Energy
Why we should be skeptical of the hydrogen economy

From the Frontier Centre for Public Policy
By Hügo Krüger and Ian Madsen
Hydrogen has a low energy density by volume, compared to well-established and practical fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and natural gas. It also has a low ignition point and is three times as explosive as natural gas, which could be either positive or negative.
At first glance, using highly variable, intermittent, inexpensive renewable energy to produce hydrogen for energy supply stabilization seems logical. However, renewable energy is not always readily available. The concept of hydrogen as a ‘buffer,’ akin to a battery, to ensure consistent renewable power is more complex than it appears.
Upon further examination, the idea is impractical and expensive for several reasons. Among them, hydrogen has a low energy density by volume, compared to well-established and practical fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and natural gas. It also has a low ignition point and is three times as explosive as natural gas, which could be either positive or negative, depending on its use.
Contrary to claims, renewable energy is neither inexpensive nor environmentally benign. Storing hydrogen in a natural gaseous state requires massive, costly storage vessels. Electrolyzing is expensive and will likely remain that way. Similarly, the cost of producing hydrogen is higher than that of deriving it from natural gas, which produces carbon dioxide, which is unwanted. There are some other techniques, such as pressure, heat, and radiolysis from radiation emitted from nuclear reactors, that are feasible, perhaps in combination. Small ‘micro nuclear reactors’ may drive down these costs. Atomic reactors are already used in U.S. Navy aircraft carriers to produce aviation and diesel synthetic fuel.
There are also a series of impractical issues. Existing pipeline infrastructure cannot transport pure hydrogen due to hydrogen embrittlement, and hydrogen cannot easily be used as a transportation fuel. A new Teflon-coated pipeline and distribution system parallel to the existing natural gas network would have to be built, costing hundreds of billions of dollars in North America alone.
While the idea of synthetic fuels using hydrogen may seem more feasible, it would likely be limited to a ‘niche role,’ potentially in natural gas-deficient nations. However, this would still necessitate significant investment. Ultimately, diverting funds to this ‘hydrogen economy’ could be a misallocation of capital from other, potentially more viable, areas.
Download the full report in PDF format here. (16 pages)
Hügo Krüger is a YouTube podcaster, writer, and civil nuclear engineer who has worked on a variety of energy related infrastructure projects ranging from Nuclear Power, LNG and Renewable Technologies. He holds a Master’s in Nuclear Civil Engineering from École Spéciale des Travaux Publics, du bâtiment et de l’industrie, Paris and a bachelor’s from the University of Pretoria.
Ian Madsen, BA (Economics, University of Alberta), MBA (Finance, University of Toronto), holds the Chartered Financial Analyst designation. He was an investment portfolio manager; owned his own investment counselling firm; published an investment newsletter; founded the professional society now known as CFA Saskatchewan in 1986; and was a director of an investment research operation in India. Since 2016, he has been the Senior Policy Analyst at the Frontier Centre for Public Policy, performing valuation analyses on federal and provincial Crown corporations in Canada, and also written numerous policy analyses. He lives in Surrey, British Columbia with his family.
2025 Federal Election
Canada Continues to Miss LNG Opportunities: Why the World Needs Our LNG – and We’re Not Ready

From EnergyNow.Ca
By Katarzyna (Kasha) Piquette, Founder and CEO, Canadian Energy Ventures
When Russia invaded Ukraine in 2022, Europe’s energy system was thrown into chaos. Much of the 150 billion cubic meters of Russian gas that once flowed through pipelines had to be replaced—fast. Europe turned to every alternative it could find: restarting coal and nuclear plants, accelerating wind and solar approvals, and most notably, launching a historic buildout of LNG import capacity.
Today, LNG terminals are built around the world. The ‘business case’ is solid. The ships are sailing. The demand is real. But where is Canada?
As of March 28, 2025, natural gas prices tell a story of extreme imbalance. While Europe and Asia are paying around $13 per million BTU, prices at Alberta’s AECO hub remain below $2.20 CAD per gigajoule—a fraction of global market levels. This is more than a pricing mismatch. It’s a signal that Canada, a country rich in natural gas and global goodwill, is failing to connect the dots between energy security abroad and economic opportunity at home.
Since 2022, Europe has added over 80 billion cubic meters of LNG import capacity, with another 80 billion planned by 2030. This infrastructure didn’t appear overnight. It came from urgency, unity, and massive investment. And while Europe was preparing to receive, Canada has yet to build at scale to supply.
We have the resource. We have the relationships. What we lack is the infrastructure.
Estimates suggest that $55 to $75 billion in investment is needed to scale Canadian LNG capacity to match our potential as a global supplier. That includes pipelines, liquefaction terminals, and export facilities on both coasts. These aren’t just economic assets—they’re tools of diplomacy, climate alignment, and Indigenous partnership. A portion of this investment can and should be met through public-private partnerships, leveraging government policy and capital alongside private sector innovation and capacity.
Meanwhile, Germany continues to grapple with the complexities of energy dependence. In January 2025, German authorities seized the Panama-flagged tanker Eventin, suspected of being part of Russia’s “shadow fleet” used to circumvent oil sanctions. The vessel, carrying approximately 100,000 tons of Russian crude oil valued at €40 million, was found adrift off the Baltic Sea island of Rügen and subsequently detained. This incident underscores the ongoing challenges Europe faces in enforcing energy sanctions and highlights the pressing need for reliable, alternative energy sources like Canadian LNG.
What is often left out of the broader energy conversation is the staggering environmental cost of the war itself. According to the Initiative on GHG Accounting of War, the war in Ukraine has produced over 230 million tonnes of CO₂ equivalent (MtCO₂e) since 2022—a volume comparable to the combined annual emissions of Austria, Hungary, the Czech Republic, and Slovakia. These emissions come from military operations, destruction of infrastructure, fires, and the energy used to rebuild and support displaced populations. Yet these emissions are largely absent from official climate accounting, exposing a major blind spot in how we track and mitigate global emissions.
This is not just about dollars and molecules. This is about vision. Canada has an opportunity to offer democratic, transparent, and lower-emission energy to a world in flux. Canadian LNG can displace coal in Asia, reduce reliance on authoritarian suppliers in Europe, and provide real returns to our provinces and Indigenous communities. There is also growing potential for strategic energy cooperation between Canada, Poland, and Ukraine—linking Canadian LNG supply with European infrastructure and Ukrainian resilience, creating a transatlantic corridor for secure and democratic energy flows.
Moreover, LNG presents Canada with a concrete path to diversify its trade relationships, reducing overdependence on the U.S. market by opening new, high-value markets in Europe and Asia. This kind of energy diplomacy would not only strengthen Canada’s strategic position globally but also generate fiscal capacity to invest in national priorities—including increased defense spending to meet our NATO commitments.
Let’s be clear: LNG is not the endgame. Significant resources are being dedicated to building out nuclear capacity—particularly through Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)—alongside the rapid expansion of renewables and energy storage. But in the near term, LNG remains a vital bridge, especially when it’s sourced from a country committed to environmental responsibility, human rights, and the rule of law.
We are standing at the edge of a global shift. If we don’t step up, others will step in. The infrastructure gap is closing—but not in our favor.
Canada holds the key. The world is knocking. It’s time we opened the door.

Sources:
- Natural Gas Prices by Region (March 28, 2025): Reuters
- European LNG Import Capacity Additions: European Commission
- German Seizure of Russian Shadow Fleet Tanker: Reuters
- War Emissions Estimate (230 MtCO₂e): Planetary Security Initiative
Energy
Trump Takes More Action To Get Government Out Of LNG’s Way


From the Daily Caller News Foundation
By David Blackmon
The Trump administration moved this week to eliminate another Biden-era artificial roadblock to energy infrastructure development which is both unneeded and counterproductive to U.S. energy security.
In April 2023, Biden’s Department of Energy, under the hyper-politicized leadership of Secretary Jennifer Granholm, implemented a new policy requiring LNG projects to begin exports within seven years of receiving federal approval. Granholm somewhat hilariously claimed the policy was aimed at ensuring timely development and aligning with climate goals by preventing indefinite delays in energy projects that could impact emissions targets.
This claim was rendered incredibly specious just 8 months later, when Granholm aligned with then-President Joe Biden’s “pause” in permitting for new LNG projects due to absurd fears such exports might actually create higher emissions than coal-fired power plants. The draft study that served as the basis for the pause was thoroughly debunked within a few months, yet Granholm and the White House steadfastly maintained their ruse for a full year until Donald Trump took office on Jan. 20 and reversed Biden’s order.
Certainly, any company involved in the development of a major LNG export project wants to proceed to first cargoes as expeditiously as possible. After all, the sooner a project starts generating revenues, the more rapid the payout becomes, and the higher the returns on investments. That’s the whole goal of entering this high-growth industry. Just as obviously, unforeseen delays in the development process can lead to big cost overruns that are the bane of any major infrastructure project.
On the other hand, these are highly complex, capital-intensive projects that are subject to all sorts of delay factors. As developers experienced in recent years, disruptions in supply chains caused by factors related to the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in major delays and cost overruns in projects in every facet of the economy.
Developers in the LNG industry have argued that this arbitrary timeline was too restrictive, citing these and other factors that can extend beyond seven years. Trump, responding to these concerns and his campaign promises to bolster American energy dominance, moved swiftly to eliminate this requirement. On Tuesday, Reuters reported that the U.S. was set to rescind this policy, freeing LNG projects from the rigid timeline and potentially accelerating their completion.
This policy reversal could signal a broader approach to infrastructure under Trump. The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, enacted in 2021, allocated $1.2 trillion to rebuild roads, bridges, broadband and other critical systems, with funds intended to be awarded over five years, though some projects naturally extend beyond that due to construction timelines. The seven-year LNG deadline was a specific energy-related constraint, but Trump’s administration has shown a willingness to pause or redirect Biden-era infrastructure funding more generally. For instance, Trump’s Jan.20 executive order, “Unleashing American Energy,” directed agencies to halt disbursements under the IIJA and IRA pending a 90-day review, raising questions about whether similar time-bound restrictions across infrastructure sectors might also be loosened or eliminated.
Critics argue that scrapping deadlines risks stalling projects indefinitely, undermining the urgency Biden sought to instill in modernizing U.S. infrastructure. Supporters argue that developers already have every profit-motivated incentive to proceed as rapidly as possible and see the elimination of this restriction as a pragmatic adjustment, allowing flexibility for states and private entities to navigate permitting, labor shortages and supply chain issues—challenges that have persisted into 2025.
For example, the $294 billion in unawarded IIJA funds, including $87.2 billion in competitive grants, now fall under Trump’s purview, and his more energy-focused administration could prioritize projects aligned with his energy and economic goals over Biden’s climate and DEI-focused initiatives.
Ultimately, Trump’s decision to end the seven-year LNG deadline exemplifies his intent to reshape infrastructure policy by prioritizing speed, flexibility and industry needs. Whether this extends formally to all U.S. infrastructure projects remains unclear, but seems likely given the Trump White House’s stated objectives and priorities.
This move also clearly aligns with the overall Trump philosophy of getting the government out of the way, allowing the markets to work and freeing the business community to restore American Energy Dominance in the most expeditious way possible.
David Blackmon is an energy writer and consultant based in Texas. He spent 40 years in the oil and gas business, where he specialized in public policy and communications.
-
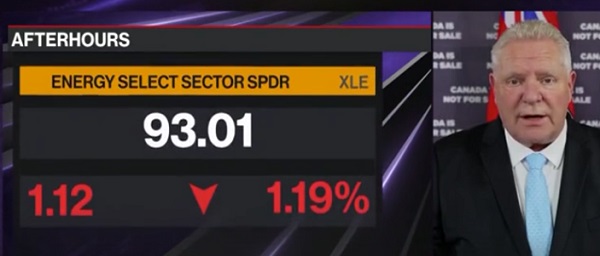
 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days ago‘I’m Cautiously Optimistic’: Doug Ford Strongly Recommends Canada ‘Not To Retaliate’ Against Trump’s Tariffs
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoBig win for Alberta and Canada: Statement from Premier Smith
-

 Catherine Herridge2 days ago
Catherine Herridge2 days agoFBI imposed Hunter Biden laptop ‘gag order’ after employee accidentally confirmed authenticity: report
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoCanada may escape the worst as Trump declares America’s economic independence with Liberation Day tariffs
-

 Canadian Energy Centre1 day ago
Canadian Energy Centre1 day agoSaskatchewan Indigenous leaders urging need for access to natural gas
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoB.C. Credit Downgrade Signals Deepening Fiscal Trouble
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoHighly touted policies the Liberal government didn’t actually implement
-
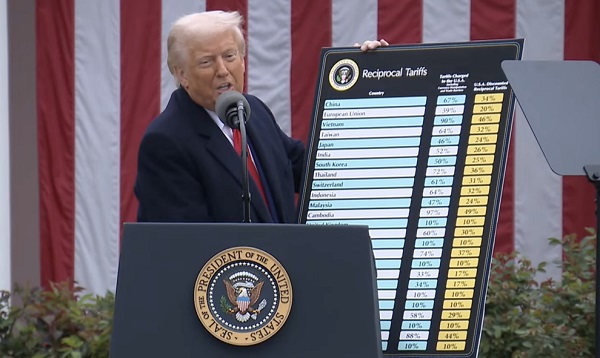
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump orders 10% baseline tariff on imports, closes de minimis loophole





