Economy
Hydrocarbons Are The Backbone of Global Progress

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
By Ian Madsen
The use of hydrocarbons is a necessity for modern life.
Climate Crusaders claim that our society could do without oil and natural gas by proceeding to a Utopia of ‘Net Zero’ by 2050, extracting CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions from the atmosphere. However, as the Canadian Energy Centre notes, that cherished goal cannot be realized. This is true of fueling transport, heating or electric power, and all other uses of hydrocarbon fossil fuels.
People use oil and natural gas constituents for more than just burning. They use them in every sector of the economy, including military equipment and non profit organizations such as universities and hospitals.
The main component is ethane, C2H6, a ‘natural gas liquid’, extracted from raw natural gas. Ethane is then converted to ethylene, a versatile building block for many other chemicals, Other natural gas liquids, such as propane and butane, are generally used as fuel, in petrochemical production, and as some oil components.
Ethylene is used in various plastics, textiles, detergents and antifreeze. Plastics are used for containers, in countless household and industrial products, and tubing, filters, surgical masks, gloves, gowns, bandages, disinfectants and other medical products. Petrochemical-sourced materials are in the outer casing of medical devices and their components– important instruments such as blood diagnostics machines, DNA sequencers, MRI devices, ultra-sound and CAT and PET scanners.
Styrene, an ethylene end-product, makes synthetic rubber in tires. Synthetic rubber and related products are vital for the gaskets, seals, hoses and tubes in internal combustion, jet and diesel engines. Diesel engines are used in long-distance trucks bringing food to supermarkets. They also power excavating equipment that mines ores to refine into metals, fire trucks, and other machines, such as combines and tractors, which are vital to agriculture.
Petrochemicals also go into polymer fabrics such as polyester, spandex, acrylic and ‘breathable’ fabrics used by themselves or with ‘natural’ materials such as wool, cotton, silk and linen to make a great variety of items like clothes, underclothes, athletic wear, waterproof or winter jackets, hosiery, belts, handbags, upholstery material, furniture coverings, lawn and garden furniture, slope-stabilizing geotechnical fabrics, retractable arenas’ roof coverings, bedding materials, curtains, drapes, and tablecloths.
The same for the construction industries. Such products include paints, solvents, lacquers, countertops, knobs, flooring, adhesives, abrasives, pipes, plumbing and lighting fixtures. Two major insulation products builders and renovators are compelled to add to homes and office buildings make use of petrochemicals: polyurethane foam and styrofoam. Plastics go into the insulation’s outer sheath and for house wrap.
Plastics and related synthetic materials are also used in the latest generation of high-insulation windows, solar panels and wind turbines. Hence, petroleum based products are crucial to climate crusaders’ goal of lower energy consumption.
Plastics indeed add to the garbage volumes people generate. But plastic trash is manageable. Current recycling programs are ineffective, says the journal Nature. Despite rampant alarmism, waste-to-energy plastic destruction, as is bacterial digestion, is a viable alternative.
Petrochemicals and plastics make modern life possible. While substitutes are now under development, they are unlikely to become common anytime soon. So forbidding plastics would be detrimental, especially for emerging economies. Petrochemicals and plastics derived from hydrocarbons are crucial to making less-developed nations healthy and prosperous. Depriving them of that opportunity would be cruel and unnecessary.
Ian Madsen is the Senior Policy Analyst at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
Business
Saskatchewan becomes first Canadian province to fully eliminate carbon tax

From LifeSiteNews
Saskatchewan has become the first Canadian province to free itself entirely of the carbon tax.
On March 27, Saskatchewan Premier Scott Moe announced the removal of the provincial industrial carbon tax beginning April 1, boosting the province’s industry and making Saskatchewan the first carbon tax free province.
Under Moe’s direction, Saskatchewan has dropped the industrial carbon tax which he says will allow Saskatchewan to thrive under a “tariff environment.”
“I would hope that all of the parties running in the federal election would agree with those objectives and allow the provinces to regulate in this area without imposing the federal backstop,” he continued.
The removal of the tax is estimated to save Saskatchewan residents up to 18 cents a liter in gas prices.
The removal of the tax will take place on April 1, the same day the consumer carbon tax will reduce to 0 percent under Prime Minister Mark Carney’s direction. Notably, Carney did not scrap the carbon tax legislation: he just reduced its current rate to zero. This means it could come back at any time.
Furthermore, while Carney has dropped the consumer carbon tax, he has previously revealed that he wishes to implement a corporation carbon tax, the effects of which many argued would trickle down to all Canadians.
The Saskatchewan Association of Rural Municipalities (SARM) celebrated Moe’s move, noting that the carbon tax was especially difficult on farmers.
“I think the carbon tax has been in place for approximately six years now coming up in April and the cost keeps going up every year,” SARM president Bill Huber said.
“It puts our farming community and our business people in rural municipalities at a competitive disadvantage, having to pay this and compete on the world stage,” he continued.
“We’ve got a carbon tax on power — and that’s going to be gone now — and propane and natural gas and we use them more and more every year, with grain drying and different things in our farming operations,” he explained.
“I know most producers that have grain drying systems have three-phase power. If they haven’t got natural gas, they have propane to fire those dryers. And that cost goes on and on at a high level, and it’s made us more noncompetitive on a world stage,” Huber decalred.
The carbon tax is wildly unpopular and blamed for the rising cost of living throughout Canada. Currently, Canadians living in provinces under the federal carbon pricing scheme pay $80 per tonne.
2025 Federal Election
Fight against carbon taxes not over yet

As the federal government removes the consumer carbon tax, the Canadian Taxpayers Federation is calling on all party leaders to oppose all carbon taxes, including the hidden tax on business.
“Canadians fought hard to force Ottawa to back down on its consumer carbon tax and now the fight moves to stopping the hidden carbon tax on business,” said Franco Terrazzano, CTF Federal Director. “Canadians can’t afford a carbon tax on business that pushes up prices at the gas station and makes it harder for our businesses to compete while they’re already struggling with a trade war.”
Today, the federal government cut the consumer carbon tax rate to $0. This will reduce taxes by about 17 cents per litre of gasoline, 21 cents per litre of diesel and 15 cents per cubic metre of natural gas.
The federal government still imposes an industrial carbon tax on oil and gas, steel and fertilizer businesses, among others.
During the Liberal Party leadership race, Prime Minister Mark Carney said he would “improve and tighten” the industrial carbon tax and “extend the framework to 2035.”
Just 12 per cent of Canadians believe businesses pay most of the cost of the industrial carbon tax, according to a Leger poll commissioned by the CTF. Meanwhile, 70 per cent said businesses would pass most or some carbon tax costs on to consumers.
Conservative Party Leader Pierre Poilievre said he will “repeal the entire carbon tax law, including the tax on Canadian businesses and industries.”
“Carbon taxes on refineries make gas more expensive, carbon taxes on utilities make home heating more expensive and carbon taxes on fertilizer plants increase costs for farmers and that makes groceries more expensive,” Terrazzano said. “Canadians know Poilievre will end all carbon taxes and Canadians know Carney’s carbon tax costs won’t be zero.
“Carney owes Canadians a clear answer: How much will your carbon tax cost?”
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
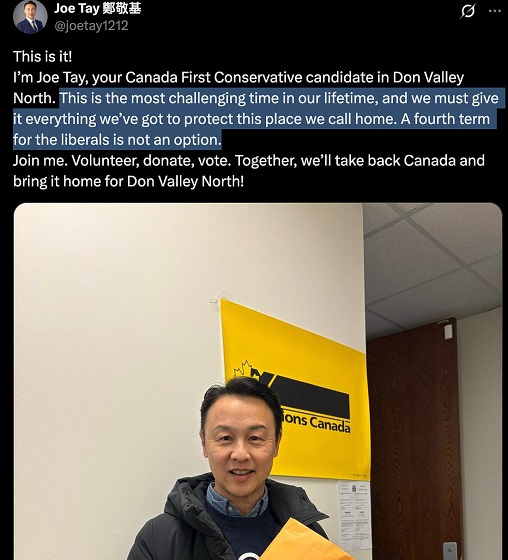
2025 Federal Election1 day agoJoe Tay Says He Contacted RCMP for Protection, Demands Carney Fire MP Over “Bounty” Remark
-
 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoHong Kong-Canadian Groups Demand PM Carney Drop Liberal Candidate Over “Bounty” Remark Supporting CCP Repression
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoPoilievre To Create ‘Canada First’ National Energy Corridor
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoAlcohol tax and MP pay hike tomorrow (April 1)
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoChinese Election Interference – NDP reaction to bounty on Conservative candidate
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoChina Election Interference – Parties Received Security Briefing Days Ago as SITE Monitors Threats to Conservative Candidate Joe Tay
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoFixing Canada’s immigration system should be next government’s top priority
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin1 day ago
Bruce Dowbiggin1 day agoAre the Jays Signing Or Declining? Only Vladdy & Bo Know For Sure