Addictions
Canada’s ‘safer supply’ patients are receiving staggering amounts of narcotics

Image courtesy of Midjourney.
|
|
How a Small Population Fuels a Black Market Epidemic, Echoing Troubling Parallels in Sweden
A significant amount of safer supply opioids are obviously being diverted to the black market, but some influential voices are vehemently downplaying this problem. They often claim that there are simply too few safer supply clients for diversion to be a real issue – but this argument is misleading because it glosses over the fact that these clients receive truly staggering amounts of narcotics relative to everyone else.
“Safer supply” refers to the practice of prescribing free recreational drugs as an alternative to potentially-tainted street substances. In Canada, that typically means distributing eight-mg tablets of hydromorphone, an opioid as potent as heroin, to mitigate the use of illicit fentanyl.
There is clear evidence that most safer supply clients regularly sell or trade almost all of their hydromorphone tablets for stronger illicit substances, and that this is flooding communities with the drug and fuelling new addictions and relapses. Just five years ago, the street price of an eight-mg hydromorphone tablet was around $20 in major Canadian cities – now they often go for as little as $1.
But advocates repeatedly emphasize that, even if such diversion is occurring, it must be a minor issue because there are only a few thousand safer supply clients in Canada. They believe that it is simply impossible for such a small population to have a meaningful impact on the overall black market for diverted pharmaceuticals, and that the sudden collapse of hydromorphone prices must have been caused by other factors.
This is an earnest belief – but an extremely ill-informed one.
It is difficult to analyze safer supply at the national level, as each province publishes different drug statistics that make interprovincial comparisons near-impossible. So, for the sake of clarity, let’s focus primarily on B.C., where the debate over safer supply has raged hottest.
According to a dashboard published by the British Columbia Centre for Disease Control, there were only 4,450 safer supply clients in the province in December 2023, of which 4,250 received opioids. In contrast, the 2018/19 British Columbia Controlled Prescription Drug Atlas (more recent data is unavailable) states that there were approximately 80,000 hydromorphone patients in the province that year – a number that is unlikely to have decreased significantly since then.
We can thus reasonably assume that safer supply clients represent around 5 per cent of the province’s total hydromorphone patients – but if so few people are on safer supply, how could they have a profound impact on the black market? The answer is simple: these clients receive astonishing sums of the drug, and divert at an unparalleled level, compared to everyone else.
Safer supply clients generally receive 4-8 eight-mg tablets per day at first, but almost all of them are quickly moved up to higher doses. In B.C., most patients are kept at 14 tablets (112-mg in total) per day, which is the maximum allowed by the province’s guidelines. For comparison, patients in Ontario can receive as many as 30 tablets a day (240-mg in total).
These are huge amounts.
The typical hydromorphone dose used to treat post-surgery pain in hospital settings is two-mg every 4-6 hours – or roughly 12-mg per day. So that means that safer supply clients can receive roughly 10-20 times the daily dose given to acute pain patients, depending on which province they’re located in. And while acute pain patients are tapered off hydromorphone after a few weeks, safer supply clients receive their tablets indefinitely.
Some chronic pain patients (i.e. people struggling with severe arthritis) are also prescribed hydromorphone – but, in most cases, their daily dose is 12-mg or less. The exception here is terminally ill cancer patients, who may receive up to around 100-mg of hydromorphone per day. However, this population is relatively small, so we once again have a situation where safer supply patients are, for the most part, receiving much more hydromorphone than their peers.
Not only do safer supply patients receive incredible amounts of the drug, they also seem to divert it at much higher rates – which is a frequently overlooked factor.
The clandestine nature of prescription drug diversion makes it near-impossible to measure, but a 2017 peer-reviewed study estimated that, in the United States, up to 3 per cent of all prescription opioids end up on the black market.
In contrast, it appears that safer supply patients divert 80-90 per cent of their hydromorphone.
These numbers should be taken with a grain of salt, as there have been no attempts to measure safer supply diversion – harm reduction researchers tend to simply ignore the problem, which means that we must rely on journalistic evidence that is necessarily anecdotal in nature. While this evidence has its limits, it can, at the very least, illustrate the rough scale of the problem.
For example, in London, Ontario, I interviewed six former drug users last summer who said that, of the safer supply clients they knew, 80 per cent sold almost all of their hydromorphone – just one interviewee placed the number closer to 50 per cent. More recently, I interviewed an addiction outreach worker in Ottawa who estimated that 90 per cent of safer supply clients diverted their drugs. These numbers are consistent with the testimony of dozens of addiction physicians who have said that safer supply diversion is ubiquitous.
Let us take a conservative estimate and imagine that only 30 per cent of safer supply hydromorphone is diverted – even this would be potentially catastrophic.
So we can see why any serious attempt to discuss safer supply diversion cannot narrowly focus on patient numbers – to ignore differences in doses and diversion rates is inexcusably misleading.
But we don’t need to rely on theory to make this point, because the recent parliamentary testimony of Fiona Wilson, who is deputy chief of the Vancouver Police Department and president of the B.C. Association of Chiefs of Police (BCACP), illustrates the situation quite neatly.
Wilson testified to the House of Commons health committee earlier this month that half of the hydromorphone recently seized in B.C. can be attributed to safer supply. As she did not specify whether the other half was attributed to other sources, or simply of indeterminate origin, the actual rate of safer supply hydromorphone seizures may actually be even higher.
As, once again, safer supply clients constitute roughly 5 per cent of the total hydromorphone patient population, Wilson’s testimony suggests that, on a per capita basis, safer supply patients divert at least 18 times more of the drug than everyone else.
This is exactly what one would expect to find given our earlier analysis, and these facts, by themselves, repudiate the argument that safer supply diversion is insignificant. When a small population is at least doubling the street supply of a dangerous pharmaceutical opioid, this is a problem.
The fact that so few people can cause substantial, system-wide harm is not unprecedented. In fact, this exact same problem was observed in Sweden, which, from 1965-1967, experimented with a model of safer supply that closely resembled what is being done in Canada today. A small number of patients – barely more than a hundred – were given near-unlimited access to free recreational drugs under the assumption that this would keep them “safe.”
But these patients simply sold the bulk of their drugs, which caused addiction and crime rates to skyrocket across Stockholm. Commentators at the time referred to safer supply as “the worst scandal in Swedish medical history,” and, even today, the experiment remains a cautionary tale among the country’s drug researchers.
It is simply wrong to say that there are too few safer supply clients to cause a diversion crisis. People who make this claim are ignorant of contemporary and historical facts, and those who wish to position themselves as drug experts should be mindful of this, lest they mislead the public about a destructive drug crisis.
This article was originally published in The Bureau, a Canadian publication devoted to using investigative journalism to tackle corruption and foreign influence campaigns. You can find this article on their website here.
Addictions
There’s No Such Thing as a “Safer Supply” of Drugs

By Adam Zivo
Sweden, the U.K., and Canada all experimented with providing opioids to addicts. The results were disastrous.
[This article was originally published in City Journal, a public policy magazine and website published by the Manhattan Institute for Policy Research. We encourage our readers to subscribe to them for high-quality analysis on urban issues]
Last August, Denver’s city council passed a proclamation endorsing radical “harm reduction” strategies to address the drug crisis. Among these was “safer supply,” the idea that the government should give drug users their drug of choice, for free. Safer supply is a popular idea among drug-reform activists. But other countries have already tested this experiment and seen disastrous results, including more addiction, crime, and overdose deaths. It would be foolish to follow their example.
The safer-supply movement maintains that drug-related overdoses, infections, and deaths are driven by the unpredictability of the black market, where drugs are inconsistently dosed and often adulterated with other toxic substances. With ultra-potent opioids like fentanyl, even minor dosing errors can prove fatal. Drug contaminants, which dealers use to provide a stronger high at a lower cost, can be just as deadly and potentially disfiguring.
Because of this, harm-reduction activists sometimes argue that governments should provide a free supply of unadulterated, “safe” drugs to get users to abandon the dangerous street supply. Or they say that such drugs should be sold in a controlled manner, like alcohol or cannabis—an endorsement of partial or total drug legalization.
But “safe” is a relative term: the drugs championed by these activists include pharmaceutical-grade fentanyl, hydromorphone (an opioid as potent as heroin), and prescription meth. Though less risky than their illicit alternatives, these drugs are still profoundly dangerous.
The theory behind safer supply is not entirely unreasonable, but in every country that has tried it, implementation has led to increased suffering and addiction. In Europe, only Sweden and the U.K. have tested safer supply, both in the 1960s. The Swedish model gave more than 100 addicts nearly unlimited access through their doctors to prescriptions for morphine and amphetamines, with no expectations of supervised consumption. Recipients mostly sold their free drugs on the black market, often through a network of “satellite patients” (addicts who purchased prescribed drugs). This led to an explosion of addiction and public disorder.
Most doctors quickly abandoned the experiment, and it was shut down after just two years and several high-profile overdose deaths, including that of a 17-year-old girl. Media coverage portrayed safer supply as a generational medical scandal and noted that the British, after experiencing similar problems, also abandoned their experiment.
While the U.S. has never formally adopted a safer-supply policy, it experienced something functionally similar during the OxyContin crisis of the 2000s. At the time, access to the powerful opioid was virtually unrestricted in many parts of North America. Addicts turned to pharmacies for an easy fix and often sold or traded their extra pills for a quick buck. Unscrupulous “pill mills” handed out prescriptions like candy, flooding communities with OxyContin and similar narcotics. The result was a devastating opioid epidemic—one that rages to this day, at a cumulative cost of hundreds of thousands of American lives. Canada was similarly affected.
The OxyContin crisis explains why many experienced addiction experts were aghast when Canada greatly expanded access to safer supply in 2020, following a four-year pilot project. They worried that the mistakes of the recent past were being made all over again, and that the recently vanquished pill mills had returned under the cloak of “harm reduction.”
Subscribe for free to get BTN’s latest news and analysis – or donate to our investigative journalism fund.
Most Canadian safer-supply prescribers dispense large quantities of hydromorphone with little to no supervised consumption. Patients can receive up to 40 eight-milligram pills per day—despite the fact that just two or three are enough to cause an overdose in someone without opioid tolerance. Some prescribers also provide supplementary fentanyl, oxycodone, or stimulants.
Unfortunately, many safer-supply patients sell or trade a significant portion of these drugs—primarily hydromorphone—in order to purchase more potent illicit substances, such as street fentanyl.
The problems with safer supply entered Canada’s consciousness in mid-2023, through an investigative report I wrote for the National Post. I interviewed 14 addiction physicians from across the country, who testified that safer-supply diversion is ubiquitous; that the street price of hydromorphone collapsed by up to 95 percent in communities where safer supply is available; that youth are consuming and becoming addicted to diverted safer-supply drugs; and that organized crime traffics these drugs.
Facing pushback, I interviewed former drug users, who estimated that roughly 80 percent of the safer-supply drugs flowing through their social circles was getting diverted. I documented dozens of examples of safer-supply trafficking online, representing tens of thousands of pills. I spoke with youth who had developed addictions from diverted safer supply and adults who had purchased thousands of such pills.
After months of public queries, the police department of London, Ontario—where safer supply was first piloted—revealed last summer that annual hydromorphone seizures rose over 3,000 percent between 2019 and 2023. The department later held a press conference warning that gangs clearly traffic safer supply. The police departments of two nearby midsize cities also saw their post-2019 hydromorphone seizures increase more than 1,000 percent.
The Canadian government quietly dropped its support for safer supply last year, cutting funding for many of its pilot programs. The province of British Columbia (the nexus of the harm-reduction movement) finally pulled back support last month, after a leaked presentation confirmed that safer-supply drugs are getting sold internationally and that the government is investigating 60 pharmacies for paying kickbacks to safer-supply patients. For now, all safer-supply drugs dispensed within the province must be consumed under supervision.
Harm-reduction activists have insisted that no hard evidence exists of widespread diversion of safer-supply drugs, but this is only because they refuse to study the issue. Most “studies” supporting safer supply are produced by ideologically driven activist-scholars, who tend to interview a small number of program enrollees. These activists also reject attempts to track diversion as “stigmatizing.”
The experiences of Sweden, the United Kingdom, and Canada offer a clear warning: safer supply is a reliably harmful policy. The outcomes speak for themselves—rising addiction, diversion, and little evidence of long-term benefit.
As the debate unfolds in the United States, policymakers would do well to learn from these failures. Americans should not be made to endure the consequences of a policy already discredited abroad simply because progressive leaders choose to ignore the record. The question now is whether we will repeat others’ mistakes—or chart a more responsible course.
Our content is always free –
but if you want to help us commission more high-quality journalism,
consider getting a voluntary paid subscription.
Addictions
Should fentanyl dealers face manslaughter charges for fatal overdoses?
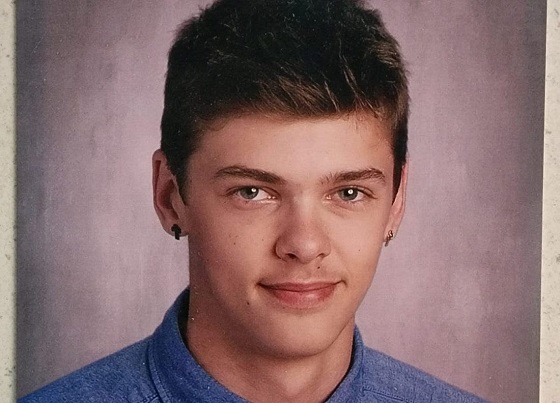

Tyler Ginn prior to his death from a fentanyl overdose in 2021. [Photo credit: Gayle Fowlie]
By Alexandra Keeler
Police are charging more drug dealers with manslaughter in fentanyl overdose deaths. But the shift is not satisfying everyone
Four years ago, Tyler Ginn died of a fentanyl overdose at the age of 18. Tyler’s father found his son unresponsive in the bedroom of their Brooklin, Ont., home.
For Tyler’s mother, Gayle Fowlie, the pain of his loss remains raw.
“He was my kid that rode his bike to the store to buy me a chocolate bar on my birthday, you know?” she told Canadian Affairs in an interview.
Police charged Jacob Norn, the drug dealer who sold Tyler his final, fatal dose, with manslaughter. More than three years after Tyler’s death, Norn was convicted and sentenced to six years in prison.
“I don’t think you can grasp how difficult going through a trial is,” Fowlie said. “On TV, it’s a less than an hour process. But the pain of it, and going over every detail and then going over every detail again … it provides details you wish you didn’t know.”
But Fowlie is glad Norn was convicted. If anything, she would have liked him to serve a longer sentence. Lawyers have told her Norn is likely to serve only two to four years of his sentence in prison.
“My son’s never coming back [and] his whole family has a life sentence of missing him the rest of our lives,” she said. “So do I think four years is fair? No.”
Norn’s case reflects a growing trend of drug dealers being charged with manslaughter when their drug sales lead to fatal overdoses.
But this shift has not satisfied everyone. Some would like to see drug dealers face harsher or different penalties.
“If we say that it was 50 per cent Tyler’s fault for buying it and 50 per cent Jacob’s fault for selling it … then I think he should have a half-a-life sentence,” said Fowlie.
Others say the legal system’s focus on prosecuting low-level drug dealers misses the broader issues at play.
“[Police] decided, in the Jacob Norn case, they were going to go one stage back,” said Peter Thorning, who was Norn’s defence lawyer.
“What about the person who gave Jacob that substance? What about the person who supplied the substance to [that person]? There was no investigation into where it came from and who was ultimately responsible for the death of that young man.”
Manslaughter charge
At least 50,000 Canadians have died from drug overdoses since 2016. Last year, an average of 21 individuals died each day, with fentanyl accounting for nearly 80 per cent of those deaths.
Fentanyl, a synthetic opioid, is up to 50 times stronger than heroin and 100 times stronger than morphine. A dose as small as a few grains of salt can be lethal.
Given its potency, police and prosecutors have increasingly turned to manslaughter charges when a dealer’s product results in a fatal overdose.
A recent study in the Canadian Journal of Law and Society found that the number of manslaughter charges laid for drug-related deaths in Canada surged from three cases in 2016 to 135 in 2021.
Individuals can be convicted of manslaughter for committing unlawful, reckless or negligent acts that result in death but where there was no intention to kill. Sentences can range from probation (in rare cases) to life.
Murder charges, by contrast, require an intent to kill or cause fatal harm. Drug dealers typically face manslaughter charges in overdose cases, as their intent is to distribute drugs, not to kill those who purchase them.
Joanne Bortoluss, a spokesperson for the Durham Regional Police, which charged Norn, said that each of their investigations follows the same fundamental process.
“Investigators consider the strength of the evidence, the dealer’s level of involvement, and applicable laws when determining whether to pursue charges like manslaughter,” she said.
The Canadian Journal of Law and Society study also found that prosecutions often target low-level dealers, many of whom are drug users themselves and have personal connections to the deceased.
Norn’s case fits this pattern. He struggled with substance abuse, including addiction to fentanyl, Xanax and Percocet. Tyler and Norn were friends, the judge said in the court ruling, although Fowlie disputes this claim.
“[Those words] are repulsive to me,” she said.
The Crown argued Norn demonstrated “a high degree of moral blameworthiness” by warning Ginn of the fentanyl’s potency while still selling it to him. In a call to Ginn, he warned him “not to do a lot of the stuff” because he “didn’t want to be responsible for anything that happened.”
Fowlie’s outrage over Norn’s lenient sentencing is compounded by the fact that Norn was found trafficking fentanyl again after her son’s death.
“So we’ve killed somebody, and we’re still … trafficking? We’re not worried who else we kill?” Fowlie said.

Trafficking
Some legal sources noted that manslaughter charges do not necessarily lead to harsh sentences or deterrence.
“If you look at how diverse and … lenient some sentences are for manslaughter, I don’t think it really pushes things in the direction that [victims’ families] want,” said Kevin Westell, a Vancouver-based trial lawyer and former chair of the Canadian Bar Association.
Westell noted that the term “manslaughter” is misleading. “Manslaughter is a brutal-sounding title, but it encapsulates a very broad span of criminal offences,” he said.
In Westell’s view, consistently charging dealers with drug trafficking could be more effective for deterring the practice.
“What really matters is how long the sentence is, and you’re better off saying, ‘We know fentanyl is dangerous, so we’re setting the sentence quite high,’ rather than making it harder to prove with a manslaughter charge,” he said.
Trafficking is a distinct charge from manslaughter that involves the distribution, sale or delivery of illicit drugs. The sentencing range for fentanyl trafficking is eight to 15 years, Kwame Bonsu, a media relations representative for the Department of Justice, told Canadian Affairs.
“Courts must impose sentences that are proportionate to the gravity of the offence and the degree of responsibility of the offender,” Bonsu said, referencing a 2021 Supreme Court of Canada decision. Bonsu noted that aggravating factors such as lack of remorse or trafficking large quantities can lead to harsher sentences.
‘Head of the snake’
Some legal experts noted the justice system often fails to target those higher up in the drug supply chain.
“We don’t know how many hands that drug goes through,” said Thorning, the defence lawyer.
“Are the police going to prosecute every single person who provides fentanyl to another person? Jacob [Norn] was himself an addict trafficker — what about the person who supplied the substance to him?”
Thorning also questioned whether government agencies bear some responsibility. “Is some government agency’s failure to investigate how that drug came into the country partly responsible for the young man’s death?”
Westell, who has served as both a Crown prosecutor and criminal defence lawyer, acknowledged the difficulty of targeting higher-level traffickers.
“Cutting off the head of the snake does not align very well with the limitations of the international borders,” he said.
“Yes, there are transnational justice measures, but a lot gets lost, and as soon as you cross an international border of any kind, it becomes incredibly difficult to follow the chain in a linear way.”
Bortoluss, of the Durham police, said even prosecuting what appear to be obvious fentanyl-related deaths — such as Tyler Ginn’s — can be challenging. Witnesses can be reluctant to cooperate, fearing legal consequences. It can also be difficult to identify the source of drugs, as “transactions often involve multiple intermediaries and anonymous online sales.”
Another challenge in deterring fentanyl trafficking is the strong financial incentives of the trade.
“Even if [Norn] serves two to four years for killing somebody, but he could make a hundred thousand off of selling drugs, is it worth it?” Fowlie said.
Thorning agreed that the profit incentive can be incredibly powerful, outweighing the risk of a potential sentence.
“The more risky you make the behaviour, the greater the profit for a person who’s willing to break our laws, and the profit is the thing that generates the conduct,” he said.
A blunt instrument
Legal experts also noted the criminal justice system alone cannot solve the fentanyl crisis.
“Most people who have [lost] a loved one [to drug overdose] want to see a direct consequence to the person that’s responsible,” said Westell. “But I think they would also like to see something on a more macro level that helps eliminate the problem more holistically, and that can’t be [achieved through] crime and punishment alone.”
Thorning agrees.
“These are mental health .. [and] medical issues,” he said. “Criminal law is a blunt instrument [that is] not going to deal with these things effectively.”
Even Fowlie sees the problem as bigger than sentencing. Her son struggled with the stigma associated with therapy and medication, which made it difficult for him to seek help.
“We need to normalize seeing a therapist, like we normalize getting your eyes checked every year,” she said.
“Pot isn’t the gateway drug, trauma is a gateway drug.”
This article was produced through the Breaking Needles Fellowship Program, which provided a grant to Canadian Affairs, a digital media outlet, to fund journalism exploring addiction and crime in Canada. Articles produced through the Fellowship are co-published by Break The Needle and Canadian Affairs.
Subscribe to Break The Needle – or donate to our investigative journalism fund.
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days ago28 energy leaders call for eliminating ALL energy subsidies—even ones they benefit from
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoCarney’s Cap on Alberta Energy Costing Canada Billions
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump Tariffs are not going away. Canada needs to adapt or face the consequences
-

 Economy1 day ago
Economy1 day agoSupport For National Pipelines And LNG Projects Gain Momentum, Even In Quebec
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoDr. Pierre Kory Exposes the Truth About the Texas ‘Measles Death’ Hoax
-
 Business19 hours ago
Business19 hours agoDOGE discovered $330M in Small Business loans awarded to children under 11
-
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoWhy a domestic economy upgrade trumps diversification
-

 COVID-1917 hours ago
COVID-1917 hours ago17-year-old died after taking COVID shot, but Ontario judge denies his family’s liability claim



