Economy
Prime minister and premier combine to reduce living standards in B.C.

From the Fraser Institute
By Jake Fuss
In B.C., the Eby government is following the prime minister’s lead. After nearly two decades of spending restraint (1999/00 to 2016/17), the province has experienced an explosion in government spending. Program spending will increase from $46.1 billion in 2016-17 to a projected $85.3 billion this year, a nominal increase of more than 85 per cent.
Recently, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and Premier David Eby had a tête-à-tête and vowed to always “work together on important issues.” While they belong to two different political parties, their visions rely on a larger role for government, which includes more spending, regulation, borrowing and higher taxes. Unsurprisingly, this economic strategy hasn’t worked and has instead led to stagnant living standards in British Columbia and across Canada.
Under the NDP, British Columbians have seen their incomes completely stagnate. B.C.’s per-person GDP, a broad measure of living standards, is expected to be lower this year than in 2018, and decline by an average annual rate of 0.9 per cent from 2022 to 2024—the third biggest drop among the provinces during this period.
This represents a marked departure from the economic results under the previous government. From 2001 to 2017, per-person GDP grew (on average) by 1.4 per cent. And the average British Columbian’s income increased by 27 per cent over these 16 years.
The decline in living standards is also occurring nationally. Canada’s per-person GDP was lower at the end of 2023 than it was in 2014.
Why?
Since first elected in 2015, Prime Minister Trudeau has greatly expanded the federal government’s role in the Canadian economy. Federal program spending (total spending excluding debt interest costs) will increase from $256.2 billion in the final full year of the Harper government to a projected $483.6 billion in 2024-25, an increase of nearly 90 per cent over a decade. The government has financed this spending surge through tax increases and borrowing.
Specifically, the Trudeau government in 2016 raised the top personal income tax rate (which applies to many entrepreneurs and businessowners) and also opaquely increased taxes on middle-income Canadians by eliminating several tax credits (as a result, 86 per cent of middle-income families now pay higher taxes). Federal debt has spiked considerably to finance the government’s insatiable appetite for spending, reaching nearly $2.1 trillion this year, almost double the level in 2014-15.
In B.C., the Eby government is following the prime minister’s lead. After nearly two decades of spending restraint (1999/00 to 2016/17), the province has experienced an explosion in government spending. Program spending will increase from $46.1 billion in 2016-17 to a projected $85.3 billion this year, a nominal increase of more than 85 per cent.
With Premier Eby’s plan to ramp up spending further in the next few years and incur substantial deficits, B.C.’s net government debt is projected to reach a whopping $128.8 billion by 2026/27—a 227 per cent increase since 2016-17.
The B.C. NDP has also raised one tax after another to feed its appetite for spending. The government hiked personal income tax rates from 14.7 per cent to 16.8 per cent on income between roughly $181,000 and $253,000, and introduced a new top tax rate of 20.5 per cent for top-income earners. And raised the business tax rate from 11.0 to 12.0 per cent in 2018, deterring badly needed investment in the province.
Prime Minister Trudeau and Premier Eby are pursuing the same policies and achieving the same miserable economic results. Simply put, the Trudeau-Eby zero economic growth alliance has reduced the living standards of British Columbians and Canadians.
Author:
Alberta
Carney forces Alberta to pay a steep price for the West Coast Pipeline MOU

From the Fraser Institute
The stiffer carbon tax will make Alberta’s oil sector more expensive and thus less competitive at a time when many analysts expect a surge in oil production. The costs of mandated carbon capture will similarly increase costs in the oilsands and make the province less cost competitive.
As we enter the final days of 2025, a “deal” has been struck between Carney government and the Alberta government over the province’s ability to produce and interprovincially transport its massive oil reserves (the world’s 4th-largest). The agreement is a step forward and likely a net positive for Alberta and its citizens. However, it’s not a second- or even third-best option, but rather a fourth-best option.
The agreement is deeply rooted in the development of a particular technology—the Pathways carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) project, in exchange for relief from the counterproductive regulations and rules put in place by the Trudeau government. That relief, however, is attached to a requirement that Alberta commit to significant spending and support for Ottawa’s activist industrial policies. Also, on the critical issue of a new pipeline from Alberta to British Columbia’s coast, there are commitments but nothing approaching a guarantee.
Specifically, the agreement—or Memorandum of Understanding (MOU)—between the two parties gives Alberta exemptions from certain federal environmental laws and offers the prospect of a potential pathway to a new oil pipeline to the B.C. coast. The federal cap on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the oil and gas sector will not be instituted; Alberta will be exempt from the federal “Clean Electricity Regulations”; a path to a million-barrel-per day pipeline to the BC coast for export to Asia will be facilitated and established as a priority of both governments, and the B.C. tanker ban may be adjusted to allow for limited oil transportation. Alberta’s energy sector will also likely gain some relief from the “greenwashing” speech controls emplaced by the Trudeau government.
In exchange, Alberta has agreed to implement a stricter (higher) industrial carbon-pricing regime; contribute to new infrastructure for electricity transmission to both B.C. and Saskatchewan; support through tax measures the building of a massive “sovereign” data centre; significantly increase collaboration and profit-sharing with Alberta’s Indigenous peoples; and support the massive multibillion-dollar Pathways project. Underpinning the entire MOU is an explicit agreement by Alberta with the federal government’s “net-zero 2050” GHG emissions agenda.
The MOU is probably good for Alberta and Canada’s oil industry. However, Alberta’s oil sector will be required to go to significantly greater—and much more expensive—lengths than it has in the past to meet the MOU’s conditions so Ottawa supports a west coast pipeline.
The stiffer carbon tax will make Alberta’s oil sector more expensive and thus less competitive at a time when many analysts expect a surge in oil production. The costs of mandated carbon capture will similarly increase costs in the oilsands and make the province less cost competitive. There’s additional complexity with respect to carbon capture since it’s very feasibility at the scale and time-frame stipulated in the MOU is questionable, as the historical experience with carbon capture, utilization and storage for storing GHG gases sustainably has not been promising.
These additional costs and requirements are why the agreement is the not the best possible solution. The ideal would have been for the federal government to genuinely review existing laws and regulations on a cost-benefit basis to help achieve its goal to become an “energy superpower.” If that had been done, the government would have eliminated a host of Trudeau-era regulations and laws, or at least massively overhauled them.
Instead, the Carney government, and now with the Alberta government, has chosen workarounds and special exemptions to the laws and regulations that still apply to everyone else.
Again, it’s very likely the MOU will benefit Alberta and the rest of the country economically. It’s no panacea, however, and will leave Alberta’s oil sector (and Alberta energy consumers) on the hook to pay more for the right to move its export products across Canada to reach other non-U.S. markets. It also forces Alberta to align itself with Ottawa’s activist industrial policy—picking winning and losing technologies in the oil-production marketplace, and cementing them in place for decades. A very mixed bag indeed.
Business
Man overboard as HMCS Carney lists to the right
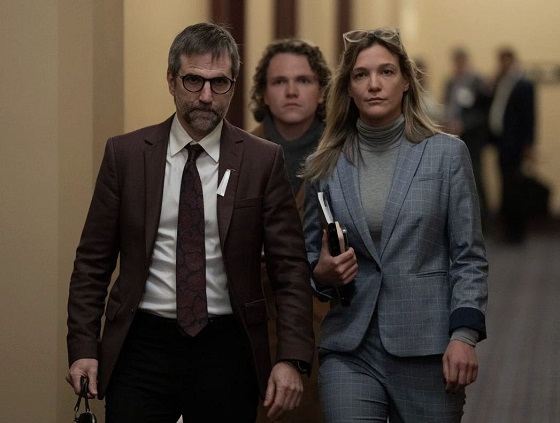

Steven Guilbeault, Heritage Minister and Quebec lieutenant, leaves cabinet this week with his chief of staff, Ann-Clara Vaillancourt. He resigned on Thursday.
Steven Guilbeault’s resignation will help end a decade of stagnation and lost investment.
Steven Guilbeault’s resignation will come as no surprise to Mark Carney – save, perhaps, for the fact that it took so long.
The former environment minister quit on Thursday evening, after the prime minister unveiled his memorandum of understanding with Alberta premier, Danielle Smith. That deal is aimed at creating the conditions to build an oil pipeline to the West Coast and encouraging new investment in the province’s natural gas electricity generation sector. In doing so, Carney cancelled the oil and gas emissions cap and the clean electricity regulations that Guilbeault had been instrumental in constructing and imposing.
Fly Straight is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
The former environmental activist couldn’t accept the continued expansion of fossil fuel production and so walked away after six years in cabinet.
In his resignation statement, he said he strongly opposes the MOU with Alberta because it was signed without consultation with the province of British Columbia and First Nations.
He said removing the moratorium on oil tankers off the West Coast would increase the risk of accidents and suspending clean electricity regulations, which blocked new gas generation, will result in an “upwards emissions trajectory”.
In particular, he was upset about the expansion of federal tax credits to encourage enhanced oil recovery, a carbon storage technology that captures carbon dioxide from industrial emitters and injects it back underground. Guilbeault considered this a direct subsidy for oil production – a business he said he hoped the government was exiting.
In a Twitter post, I called Guilbeault “anti-Pathways” – that is, opposed to the giant carbon capture and storage development that Carney views as crucial to offsetting the building of a new pipeline.
One of Guilbeault’s defenders said he is not anti-Pathways, and that, in fact, he was part of the trifecta, along with Chrystia Freeland and Jonathan Wilkinson, who negotiated the details on the investment tax credit “that will pay 50 percent of the cost of construction to a bunch of rich oil companies”. To me, that showed Guilbeault’s (and his supporters) true colours. If he wasn’t anti-Pathways, he certainly wasn’t pro.
When he said he would back Carney’s leadership bid in January, I wrote that it was an endorsement the aspiring Liberal leader could do without.
The now-prime minister always had in his mind a plan to build, including fossil fuel production, offset by technology adoption and a stronger industrial carbon price in Alberta. Even then, he made clear he was prepared to be pragmatic in a time of crisis.
Guilbeault’s plan was to regulate the industry to death.
It was always going to end badly but, as Carney told me last winter, Guilbeault provided crucial support on the ground in Quebec and any politician’s first responsibility is to win.
Guilbeault should be respected for his deep convictions on climate change and his commitment to leaving a better world to our children.
But he should never have been allowed to dictate environmental policy in this country. He refused to view natural gas as a bridging fuel in the energy transition in a country that has reserves of a resource that will, at current production levels, last 300 years.
He made clear his lack of enthusiasm for small modular nuclear reactors and new road-building.
And he pushed an oil and gas emissions cap that he knew would hit production levels and further (if that were possible) alienate Western Canadians.
His departure – and that of Freeland – give Carney scope to pursue what he hopes is a transformative response to not only Donald Trump, but to federal policies that amounted to driving with the handbrake on. Carney has made his intent clear – to optimize Canada’s resource wealth, while attempting to minimize emissions.
Five years ago, Trudeau was nearly tarred and feathered during a visit to Calgary; Carney received two standing ovations in the same town yesterday.
For too many years under the Trudeau/Freeland duopoly the plan was to redistribute the pie. Now it is clearly about wealth creation.
In my National Post columns, I have been scathing about some of the things the Carney government has done, as is appropriate for someone whose prime directive is the public interest. The decisions to recognize a Palestinian state; apologize to Trump for the Ontario “Ronald Reagan” ad; announce a bunch of major projects that were so advanced they didn’t need to be fast-tracked; split spending into the confusing binary of “operating” or “capital”; and visit the United Arab Emirates on a trade mission in the midst of a genocide in Sudan that the Emiratis had helped to fund were all, to me, missteps.
But, so far, Carney has got the big things right. The budget and this MOU are auspicious moves aimed at ending a decade of stagnation and lost investment.
There is a new mood of anticipation in the country, summed up in the S&P/TSX index, which hit record highs this week on the back of energy and mining stocks. Canadian pension funds are taking another look at the domestic market, intrigued by the prospect of investing in the potential privatization of airports, for example.
Canada is feeling better. There has been a shift in the mindset from saying no to everything to being open to removing barriers that stop the private sector from investing.
Success and prosperity are not guaranteed. But stagnation need not be either.
Fly Straight is a reader-supported publication.
To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
-

 Opinion2 days ago
Opinion2 days agoLandmark 2025 Study Says Near-Death Experiences Can’t Be Explained Away
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoRed Deer’s Jason Stephan calls for citizen-led referendum on late-term abortion ban in Alberta
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoBlacked-Out Democracy: The Stellantis Deal Ottawa Won’t Show Its Own MPs
-

 Artificial Intelligence1 day ago
Artificial Intelligence1 day agoGoogle denies scanning users’ email and attachments with its AI software
-

 Agriculture1 day ago
Agriculture1 day agoHealth Canada pauses plan to sell unlabeled cloned meat
-

 Indigenous2 days ago
Indigenous2 days agoIndigenous activist wins landmark court ruling for financial transparency
-
 Health1 day ago
Health1 day agoOrgan donation industry’s redefinitions of death threaten living people
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoCarney forces Alberta to pay a steep price for the West Coast Pipeline MOU









