charges for fatal overdoses?
-
 Alberta2 days ago
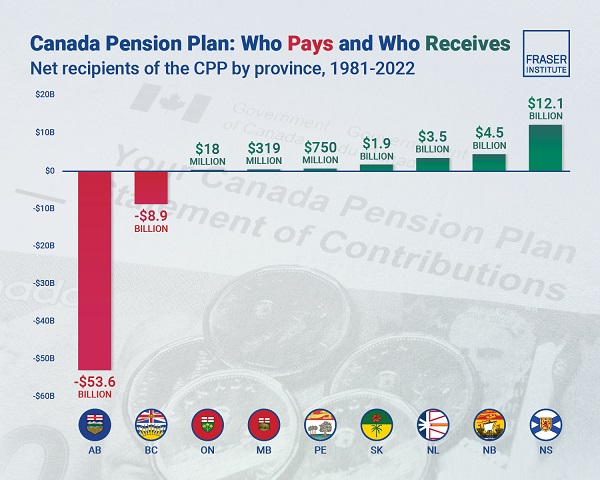
Alberta2 days agoAlbertans have contributed $53.6 billion to the retirement of Canadians in other provinces
-

 Also Interesting1 day ago
Also Interesting1 day agoThe bizarre story of Taro Tsujimoto
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoChinese Gangs Dominate Canada: Why Will Voters Give Liberals Another Term?
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoEnergy, climate, and economics — A smarter path for Canada
-
 Health24 hours ago
Health24 hours agoRFK Jr. Drops Stunning Vaccine Announcement
-

 J.D. Tuccille1 day ago
J.D. Tuccille1 day agoSignal Chat Controversy Is an Endorsement of Encryption Software








