Fraser Institute
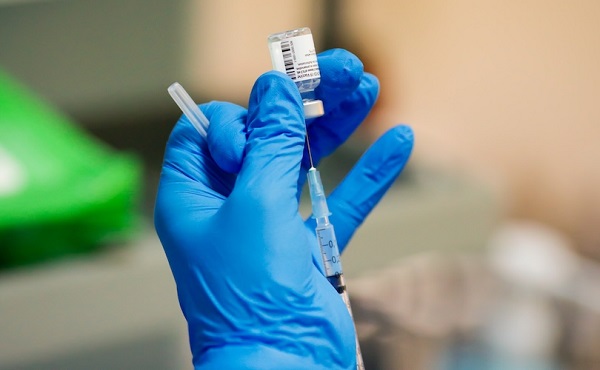
Virtual care will break the Canada Health Act—and that’s a good thing

From the Fraser Institute
The leadership of the Canadian Medical Association (CMA) is facing sharp criticism for its recent proposal to effectively ban private payment for virtual care. In a clear example of putting politics before patients, this would only erect additional barriers for those seeking care.
Moreover, it’s a desperate bid to cling to an outdated—and failed—model of health care while underestimating modern-day innovations.
Virtual care—online video doctor consultations—is a private-sector innovation. In response to our government system’s inability to provide timely care, private companies such as Maple have been offering these services to Canadians for almost a decade. In fact, the public system only pushed meaningfully into the virtual space during COVID when it established partnerships with these private companies alongside setting up new fee codes for virtual consultations.
In return for improving access to physician consultations for thousands of Canadians, these virtual care companies have been rewarded with increased government scrutiny and red tape. The weapon of choice? The Canada Health Act (CHA).
Specifically, sections 18 to 21 of the CHA prohibit user fees and extra billing for “medically necessary” services. Further, the insurance plan of a province must be publicly administered and provide “reasonable access” to 100 per cent of insured services. Provinces found in violation are punished by the federal government, which withholds a portion (or all) of federal health-care transfer payments.
Until recently, there had been no obvious conflict between the CHA and privately paid-for virtual care—primarily because the provinces are free to determine what’s medically necessary. Until recently, many provinces did not even have billing codes for virtual care. As virtual services are increasingly provided by the public sector, however, the ability to innovatively provide care for paying patients (either out-of-pocket or through private insurance) becomes restricted further.
Within this context, the CMA recently recommended formally including virtual care services within the public system, alongside measures to ensure “equitable access.” At the same time, it reiterated its recommendation that private insurance to access medically necessary services covered by the CHA be prohibited.
See where this is going?
The kicker is an additional recommendation banning dual practice (i.e. physicians working in both the public and private sector) except under certain conditions. This means doctors in the public system who could otherwise allocate their spare hours to private appointments online would now have to choose to operate exclusively in either the public or private system.
The combined effect of these policies would ensure that innovative private options for virtual care—whether paid for out-of-pocket or though private insurance—will either be overtaken by bureaucracies or disappear entirely.
But what the CMA report fails to recognize is that virtual care has expanded access to services the government fails to provide—there’s little reason to suspect a government takeover of the virtual-care sector will make things better for patients. And even if governments could somehow prevent Canadian doctors and companies providing these services privately, virtual care is not beholden to Canada’s physical borders. Patients with a little bit of technical knowhow will simply bypass the Canadian system entirely by having virtual consultations with doctors abroad. If Canadians can figure out how to access their favourite show in another country, you can be sure they’ll find a way to get a consultation with a doctor in Mumbai instead of Montreal.
Instead of forcing physicians and patients to operate within the crumbling confines of government-run health care, the CMA’s leadership should be grateful for the pressure valve that the private sector has produced. We should celebrate the private innovators who have provided Canadians better access to health care, not finding ways to shut them down in favour of more government control.
Author:
Business
Canada’s recent economic growth performance has been awful

From the Fraser Institute
By Ben Eisen and Milagros Palacios
Recently, Statistics Canada released a revision of its calculations of Canada’s gross domestic product (GDP) in recent years. GDP measures the total production in an economy in a given year, and per-person GDP is widely accepted by economists as one of the most useful metrics for assessing quality of life. The new estimate places Canada’s GDP for 2024 at 1.4 per cent larger than previously reported.
By the standards of these sorts of revisions—which are usually quite small—the recent update is significant. But make no mistake, the new numbers do not change the fundamental story of Canada’s economic performance, which has been one of historically weak growth and stagnant living standards for an unusually long stretch of time.
Let’s get into the numbers (all adjusted for inflation, in 2017 dollars) with some historical perspective. The new figures put Canada’s per-person GDP estimate for 2024 at $59,529. By comparison, in 2019 per-person GDP was slightly higher at $59,581. This means there has been no progress at all in Canadian living standards as measured by per-person GDP over the past five years. Even with the revision, five years of flat living standards is an extraordinary result.
This is historically anomalous. From 2000 to 2018—a period that was itself not especially strong by the standards of earlier decades—per-person GDP still grew at a compounded annual rate of just under one per cent. In the 1990s, growth was faster still at roughly 1.8 per cent annually. In both periods, living standards were rising meaningfully, even if the pace varied. The fact that they have completely stagnated for five years is alarming, even if our GDP numbers aren’t quite as bleak as we believed a few weeks ago.
Some pundits determined to view all economic data through a political lens have emphasized that under the new revisions, the overall rate of per-person growth during Justin Trudeau’s time as prime minister is now approximately the same as what occurred during Stephen Harper’s tenure.
However, this is more relevant as a political talking point than an economic insight. The historical data show that at an average annual growth rate of just 0.5 per cent, the Canadian economy’s performance under Harper was weak by long-term standards. This is something that Trudeau himself recognized when he first sought high office, criticizing the Harper government for “having the worst record on economic growth since R.B. Bennett in the depths of the Great Depression.”
Trudeau was right back then that Canadian economic growth during the Harper era was historically weak. As such, a revision showing that Canada’s slow growth has approximately continued for the past decade is hardly cause for celebration. It simply underscores that both governments presided over a long period of weak productivity growth and very slow improvements in living standards—and that in recent years even that sluggish growth has given way to complete stagnation.
Of course, an upward revision to recent GDP calculations is welcome news, but it must not be allowed to distract policymakers or the public from the reality of Canada’s severe long-term growth problem, which in recent years has gone from bad to worse.
Community
Charitable giving on the decline in Canada

From the Fraser Institute
By Jake Fuss and Grady Munro
There would have been 1.5 million more Canadians who donated to charity in 2023—and $755.5 million more in donations—had Canadians given to the same extent they did 10 years prior
According to recent polling, approximately one in five Canadians have skipped paying a bill over the past year so they can buy groceries. As families are increasingly hard-pressed to make ends meet, this undoubtedly means more and more people must seek out food banks, shelters and other charitable organizations to meet their basic necessities.
And each year, Canadians across the country donate their time and money to charities to help those in need—particularly around the holiday season. Yet at a time when the relatively high cost of living means these organizations need more resources, new data published by the Fraser Institute shows that the level of charitable giving in Canada is actually falling.
Specifically, over the last 10 years (2013 to 2023, the latest year of available data) the share of tax-filers who reported donating to charity fell from 21.9 per cent to 16.8 per cent. And while fewer Canadians are donating to charity, they’re also donating a smaller share of their income—during the same 10-year period, the share of aggregate income donated to charity fell from 0.55 per cent to 0.52 per cent.
To put this decline into perspective, consider this: there would have been 1.5 million more Canadians who donated to charity in 2023—and $755.5 million more in donations—had Canadians given to the same extent they did 10 years prior. Simply put, this long-standing decline in charitable giving in Canada ultimately limits the resources available for charities to help those in need.
On the bright side, despite the worrying long-term trends, the share of aggregate income donated to charity recently increased from 0.50 per cent in 2022 to 0.52 per cent in 2023. While this may seem like a marginal improvement, 0.02 per cent of aggregate income for all Canadians in 2023 was $255.7 million.
The provinces also reflect the national trends. From 2013 to 2023, every province saw a decline in the share of tax-filers donating to charity. These declines ranged from 15.4 per cent in Quebec to 31.4 per cent in Prince Edward Island.
Similarly, almost every province recorded a drop in the share of aggregate income donated to charity, with the largest being the 24.7 per cent decline seen in P.E.I. The only province to buck this trend was Alberta, which saw a 3.9 per cent increase in the share of aggregate income donated over the decade.
Just as Canada as a whole saw a recent improvement in the share of aggregate income donated, so too did many of the provinces. Indeed, seven provinces (except Manitoba, Nova Scotia and Newfoundland and Labrador) saw an increase in the share of aggregate income donated to charity from 2022 to 2023, with the largest increases occurring in Saskatchewan (7.9 per cent) and Alberta (6.7 per cent).
Canadians also volunteer their time to help those in need, yet the latest data show that volunteerism is also on the wane. According to Statistics Canada, the share of Canadians who volunteered (both formally and informally) fell by 8 per cent from 2018 to 2023. And the total numbers of hours volunteered (again, both formal and informal) fell by 18 per cent over that same period.
With many Canadians struggling to make ends meet, food banks, shelters and other charitable organizations play a critical role in providing basic necessities to those in need. Yet charitable giving—which provides resources for these charities—has long been on the decline. Hopefully, we’ll see this trend turn around swiftly.
-

 Community2 days ago
Community2 days agoCharitable giving on the decline in Canada
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCanada’s recent economic growth performance has been awful
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoCanada’s New Green Deal
-

 armed forces1 day ago
armed forces1 day agoOttawa’s Newly Released Defence Plan Crosses a Dangerous Line
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoAlberta’s huge oil sands reserves dwarf U.S. shale
-

 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoSaskatchewan woman approved for euthanasia urged to seek medical help in Canada rather than US
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCOP30 finally admits what resource workers already knew: prosperity and lower emissions must go hand in hand
-

 Indigenous1 day ago
Indigenous1 day agoResidential school burials controversy continues to fuel wave of church arsons, new data suggests