conflict
Boris Johnson lobbies Trump at RNC to back down from peace talks on Ukraine

From LifeSiteNews
By Frank Wright
The former U.K. Prime Minister Boris Johnson made a flying visit to the Republican National Conference this week, in a mission to persuade Donald Trump to continue the war in Ukraine.
Great to meet President Trump who is on top form after the shameful attempt on his life. We discussed Ukraine and I have no doubt that he will be strong and decisive in supporting that country and defending democracy. pic.twitter.com/OEVZPZsRE1
— Boris Johnson (@BorisJohnson) July 16, 2024
With Trump, his vice president pick JD Vance, and even Senator Lindsey Graham calling for an end to the proxy war against Russia, Johnson is making a second attempt to sabotage a realistic peace in Ukraine.
Johnson’s war record
Boris Johnson has used the war in Ukraine to cement a legacy for himself as a sort of latter-day Winston Churchill. Mere weeks after Russia’s invasion, he made another flying visit – this time to Kiev.
The reason for his unscheduled arrival in the office of the then-elected President Volodymyr Zelensky was that a peace deal had been agreed between Ukraine and Russia.
Brokered in Istanbul, Turkey, its existence was confirmed by former Israeli Prime Minister Naftali Bennett, who was party to the negotiations.
It was Johnson who urged Zelensky to throw this peace deal in the garbage, giving assurances that the U.K., U.S., NATO, and the EU would back Ukraine to victory in the war instead.
That deal seems impossibly attractive now. Russia would have kept only the strongly Russian-attracted Crimea, the two other Russian-speaking Donbass sections of Donetsk and Lugansk would have been made autonomous regions within Ukraine, and Ukraine would simply have had to agree to abandon any plans to join NATO.
That would have completely ended the credibility of Ukrainian and Western propaganda that Russia was planning to conquer Ukraine and then further expand its empire into more of the former Soviet Empire slave states.
However peace comes now, it is unlikely to be agreed on the generous terms rejected by the sudden, last-minute intervention by Boris Johnson, who hosted the neo-Nazi Azov battalion in the U.K. Parliament in May. It is a strange “Churchill” indeed who waves a flag inspired by the Waffen-SS.
450,000 British died during WW2 to defeat Nazi Germany. This week Boris Johnson welcomed the Ukrainian neo-Nazi Azov Battalion as “heroes” in London. No respect for those who died to stop the Nazi ideology. Now the UK Govt is using Nazis to kill Russians. pic.twitter.com/4tMq7N8npr
— Kim Dotcom (@KimDotcom) May 24, 2024
Ukraine – ‘functionally destroyed’
Johnson is responsible instead for a policy which has seen Ukraine “functionally destroyed as a country,” as JD Vance said in December 2023. The likely future U.S. vice president noted the terrible losses and declining population of Ukraine, saying, “The average age of a soldier in the Ukrainian army right now is 43.”
Pointing out the futility of continuing to send money to Ukraine, Vance sensibly asked, “What is 61 billion dollars [more] going to accomplish that a hundred billion hasn’t?”
His announcement as Trump’s VP pick, along with Trump’s miraculous survival of Saturday’s assassination attempt, has proven doubly alarming to all those whose futures are staked on that of Project Ukraine.
The end times
There can be no surer sign of the end times – whether for Ukraine or more generally – than career warmonger Lindsey Graham calling for peace.
In remarks which will likely ruin Boris Johnson’s day, Politico reported on July 17 that the childless senator had begun to echo the Trump/Vance line to stop the war in Ukraine.
“I want to end this war in Ukraine, and it’s going to be a diplomatic solution,” said Graham, adding “it’s going to take a guy like President Trump to bring this war to an end honorably.”
Graham echoed the emerging, if limited, realist viewpoint of Trump and Vance, repeating the charge that neither NATO nor Europe have been meeting the costs of their own security arrangement.
That has been paid for by the U.S., and according to Graham, that too must end. “NATO needs to pay more,” he said, recalling Vance’s speech in April in which he charged Europe of “failing to stand on its own two feet.”
The massive cost of providing the security umbrella through NATO to Europe is one reason for a revision of U.S.-European security policy. Downstream of this is the urgent need for Europe – including the U.K. – to rediscover the art of diplomacy.
Politicians such as Boris Johnson face humiliation in any peace deal with the Russians. The German and French leadership, and that of the EU itself together with many member nations, have all been totally committed to humiliating, weakening, and breaking up Russia, the regime change removal of its president, and the total victory of Ukraine. None of these goals were ever remotely realistic.
The German government has sought to criminalize the anti-war AfD, which was the second most popular party in Germany in the recent EU elections.
READ: Germany’s vice chancellor refuses to rule out criminalizing anti-globalist AfD party
Its finance minister Robert Habeck admitted, amidst a domestic financial crisis, that he had sent all the money to Ukraine.
The German government faces collapse, following years of "wrong policies" which amount to national suicide. As German farmers blockade supermarket supply chains, one AfD member asked – "Where has the money gone?" Habeck's answer "To Ukraine". Read more:https://t.co/jNtz818NNP
— Frank Wright (@frankwrighter) January 19, 2024
France’s Emmanuel Macron has made reckless statements promising to send French troops to fight Russia, and the outgoing foreign minister of the U.K. David Cameron privately admitted in late June that the British pro-Ukraine war position was “fixed” and would not change with the election of a Labour government.
UK Foreign Secretary David Cameron reveals all about the permanent pro-war Ukraine policy of Britain – to pranksters Lexus and Vovan.
For Cameron, hope lies with people like thanaterotic homosexual death cult leader Lindsey Graham – who wants to bomb Moscow. https://t.co/YmURbn8wBR
— Frank Wright (@frankwrighter) June 26, 2024
Cameron was right. It has not changed. On July 10 it was reported that the new Labour Prime Minister Keir Starmer has promised Ukraine £3 billion a year ($3.88 billion) “for as long as it takes.”
EU Chief Commissioner Ursula von der Leyen has consistently called for the ousting of Valdimir Putin and for the war to continue. She famously stated in September 2022 that “Putin will fail and Ukraine and Europe will prevail.”
Staking the political future of Europe on the impossible goal of Ukrainian victory was a reckless and unforced error, which lent an air of gravitas to a political class bereft of sane initiative.
The EU has recently selected a second pantsuited militant as its chief diplomat. Kaja Kallas, former leader of the tiny Baltic state of Estonia, called for the breakup of Russia mere weeks ago, and pledged support for “Ukraine’s victory” at last week’s NATO summit.
Europe has lost the art of diplomacy, and its leaders stand to lose all credibility as their Ukrainian war ends. This war made them appear serious, albeit serious about a delusion which promised only more death, and the dangerous potential of escalation to all out nuclear war.
To be faced with reality for these people is to be faced with political extinction. Relations with Russia will be normalized, as in the real world neither Russia nor Europe can hope for much of a future in the absence of resumed diplomatic and energy links.
It seems strange to say it, but these are strange times. The political leadership of pro-Ukraine Europe is fighting for its life to prolong a war that will risk the lives of everyone else. It is implacably opposed to peace, as this means political suicide.
Like their counterpart in Israel, Benjamin Netanyahu, these are politicians for whom peace spells doom. It is for this reason they will do anything in their power to prevent peace breaking out.
conflict
US airstrike on Iran’s nuclear facilities. Was it obliteration?

A satellite image of the Isfahan nuclear research center in Iran shows visible damage to structures and nearby tunnel entrances from recent US airstrikes. / Satellite image (c) 2025 Maxar Technologies.
 Seymour Hersh
Seymour Hersh
The US attack on Iran may not have wiped out its nuclear ambitions but it did set them back years
I started my career in journalism during the early 1960s as a reporter for the City News Bureau of Chicago, a now long-gone local news agency that was set up by the Chicago newspapers in the 1890s to cover the police and fire departments, City Hall, the courts, the morgue, and so on. It was a training ground, and the essential message for its aspiring reporters was: “If your mother says she loves you, check it out.”
It was a message I wish our cable networks would take to heart. CNN and MSNBC, basing their reporting on an alleged Defense Intelligence Agency analysis, have consistently reported that the Air Force raids in Iran on June 22 did not accomplish their primary goal: total destruction of Iran’s nuclear-weapons capacity. US newspapers also joined in, but it was the two nominally liberal cable channels, with their dislike—make that contempt—for President Donald Trump, that drove the early coverage.
There was no DIA analysis per se. All US units that engage in combat must file an “after-action report” to the DIA after a military engagement. In this case, the report would have come from the US Central Command, located at MacDill Air Force base in Tampa, Florida. CENTCOM is responsible for all US military operations in the Middle East, Egypt, Central Asia, Afghanistan, and Pakistan. One US official involved in the process told me that “the first thing out of the box is you have to tell your boss what happened.” It was that initial report of the bombing attack that was forwarded to DIA headquarters along the Potomac River in Washington and copied or summarized by someone not authorized to do so and sent to the various media outlets.
The view of many who were involved in the planning and execution of the mission is that the report was summarized and leaked “for political purposes”—to cast immediate doubt on the success of the mission. The early reports went so far as to suggest that Iran’s nuclear program has survived incapacitation by the attack. Seven US B-2 “Spirit” bombers, each carrying two deep-penetration “bunker-busters” weighing 30,000 pounds, had flown without challenge from their base in Missouri to the primary target: Iran’s Fordo nuclear facility, concealed deep inside a mountain twenty miles north of the city of Qom.
The planning for the attack began with the knowledge that the main target—the working area of the nuclear program—was buried at least 260 feet below the rocky surface at Fordo. The gas centrifuges spinning there were repeatedly enriching uranium, in what is known as a cascade, not to weapons-grade level—uranium-235 isotopes enriched to 90 percent—but to 60 percent. Further processing to create weapons grade uranium, if Iran chose to do so, could be done in a matter of weeks, or less. The Air Force planning group had also been informed before the bombing raid, most likely by the Israelis, who have a vast spy network in Iran, that more than 450 pounds of the enriched gas stored at Fordo had been shipped to safety at another vital Iranian nuclear site at Isfahan, 215 miles south of Tehran. Isfahan was the only known facility in Iran capable of converting the Fordo gas into a highly enriched metal—a critical early stage of building the bomb. Isfahan also was a separate target of the US attack on Fordo, and was pulverized by Tomahawk missiles fired by a U.S. submarine operating in the Gulf of Aden, off Yemen.
As a journalist who for decades has covered the nascent nuclear crisis in the Middle East, it seemed clear to me and to informed friends I have in Washington and Israel that if Fordo somehow survived its bunker-buster attack, as was initially suggested, and continued to enrich more uranium, Isfahan would not. No enrichment, no Iranian bomb.
I’ve been frustrated and angry at cable news coverage for years, and that includes Fox News, too, and decided to try and find the real story. If your mother says she loves you, check it out. And I checked out enough of it to share.
I was told that “the first question for the American planners was how big was the actual workspace at Fordo? Was it a structure? We had to find that out before we got rid of it.” Some of the planners estimated that the working space “was the size of two hockey rinks: 200 feet long and 85 feet wide.” It came to 34,000 square feet. The height of the underground working space was assumed to be ten-and-a-half feet—I was not told the genesis of that assumption—and the size of the target was determined to be 357,000 cubic feet.
The next step was to measure the power of the dozen or more bunker-busters that were planned to be “carefully spaced and dropped” by the US B-2 bombers, using the most advanced guidance systems. (During one high-level session in Washington, one of the Air Force planners was asked what would happen if the B-2’s guidance systems were corrupted by an outside signal. “We’d miss the target” was the answer.)
I was assured that even if the rough estimate of the working space at Fordo was far off, the bombers targeting Fordo each carried a 30,000-pound bomb with an explosive payload of as much as five thousand pounds, which was more than enough to pulverize the mythical hockey rinks, or even a much larger working space.
Some of the bombs were also outfitted with what is known as a hard target void sensing fuze, which enabled the bombs to penetrate multiple layers of a site like Fordo before detonating. This would maximize the destructive effect. Each bomb, dropped in sequence, would create a force of rubble that would cause increasing havoc in the working areas deep inside the mountain.
“The bombs made their own hole. We built a 30,000-pound steel bullet,” the official told me, referring with pride to the bunker-busters.
Most important, he said, was that there were no post-strike hints detected of radioactivity—more evidence that the 450 pounds of enriched uranium had been moved from Fordo to the reprocessing site at Isfahan prior to the US attack there, which was code-named “Midnight Hammer.” That operation included a third US strike at yet another nuclear facility at Natanz.
“The Air Force got everything on the hit list,” the official told me. “Even if Iran rebuilds some centrifuges, it will still need Isfahan. There is no conversion capability without it.”
Why not, I asked, tell the public about the success of the raid and the fact that Iran no longer has a potential nuclear weapon?
The answer: “There will be a top-secret report about all of this, but we don’t tell people how hard we work. We tell the public what we think it wants to hear.”
The US official, asked about the future of the Iranian nuclear program, quickly acknowledged that “there is a communication problem” when it comes to the fate of the program.
The intent of the strike planners, he said, “was to prevent the Iranians from building a nuclear weapon in the near term—a year or so—with the hope they would not try again. The clear understanding was that there was no expectation to ‘obliterate’ every aspect of their nuclear program. We don’t even know what that is.
“Obliteration means the glass—[eliminating] Iran’s nuclear program—is full. The planning and the results are the glass is half-full. For Trump critics, the results are the glass is half-empty—the centrifuges may have survived and four hundred pounds of 60 percent enriched uranium are missing. The bombs could not be assured to penetrate the centrifuge chamber . . . too deep, but they could cover them up [with rocks and other bomb debris] and in the process cause unknown damage to them.
“Whether the 60 percent [enriched uranium] was there or not is irrelevant because without centrifuges they cannot refine it to weapons grade. Add to this the research and refinement and conversion from gas to metal—required for a bomb—at Isfahan are also gone.
“Results? Glass is half-full . . . a couple of years of respite and uncertain future. So now Trump’s defense is Full Glass. Critics? Half-empty. Reality? Half-full. There you are.”
The immediate beneficiary of the use of US force in Iran will not be a more placid Middle East, but Israel, and Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. The Israeli Air Force and army are still killing massive numbers of Palestinians in Gaza.
There remains no evidence that Iran was on the cusp of becoming a nuclear power. But as the world has known for decades, Israel maintains a significant nuclear arsenal that it officially claims does not exist.
This is a story not about the bigger picture, which is muddled, but about a successful US mission that was the subject of a lot of sloppy reporting because of a reviled president. It would have been a breakthrough had anyone in the mainstream press spoken or written about the double standard that benefits Israel and its nuclear umbrella, but in America that remains a taboo.
Subscribe to Seymour Hersh.
For the full experience, upgrade your subscription.
conflict
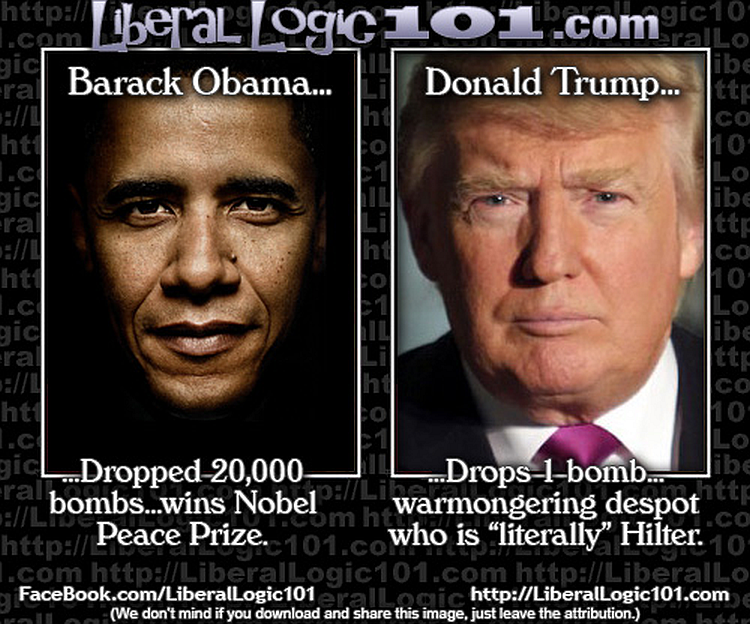
Obama Dropped Over 26K Bombs Without Congressional Approval
@miss_stacey_ Biden, Clinton, Obama & Harris on Iran #biden #clinton #obama #harris #trump #iran #nuclear
Iran has been the target for decades. Biden, Harris, and Clinton—all the Democrats have said that they would attack Iran if given the opportunity. It appears that Donald Trump is attempting to mitigate a potentially irresolvable situation. As he bluntly told reporters: We basically — we have two countries that have been fighting so long and so hard that they don’t know what the f‑‑‑ they’re doing.”
A portion of the nation believes Trump acted like a dictator by attacking Iran without Congressional approval. I explained how former President Barack Obama decimated the War Powers Resolution Act when he decided Libya was overdue for a regime change. The War Powers Act, or War Powers Resolution of 1973, grants the POTUS the ability to send American troops into battle if Congress receives a 48-hour notice. The stipulation here is that troops cannot remain in battle for over 60 days unless Congress authorizes a declaration of war. Congress could also remove US forces at any time by passing a resolution.
Libya is one of seven nations that Obama bombed without Congressional approval, yet no one remembers him as a wartime president, as the United States was not technically at war. Over 26,000 bombs were deployed across 7 nations under his command in 2016 alone. Libya, Afghanistan, Syria, Yemen, Somalia, Iraq, and Pakistan were attacked without a single vote. Donald Trump’s recent orders saw 36 bombs deployed in Iran.
The majority of those bombings happened in Syria, Libya, and Iraq under the premise of targeting extremist groups like ISIS. Drone strikes were carried out across Somalia, Yemen, and Pakistan as the Obama Administration accused those nations of hosting al-Qaeda affiliated groups. Coincidentally, USAID was also providing funding to those groups.
The 2001 Authorization for Use of Military Force (AUMF) was initially implemented to hunt down the Taliban and al-Qaeda after the 9/11 terrorist attacks. Obama broadened his interpretation of the AUMF and incorporated newly formed militant groups that were allegedly expanding across the entire Middle East. The Bureau of Investigative Journalism believes there were up to 1,100 civilian casualties in Pakistan, Yemen, and Somalia. Thousands of civilians died in Syria and Iraq but the death toll was never calculated. At least 100 innocent people died in the 2016 attacks in Afghanistan alone.
The government will always augment the law for their personal agenda. The War Powers Resolution was ignored and the AUMF was altered. Congress was, however, successful in preventing Obama from putting US troops on the ground and fighting a full-scale war. In 2013, Obama sought congressional approval for military action in Syria but was denied. Obama again attempted to deploy troops in 2015 but was denied. Congress has to redraft the AUMF to specifically prevent Obama from deploying troops in the Middle East. “The authorization… does not authorize the use of the United States Armed Forces on the ground in Syria for the purpose of combat operations.” Obama attempted to redraft the AUMF on his own by insisting he would prohibit “enduring offensive ground combat operations” or long-term deployment of troops. He was met with bipartisan disapproval as both sides believed he was attempting to drag the United States into another unnecessary war.
The United States should not be involved in any of these battles, but here we are. Those living in fear that Donald Trump is a dictator fail to recognize that past leadership had every intention of sending American men and women into battle unilaterally without a single vote cast.
-

 Crime2 days ago
Crime2 days ago“This is a total fucking disaster”
-

 Fraser Institute1 day ago
Fraser Institute1 day agoBefore Trudeau average annual immigration was 617,800. Under Trudeau number skyrocketted to 1.4 million annually
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoChicago suburb purchases childhood home of Pope Leo XIV
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days ago‘I Know How These People Operate’: Fmr CIA Officer Calls BS On FBI’s New Epstein Intel
-

 MAiD2 days ago
MAiD2 days agoCanada’s euthanasia regime is already killing the disabled. It’s about to get worse
-

 Daily Caller2 days ago
Daily Caller2 days agoBlackouts Coming If America Continues With Biden-Era Green Frenzy, Trump Admin Warns
-

 Red Deer2 days ago
Red Deer2 days agoJoin SPARC in spreading kindness by July 14th
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoPrime minister can make good on campaign promise by reforming Canada Health Act







