Alberta
NATO reps say U.S., Canada oil and gas critical for energy security

Outside NATO headquarters ahead of a flag-raising ceremony for Sweden’s accession to NATO, in Brussels on February 27, 2024. Getty Images photo
From the Canadian Energy Centre
‘The traditional energy system will not disappear in a day’
Canada and the United States now produce more oil and gas than anywhere else on Earth, including the Middle East, according to a new report by S&P Global.
This blanket of energy security extends beyond borders and is “a powerful card to play” in increasingly unstable times, researchers wrote.
They found that without oil and gas produced in the U.S. and Canada – which has more than doubled since 2008 – North America, Europe and the rest of the world would have been “notably more vulnerable” following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022.
The ‘massive social impact’ of energy insecurity
Energy insecurity is all too familiar for Lithuanian Juljius Grubliauskas, who works for the North Atlantic Treaty Alliance (NATO).
Growing up, he was on hand when the Soviet Union weaponized energy in an attempt to topple Lithuania’s fledgling independence.
“I remember clearly from my childhood in 1990 when the Russians cut off energy supplies to try to break the resolve of the Lithuanians, [and] that affected the daily lives of every citizen,” Grubliauskas told a recent webinar hosted by the Toronto-based Institute for Peace and Diplomacy.
“Having a lack of energy has a massive social impact and massive cascading effects like prices immediately jumping, massive inflation and such,” he said.
“Today obviously many things have changed and the energy landscape looks much different, but the principle that energy is closely linked to national security and the independence of nations to make their decisions still remains true.”
North America’s role in NATO energy supply
Formed following the second world war, NATO represents 31 nations in Europe and North America in shared collective defense where an attack on one is seen as an attack on all.
NATO is finalizing a strategic plan for its energy future as the world seeks to reduce emissions, focusing primarily on secure access for military forces, Grubliauskas said.
Oil and gas from North America play a critical role, said Brussels-based NATO energy security policy expert Can Ögütcü.
“We need to be sure that we’re going to have security of supply of production in the U.S. and in Canada,” he said.
“We have last one import supplier, the Russians, [and] we are in the transition to perhaps also lose another big supplier, the Middle East Gulf countries, as maritime routes become more and more insecure.”
Critical North American energy integration
While Canadian oil and gas exports currently go almost exclusively to the U.S., once they enter the integrated pipeline system, they can become so-called “re-exports” from U.S. Gulf Coast to overseas markets.
At the end last year, the U.S. imported more oil from Canada than ever before, according to the U.S. Energy Information.
At the same time, America exported a record 11.5 million barrels per day of oil and petroleum products, and a record 709 billion cubic feet of natural gas.
“North American energy integration, things like the Enbridge Line 3 pipeline and the Keystone pipeline are absolutely crucial pieces of infrastructure, not just for the energy security of North America but also increasingly for the energy security of NATO allies,” said Joseph Calnan, energy security analyst with the Canadian Global Affairs Institute.
“The traditional energy system will not disappear in a day. Climate change of course makes it imperative that we do reduce our emissions globally but the role of Canada in the short term and medium term, I believe, is to firm up this traditional energy system.
“While Canada has a major role to play in future energy technologies, the current energy technologies are in my opinion, the priority.”
Canada can do more
Canada has not done enough to improve world energy security, said Heather Exner-Pirot, a senior fellow with the Macdonald-Laurier Institute.
“In the wake of Russia’s invasion, Canada has not stepped up and there is risk on all sides from depending too much on OPEC, or Qatar or Russia, but also too much on the United States,” she said, referencing the U.S. decision to pause approvals of new liquefied natural gas (LNG) export projects.
“We can do much more shipping on the East Coast. There are projects that were in the pipeline that have been rejected by the federal government and by provincial governments that could be going to Europe. Obviously on the West Coast is more promising.”
Major projects slated to start up soon like the Trans Mountain expansion and LNG Canada terminal will grow global access to Canadian oil and gas, primarily in the Indo Pacific region, Calnan noted.
“I think we’ll see that Canada has a much larger role to play in the total global market, which will have a stepwise influence on the situation in Europe,” he said.
Alberta
Ottawa-Alberta agreement may produce oligopoly in the oilsands

From the Fraser Institute
By Jason Clemens and Elmira Aliakbari
The federal and Alberta governments recently jointly released the details of a memorandum of understanding (MOU), which lays the groundwork for potentially significant energy infrastructure including an oil pipeline from Alberta to the west coast that would provide access to Asia and other international markets. While an improvement on the status quo, the MOU’s ambiguity risks creating an oligopoly.
An oligopoly is basically a monopoly but with multiple firms instead of a single firm. It’s a market with limited competition where a few firms dominate the entire market, and it’s something economists and policymakers worry about because it results in higher prices, less innovation, lower investment and/or less quality. Indeed, the federal government has an entire agency charged with worrying about limits to competition.
There are a number of aspects of the MOU where it’s not sufficiently clear what Ottawa and Alberta are agreeing to, so it’s easy to envision a situation where a few large firms come to dominate the oilsands.
Consider the clear connection in the MOU between the development and progress of Pathways, which is a large-scale carbon capture project, and the development of a bitumen pipeline to the west coast. The MOU explicitly links increased production of both oil and gas (“while simultaneously reaching carbon neutrality”) with projects such as Pathways. Currently, Pathways involves five of Canada’s largest oilsands producers: Canadian Natural, Cenovus, ConocoPhillips Canada, Imperial and Suncor.
What’s not clear is whether only these firms, or perhaps companies linked with Pathways in the future, will have access to the new pipeline. Similarly, only the firms with access to the new west coast pipeline would have access to the new proposed deep-water port, allowing access to Asian markets and likely higher prices for exports. Ottawa went so far as to open the door to “appropriate adjustment(s)” to the oil tanker ban (C-48), which prevents oil tankers from docking at Canadian ports on the west coast.
One of the many challenges with an oligopoly is that it prevents new entrants and entrepreneurs from challenging the existing firms with new technologies, new approaches and new techniques. This entrepreneurial process, rooted in innovation, is at the core of our economic growth and progress over time. The MOU, though not designed to do this, could prevent such startups from challenging the existing big players because they could face a litany of restrictive anti-development regulations introduced during the Trudeau era that have not been reformed or changed since the new Carney government took office.
And this is not to criticize or blame the companies involved in Pathways. They’re acting in the interests of their customers, staff, investors and local communities by finding a way to expand their production and sales. The fault lies with governments that were not sufficiently clear in the MOU on issues such as access to the new pipeline.
And it’s also worth noting that all of this is predicated on an assumption that Alberta can achieve the many conditions included in the MOU, some of which are fairly difficult. Indeed, the nature of the MOU’s conditions has already led some to suggest that it’s window dressing for the federal government to avoid outright denying a west coast pipeline and instead shift the blame for failure to the Smith government.
Assuming Alberta can clear the MOU’s various hurdles and achieve the development of a west coast pipeline, it will certainly benefit the province and the country more broadly to diversify the export markets for one of our most important export products. However, the agreement is far from ideal and could impose much larger-than-needed costs on the economy if it leads to an oligopoly. At the very least we should be aware of these risks as we progress.

Elmira Aliakbari
Alberta
A Christmas wish list for health-care reform

From the Fraser Institute
By Nadeem Esmail and Mackenzie Moir
It’s an exciting time in Canadian health-care policy. But even the slew of new reforms in Alberta only go part of the way to using all the policy tools employed by high performing universal health-care systems.
For 2026, for the sake of Canadian patients, let’s hope Alberta stays the path on changes to how hospitals are paid and allowing some private purchases of health care, and that other provinces start to catch up.
While Alberta’s new reforms were welcome news this year, it’s clear Canada’s health-care system continued to struggle. Canadians were reminded by our annual comparison of health care systems that they pay for one of the developed world’s most expensive universal health-care systems, yet have some of the fewest physicians and hospital beds, while waiting in some of the longest queues.
And speaking of queues, wait times across Canada for non-emergency care reached the second-highest level ever measured at 28.6 weeks from general practitioner referral to actual treatment. That’s more than triple the wait of the early 1990s despite decades of government promises and spending commitments. Other work found that at least 23,746 patients died while waiting for care, and nearly 1.3 million Canadians left our overcrowded emergency rooms without being treated.
At least one province has shown a genuine willingness to do something about these problems.
The Smith government in Alberta announced early in the year that it would move towards paying hospitals per-patient treated as opposed to a fixed annual budget, a policy approach that Quebec has been working on for years. Albertans will also soon be able purchase, at least in a limited way, some diagnostic and surgical services for themselves, which is again already possible in Quebec. Alberta has also gone a step further by allowing physicians to work in both public and private settings.
While controversial in Canada, these approaches simply mirror what is being done in all of the developed world’s top-performing universal health-care systems. Australia, the Netherlands, Germany and Switzerland all pay their hospitals per patient treated, and allow patients the opportunity to purchase care privately if they wish. They all also have better and faster universally accessible health care than Canada’s provinces provide, while spending a little more (Switzerland) or less (Australia, Germany, the Netherlands) than we do.
While these reforms are clearly a step in the right direction, there’s more to be done.
Even if we include Alberta’s reforms, these countries still do some very important things differently.
Critically, all of these countries expect patients to pay a small amount for their universally accessible services. The reasoning is straightforward: we all spend our own money more carefully than we spend someone else’s, and patients will make more informed decisions about when and where it’s best to access the health-care system when they have to pay a little out of pocket.
The evidence around this policy is clear—with appropriate safeguards to protect the very ill and exemptions for lower-income and other vulnerable populations, the demand for outpatient healthcare services falls, reducing delays and freeing up resources for others.
Charging patients even small amounts for care would of course violate the Canada Health Act, but it would also emulate the approach of 100 per cent of the developed world’s top-performing health-care systems. In this case, violating outdated federal policy means better universal health care for Canadians.
These top-performing countries also see the private sector and innovative entrepreneurs as partners in delivering universal health care. A relationship that is far different from the limited individual contracts some provinces have with private clinics and surgical centres to provide care in Canada. In these other countries, even full-service hospitals are operated by private providers. Importantly, partnering with innovative private providers, even hospitals, to deliver universal health care does not violate the Canada Health Act.
So, while Alberta has made strides this past year moving towards the well-established higher performance policy approach followed elsewhere, the Smith government remains at least a couple steps short of truly adopting a more Australian or European approach for health care. And other provinces have yet to even get to where Alberta will soon be.
Let’s hope in 2026 that Alberta keeps moving towards a truly world class universal health-care experience for patients, and that the other provinces catch up.
-

 Bruce Dowbiggin2 days ago
Bruce Dowbiggin2 days agoHunting Poilievre Covers For Upcoming Demographic Collapse After Boomers
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoState of the Canadian Economy: Number of publicly listed companies in Canada down 32.7% since 2010
-

 Censorship Industrial Complex1 day ago
Censorship Industrial Complex1 day agoCanadian university censors free speech advocate who spoke out against Indigenous ‘mass grave’ hoax
-

 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoHousing in Calgary and Edmonton remains expensive but more affordable than other cities
-

 Artificial Intelligence2 days ago
Artificial Intelligence2 days agoUK Police Pilot AI System to Track “Suspicious” Driver Journeys
-
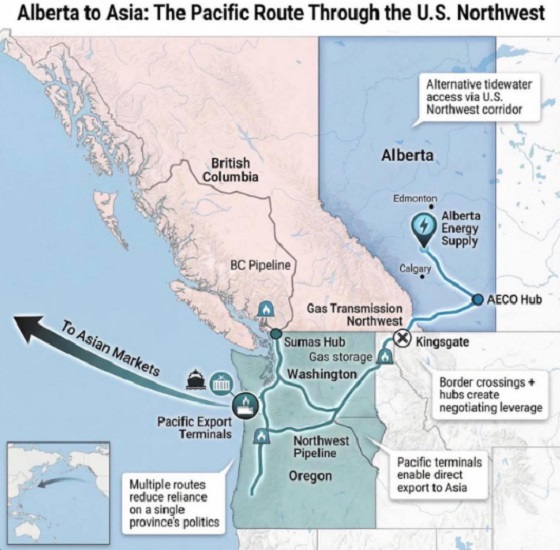
 Alberta1 day ago
Alberta1 day agoWhat are the odds of a pipeline through the American Pacific Northwest?
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoWarning Canada: China’s Economic Miracle Was Built on Mass Displacement
-

 Agriculture2 days ago
Agriculture2 days agoThe Climate Argument Against Livestock Doesn’t Add Up







