Economy
Canadians face serious economic costs due to health-care wait times

From the Fraser Institute
Not only does Canada pay the most for health care (as a share of its economy) among high-income countries with universal health care (after adjusting for differences in the age structure of the population), it also has some of the fewest medical resources and the worst access to timely medical care.
We hear a lot about how much money we must spend to simply maintain the status quo in health care, with billions of new dollars from Ottawa just to keep the same system afloat.
The irony, of course, is that maintaining the status quo imposes some of the harshest costs on Canadians. Last year, Canadians could expect to wait an average of 13.1 weeks to receive treatment after receiving a specialist consultation. Not only was this wait more than two times longer than in 1993, it resulted in an estimated 1.2 million procedures being waited for across the country.
And at one month longer than the wait doctors consider reasonable, these delays are not benign. In fact, they can produce devastating physical and psychological consequences.
While it may be tempting to blame our current predicament on the aftereffects of the pandemic, in reality, long waits were the norm long before COVID. In fact, in 2019 the wait between a specialist consultation and receiving care was nearly two and a half weeks less than today, and the number of procedures being waited for (1.1 million) was slightly less than the number today (1.2 million).
In addition to the physical and psychological costs of waiting, there are also serious economic costs. According to a new study, wait times for non-emergency treatment in 2023 cost Canadians $3.5 billion in lost wages and productivity, or $2,871 per person waiting for a procedure. For perspective, this is more than double the cost in 2004 (inflation-adjusted). After we account for patient leisure time outside of work, the estimate for 2023 increases to $10.6 billion or $8,730 per person waiting.
Some advocates of the status quo suggest these costs are necessary to maintain our universal health-care system but international evidence indicates the opposite. In fact, not only does Canada pay the most for health care (as a share of its economy) among high-income countries with universal health care (after adjusting for differences in the age structure of the population), it also has some of the fewest medical resources and the worst access to timely medical care.
What do other higher-performing universal health-care systems do differently?
To varying degrees, they embrace the private sector as a partner. For example, Australia now delivers the majority of non-emergency surgeries and care through private hospitals, while frequently outperforming Canada and spending less than we do (as a share of the economy).
Here at home, we’ve seen what real reform, which embraces the private sector, can do. In Saskatchewan between 2010 and 2014, the government contracted out publicly-financed procedures to private clinics, which helped lower the province’s wait times from some of the longest in the country (26.5 weeks in 2010) to some of the shortest (14.2 weeks in 2014). Quebec, which has consistently “low” wait times, in recent years has contracted out one in six day-surgeries to private clinics.
Despite objections from defenders of today’s unworkable status quo, there’s in fact a way to improve Canada’s health-care system while preserving its universality. However, until we’re willing to pursue that path, wait times and their associated costs will continue to burden Canadian patients and their loved ones.
Author:
Alberta
Federal budget: It’s not easy being green

From Resource Works
Canada’s climate rethink signals shift from green idealism to pragmatic prosperity.
Bill Gates raised some eyebrows last week – and probably the blood pressure of climate activists – when he published a memo calling for a “strategic pivot” on climate change.
In his memo, the Microsoft founder, whose philanthropy and impact investments have focused heavily on fighting climate change, argues that, while global warming is still a long-term threat to humanity, it’s not the only one.
There are other, more urgent challenges, like poverty and disease, that also need attention, he argues, and that the solution to climate change is technology and innovation, not unaffordable and unachievable near-term net zero policies.
“Unfortunately, the doomsday outlook is causing much of the climate community to focus too much on near-term emissions goals, and it’s diverting resources from the most effective things we should be doing to improve life in a warming world,” he writes.
Gates’ memo is timely, given that world leaders are currently gathered in Brazil for the COP30 climate summit. Canada may not be the only country reconsidering things like energy policy and near-term net zero targets, if only because they are unrealistic and unaffordable.
It could give some cover for Canadian COP30 delegates, who will be at Brazil summit at a time when Prime Minister Mark Carney is renegotiating his predecessor’s platinum climate action plan for a silver one – a plan that contains fewer carbon taxes and more fossil fuels.
It is telling that Carney is not at COP30 this week, but rather holding a summit with Alberta Premier Danielle Smith.
The federal budget handed down last week contains kernels of the Carney government’s new Climate Competitiveness Strategy. It places greater emphasis on industrial strategy, investment, energy and resource development, including critical minerals mining and LNG.
Despite his Davos credentials, Carney is clearly alive to the fact it’s a different ballgame now. Canada cannot afford a hyper-focus on net zero and the green economy. It’s going to need some high octane fuel – oil, natural gas and mining – to prime Canada’s stuttering economic engine.
The prosperity promised from the green economy has not quite lived up to its billing, as a recent Fraser Institute study reveals.
Spending and tax incentives totaling $150 billion over a decade by Ottawa, B.C, Ontario, Alberta and Quebec created a meagre 68,000 jobs, the report found.
“It’s simply not big enough to make a huge difference to the overall performance of the economy,” said Jock Finlayson, chief economist for the Independent Contractors and Business Association and co-author of the report.
“If they want to turn around what I would describe as a moribund Canadian economy…they’re not going to be successful if they focus on these clean, green industries because they’re just not big enough.”
There are tentative moves in the federal budget and Climate Competitiveness Strategy to recalibrate Canada’s climate action policies, though the strategy is still very much in draft form.
Carney’s budget acknowledges that the world has changed, thanks to deglobalization and trade strife with the U.S.
“Industrial policy, once seen as secondary to market forces, is returning to the forefront,” the budget states.
Last week’s budget signals a shift from regulations towards more investment-based measures.
These measures aim to “catalyse” $500 billion in investment over five years through “strengthened industrial carbon pricing, a streamlined regulatory environment and aggressive tax incentives.”
There is, as-yet, no commitment to improve the investment landscape for Alberta’s oil industry with the three reforms that Alberta has called for: scrapping Bill C-69, a looming oil and gas emissions cap and a West Coast oil tanker moratorium, which is needed if Alberta is to get a new oil pipeline to the West Coast.
“I do think, if the Carney government is serious about Canada’s role, potentially, as an global energy superpower, and trying to increase our exports of all types of energy to offshore markets, they’re going to have to revisit those three policy files,” Finlayson said.
Heather Exner-Pirot, director of energy, natural resources and environment at the Macdonald-Laurier Institute, said she thinks the emissions cap at least will be scrapped.
“The markets don’t lie,” she said, pointing to a post-budget boost to major Canadian energy stocks. “The energy index got a boost. The markets liked it. I don’t think the markets think there is going to be an emissions cap.”
Some key measures in the budget for unlocking investments in energy, mining and decarbonization include:
- incentives to leverage $1 trillion in investment over the next five years in nuclear and wind power, energy storage and grid infrastructure;
- an expansion of critical minerals eligible for a 30% clean technology manufacturing investment tax credit;
- $2 billion over five years to accelerate critical mineral production;
- tax credits for turquoise hydrogen (i.e. hydrogen made from natural gas through methane pyrolysis); and
- an extension of an investment tax credit for carbon capture utilization and storage through to 2035.
As for carbon taxes, the budget promises “strengthened industrial carbon pricing.”
This might suggest the government’s plan is to simply simply shift the burden for carbon pricing from the consumer entirely onto industry. If that’s the case, it could put Canadian resource industries at a disadvantage.
“How do we keep pushing up the carbon price — which means the price of energy — for these industries at a time when the United States has no carbon pricing at all?” Finlayson wonders.
Overall, Carney does seem to be moving in the right direction in terms of realigning Canada’s energy and climate policies.
“I think this version of a Liberal government is going to be more focused on investment and competitiveness and less focused around the virtue-signaling on climate change, even though Carney personally has a reputation as somebody who cares a lot about climate change,” Finlayson said.
“It’s an awkward dance for them. I think they are trying to set out a different direction relative to the Trudeau years, but they’re still trying to hold on to the Trudeau climate narrative.”
Pictured is Mark Carney at COP26 as UN Special Envoy on Climate Action and Finance. He is not at COP30 this week. UNRIC/Miranda Alexander-Webber
Resource Works News
Business
Carney government needs stronger ‘fiscal anchors’ and greater accountability

From the Fraser Institute
By Tegan Hill and Grady Munro
Following the recent release of the Carney government’s first budget, Fitch Ratings (one of the big three global credit rating agencies) issued a warning that the “persistent fiscal expansion” outlined in the budget—characterized by high levels of spending, borrowing and debt accumulation—will erode the health of Canada’s finances and could lead to a downgrade in Canada’s credit rating.
Here’s why this matters. Canada’s credit rating impacts the federal government’s cost of borrowing money. If the government’s rating gets downgraded—meaning Canadian federal debt is viewed as an increasingly risky investment due to fiscal mismanagement—it will likely become more expensive for the government to borrow money, which ultimately costs taxpayers.
The cost of borrowing (i.e. the interest paid on government debt) is a significant part of the overall budget. This year, the federal government will spend a projected $55.6 billion on debt interest, which is more than one in every 10 dollars of federal revenue, and more than the government will spend on health-care transfers to the provinces. By 2029/30, interest costs will rise to a projected $76.1 billion or more than one in every eight dollars of revenue. That’s taxpayer money unavailable for programs and services.
Again, if Canada’s credit rating gets downgraded, these costs will grow even larger.
To maintain a good credit rating, the government must prevent the deterioration of its finances. To do this, governments establish and follow “fiscal anchors,” which are fiscal guardrails meant to guide decisions regarding spending, taxes and borrowing.
Effective fiscal anchors ensure governments manage their finances so the debt burden remains sustainable for future generations. Anchors should be easily understood and broadly applied so that government cannot get creative with its accounting to only technically abide by the rule, but still give the government the flexibility to respond to changing circumstances. For example, a commonly-used rule by many countries (including Canada in the past) is a ceiling/target for debt as a share of the economy.
The Carney government’s budget establishes two new fiscal anchors: balancing the federal operating budget (which includes spending on day-to-day operations such as government employee compensation) by 2028/29, and maintaining a declining deficit-to-GDP ratio over the years to come, which means gradually reducing the size of the deficit relative to the economy. Unfortunately, these anchors will fail to keep federal finances from deteriorating.
For instance, the government’s plan to balance the “operating budget” is an example of creative accounting that won’t stop the government from borrowing money each year. Simply put, the government plans to split spending into two categories: “operating spending” and “capital investment” —which includes any spending or tax expenditures (e.g. credits and deductions) that relates to the production of an asset (e.g. machinery and equipment)—and will only balance operating spending against revenues. As a result, when the government balances its operating budget in 2028/29, it will still incur a projected deficit of $57.9 billion when spending on capital is included.
Similarly, the government’s plan to reduce the size of the annual deficit relative to the economy each year does little to prevent debt accumulation. This year’s deficit is expected to equal 2.5 per cent of the overall economy—which, since 2000, is the largest deficit (as a share of the economy) outside of those run during the 2008/09 financial crisis and the pandemic. By measuring its progress off of this inflated baseline, the government will technically abide by its anchor even as it runs relatively large deficits each and every year.
Moreover, according to the budget, total federal debt will grow faster than the economy, rising from a projected 73.9 per cent of GDP in 2025/26 to 79.0 per cent by 2029/30, reaching a staggering $2.9 trillion that year. Simply put, even the government’s own fiscal plan shows that its fiscal anchors are unable to prevent an unsustainable rise in government debt. And that’s assuming the government can even stick to these anchors—which, according to a new report by the Parliamentary Budget Officer, is highly unlikely.
Unfortunately, a federal government that can’t stick to its own fiscal anchors is nothing new. The Trudeau government made a habit of abandoning its fiscal anchors whenever the going got tough. Indeed, Fitch Ratings highlighted this poor track record as yet another reason to expect federal finances to continue deteriorating, and why a credit downgrade may be on the horizon. Again, should that happen, Canadian taxpayers will pay the price.
Much is riding on the Carney government’s ability to restore Canada’s credibility as a responsible fiscal manager. To do this, it must implement stronger fiscal rules than those presented in the budget, and remain accountable to those rules even when it’s challenging.
-

 Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days ago
Frontier Centre for Public Policy2 days agoRichmond Mayor Warns Property Owners That The Cowichan Case Puts Their Titles At Risk
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoSluggish homebuilding will have far-reaching effects on Canada’s economy
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoMark Carney Seeks to Replace Fiscal Watchdog with Loyal Lapdog
-
 COVID-191 day ago
COVID-191 day agoMajor new studies link COVID shots to kidney disease, respiratory problems
-
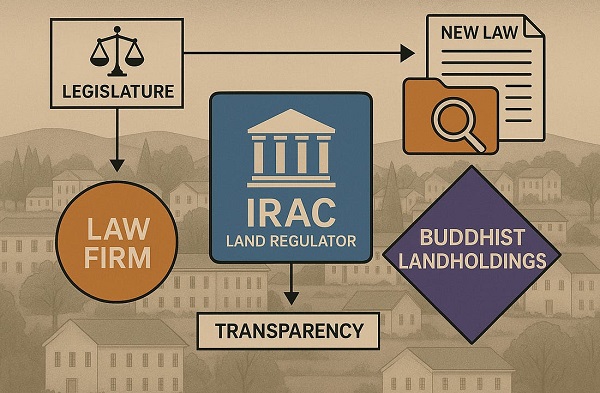
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoP.E.I. Moves to Open IRAC Files, Forcing Land Regulator to Publish Reports After The Bureau’s Investigation
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoCanada’s oilpatch shows strength amid global oil shakeup
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoState Department designates European Antifa groups foreign terror organizations
-

 International1 day ago
International1 day agoBondi and Patel deliver explosive “Clinton Corruption Files” to Congress