Business
Job growth in government exceeded the private sector in 8 out of 10 provinces from 2019-23
From the Fraser Institute
By Ben Eisen and Milagros Palacios
In eight of 10 provinces the rate of government job growth has been higher than the private sector, finds a new study published today by the Fraser Institute, an independent, non-partisan Canadian public policy think-tank.
“Canada’s net job creation in recent years has been disproportionately driven by growth in government employment rather than growth in the private sector, and as of 2019, government employment as a share of total employment in the country is at its highest point since the mid-1990s,” said Ben Eisen, Fraser Institute senior fellow and co-author of Economic Recovery in Canada before and after COVID: Job Growth in the Government and Private Sectors.
The study finds that historically, no other recent era of recession and recovery in Canada have been so dominated by government sector job growth compared to private sector job growth.
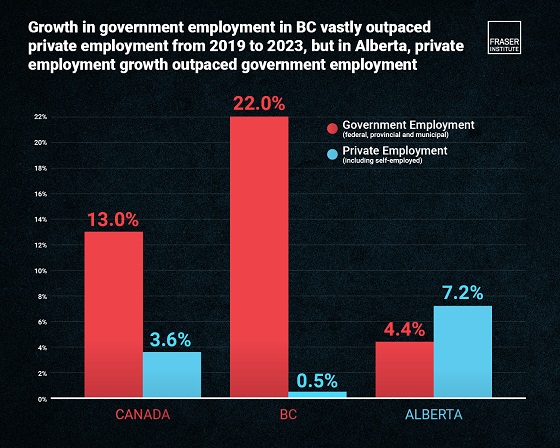
During the recession and recovery periods related to the COVID-19 recession (2019-2023), government employment across the country, including federal, provincial and municipal increased by 13.0 per cent compared to just 3.6 per cent in the private sector (including self-employment.)
In every Canadian province save for Alberta and Nova Scotia, employment in the government sector expanded at a higher rate than the private sector. In BC, employment growth in the private sector (including self-employment) rose only by 0.5 per cent during the period compared to 22.0 per cent in the government sector. Ontario’s public sector experienced triple the growth the private sector had, with 14.6 per cent and 4.8 per cent, respectively.
The study also compares the current recession and recovery in Canada to the United States, where the private sector has generated a large majority of all new jobs in recent years. In Canada, the government sector is responsible for 46.7 per cent of total job growth from 2019-203 compared to 16.1 per cent in the United States.
“Canada has seen a much higher rate of job growth in the government sector than the private sector in recent years, which is a concerning trend given that job growth and wealth creation in the private sector are needed to finance the activities of governments,” said Eisen.

- Several past analyses published by the Fraser Institute have shown that in recent years net job creation in the government sector has dramatically outstripped private-sector job creation.
- This publication updates these data, showing that during the recession brought on by the COVID-19 pandemic and the following recovery (2019–2023), government employment has increased by 13.0% while employment in the private sector (including self-employment) increased just 3.6%
- We further expand past analysis by comparing the ongoing recovery from the COVID-19 recession to past periods of economic recession and recovery.
- We find that the extent to which the current economic recovery is driven by government job growth is historically unusual. We compare the current economic environment to five past economic recessions and slowdowns and find that none of those recoveries were nearly as reliant on job creation in the government sector.
- We also compare the current recession and recovery in Canada to that in the United States, which differs sharply. In the United States, the private sector has generated a large majority of all new jobs in recent years and the rate of net job creation in the private sector has been nearly identical to that in the government sector.
- As a result of disproportionately faster growth in the public-sector employment, government’s share of employment post-COVID is higher than at any point since the fiscal consolidations of the 1990s.
Authors:
Business
Federal funds FROZEN after massive fraud uncovered: Trump cuts off Minnesota child care money

The Trump administration has cut off all federal child care payments to Minnesota, ordering a sweeping audit of the state’s day care system as investigators dig into what officials describe as one of the largest fraud schemes ever tied to social service programs.
“We have frozen all child care payments to the state of Minnesota,” Deputy Health and Human Services Secretary Jim O’Neill wrote Tuesday afternoon, saying the move comes after mounting evidence that taxpayer dollars were being siphoned to sham or non-operational day care centers. The freeze follows a viral investigative video that put a national spotlight on facilities across Minneapolis that were receiving large sums of public money despite appearing closed or barely functioning.
According to Alex Adams, assistant secretary at HHS’s Administration for Children and Families, Minnesota has already received roughly $185 million in federal child care funding this year alone. Those funds, the administration says, will remain locked down until the state can demonstrate that payments are being used lawfully. “Funds will be released only when states prove they are being spent legitimately,” Adams said.
We have frozen all child care payments to the state of Minnesota.
You have probably read the serious allegations that the state of Minnesota has funneled millions of taxpayer dollars to fraudulent daycares across Minnesota over the past decade.
Today we have taken three actions… pic.twitter.com/VYbyf3WGop
— Deputy Secretary Jim O'Neill (@HHS_Jim) December 30, 2025
O’Neill accused Minnesota officials of allowing abuse to fester for years, alleging the state has “funneled millions of taxpayer dollars to fraudulent daycares across Minnesota over the past decade.” To halt further losses, HHS outlined a series of immediate enforcement steps. Going forward, states seeking reimbursement through the Administration for Children and Families will be required to provide receipts or photographic proof documenting how funds are spent.
The department has also formally demanded that Gov. Tim Walz order a “comprehensive audit” of the day care centers flagged by investigators. O’Neill said the review must include attendance records, licensing documents, complaints, investigative files, and inspection reports. He pointed directly to a video published Friday by YouTuber Nick Shirley, who visited multiple Minneapolis-area centers listed as receiving millions in public funds but found locations that appeared closed or inactive.
In addition, HHS has launched a dedicated fraud hotline and email address at childcare.gov to encourage tips from parents, providers, and the public. “We have turned off the money spigot and we are finding the fraud,” O’Neill said, urging anyone with information to come forward.
Federal prosecutors say the scope of the alleged abuse is staggering. Authorities have already confirmed at least $1 billion in fraud tied to Minnesota child care programs, with 92 people charged so far. The U.S. Attorney’s Office has warned the total could ultimately reach as high as $9 billion as investigators continue combing through records.
The funding freeze marks one of the most aggressive crackdowns yet by the Trump administration on state-run social programs accused of lax oversight, sending a clear message that federal dollars will not flow until Minnesota can account for where the money went — and who was cashing in.
Business
The Real Reason Canada’s Health Care System Is Failing

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
By Conrad Eder
Conrad Eder supports universal health care, but not Canada’s broken version. Despite massive spending, Canadians face brutal wait times. He argues it’s time to allow private options, as other countries do, without abandoning universality.
It’s not about money. It’s about the rules shaping how Canada’s health care system works
Canada’s health care system isn’t failing because it lacks funding or public support. It’s failing because governments have tied it to restrictive rules that block private medical options used in other developed countries to deliver timely care.
Canada spends close to $400 billion a year on health care, placing it among the highest-spending countries in the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Yet the system continues to struggle with some of the longest waits for care, the fewest doctors per capita and among the lowest numbers of hospital beds in the OECD. This is despite decades of spending increases, including growth of 4.5 per cent in 2023 and 5.7 per cent in 2024, according to estimates from the Canadian Institute for Health Information.
Canadians are losing confidence that government spending is the solution. In fact, many don’t even think it’s making a difference.
And who could blame them? Median health care wait times reached 30 weeks in 2024, up from 27.7 weeks in 2023, which was up from 27.4 weeks in 2022, according to annual surveys by the Fraser Institute.
Nevertheless, politicians continue to tout our universal health care system as a source of national pride and, according to national surveys, 74 per cent of Canadians agree. Yet only 56 per cent are satisfied with it. This gap reveals that while Canadians value universal health care in principle, they are frustrated with it in practice.
But it isn’t universal health care that’s the problem; it’s Canada’s uniquely restrictive version of it. In most provinces, laws restrict physicians from working simultaneously in public and private systems and prohibit private insurance for medically necessary services covered by medicare, constraints that do not exist in most other universal health care systems.
The United Kingdom, France, Germany and the Netherlands all maintain universal health care systems. Like Canada, they guarantee comprehensive insurance coverage for essential health care services. Yet they achieve better access to care than Canada, with patients seeing doctors sooner and benefiting from shorter surgical wait times.
In Germany, there are both public and private hospitals. In France, universal insurance covers procedures whether patients receive them in public hospitals or private clinics. In the Netherlands, all health insurance is private, with companies competing for customers while coverage remains guaranteed. In the United Kingdom, doctors working in public hospitals are allowed to maintain private practices.
All of these countries preserved their commitment to universal health care while allowing private alternatives to expand choice, absorb demand and deliver better access to care for everyone.
Only 26 per cent of Canadians can get same-day or next-day appointments with their family doctor, compared to 54 per cent of Dutch and 47 per cent of English patients. When specialist care is needed, 61 per cent of Canadians wait more than a month, compared to 25 per cent of Germans. For elective surgery, 90 per cent of French patients undergo procedures within four months, compared to 62 per cent of Canadians.
If other nations can deliver timely access to care while preserving universal coverage, so can Canada. Two changes, inspired by our peers, would preserve universal coverage and improve access for all.
First, allow physicians to provide services to patients in both public and private settings. This flexibility incentivizes doctors to maximize the time they spend providing patient care, expanding service capacity and reducing wait times for all patients. Those in the public system benefit from increased physician availability, as private options absorb demand that would otherwise strain public resources.
Second, permit private insurance for medically necessary services. This would allow Canadians to obtain coverage for private medical services, giving patients an affordable way to access health care options that best suit their needs. Private insurance would enable Canadians to customize their health coverage, empowering patients and supporting a more responsive health care system.
These proposals may seem radical to Canadians. They are not. They are standard practice everywhere else. And across the OECD, they coexist with universal health care. They can do the same in Canada.
Alberta has taken an important first step by allowing some physicians to work simultaneously in public and private settings through its new dual-practice model. More Canadian provinces should follow Alberta’s lead and go one step further by removing legislative barriers that prohibit private health insurance for medically necessary services. Private insurance is the natural complement to dual practice, transforming private health care from an exclusive luxury into a viable option for Canadian families.
Canadians take pride in their health care system. That pride should inspire reform, not prevent it. Canada’s health care crisis is real. It’s a crisis of self-imposed constraints preventing our universal system from functioning at the level Canadians deserve.
Policymakers can, and should, preserve universal health care in this country. But maintaining it will require a willingness to learn from those who have built systems that deliver universality and timely access to care, something Canada’s current system does not.
Conrad Eder is a policy analyst at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy.
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoICYMI: Largest fraud in US history? Independent Journalist visits numerous daycare centres with no children, revealing massive scam
-

 Alberta23 hours ago
Alberta23 hours agoAlberta project would be “the biggest carbon capture and storage project in the world”
-

 Energy20 hours ago
Energy20 hours agoCanada’s debate on energy levelled up in 2025
-

 Business21 hours ago
Business21 hours agoSocialism vs. Capitalism
-

 Energy22 hours ago
Energy22 hours agoNew Poll Shows Ontarians See Oil & Gas as Key to Jobs, Economy, and Trade
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDOOR TO DOOR: Feds descend on Minneapolis day cares tied to massive fraud
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCanada needs serious tax cuts in 2026
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoIn Contentious Canada Reality Is Still Six Degrees Of Hockey







