National
Online Harms Act threatens free expression in Canada

News release from the Justice Centre for Constitutional Freedoms
This repudiates centuries of legal tradition that rightly reserved punishment for what a person had done, not for what a person might do. Under this new provision, a complainant can assert to a provincial court that they “fear” that someone will promote genocide, hate or antisemitism.
On February 26, Minister of Justice and Attorney General of Canada Arif Virani introduced Bill C-63, the Online Harms Act, in the House of Commons. The Online Harms Act is presented by the government as a means to promote the online safety of persons in Canada and reduce harmful content online. The Online Harms Act would impose severe penalties for online and offline hate speech, including life imprisonment, which is the most severe criminal punishment in Canada. This new legislation would establish a new Digital Safety Commission with power to enforce new regulations created by the federal cabinet. The Canadian Human Rights Commission would acquire new powers to prosecute and punish non-criminal hate speech.
Good intentions should be applauded
Although the Online Harms Act seriously threatens free expression in Canada, there are good intentions behind some of its provisions. It is a laudable goal to force online platforms to remove revenge porn and other non-consensual sharing of intimate images, content that bullies children, content that sexually victimizes children, content that encourages children to harm themselves, and content that incites violence, terrorism or hatred.
Unnecessary duplication of the Criminal Code
However, good intentions do not justify passing additional laws that duplicate what is already prohibited by Canada’s Criminal Code. Additional laws that duplicate existing laws are a poor substitute for good law enforcement.
Section 162.1(1) of Canada’s Criminal Code already prohibits online and offline publication of an intimate image without consent. Section 163 already prohibits publication of obscene materials and child pornography. Thus, it is already illegal to post online content that sexually victimizes a child or revictimizes a survivor.
Section 264(1) already prohibits criminal harassment. Section 319(1) already prohibits the public incitement of hatred towards a group that is identifiable by race, ethnicity, religion, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and other personal characteristics. Section 59(1) criminalizes sedition: advocating the use of force to achieve governmental change within Canada. Sections 83.21 and 83.22 criminalize instructing to carry out terrorist activity; any online content that incites terrorism is already illegal.
Further, Section 22 of Canada’s Criminal Code prohibits counselling, procuring, soliciting or inciting another person “to be a party to an offence.” Any person who counsels, procures, solicits or incites another person to be a party to an offence will be found guilty if the person receiving such counsel commits the offence in question. This applies to terrorism and other violent crimes, and even to minor criminal offenses like shoplifting. Further, section 464 of the Criminal Code criminalizes counselling another person to commit an offence even if that offence is not committed.
Those who support the Online Harms Act should explain why they believe that existing legislation is inadequate to address “harmful” online expression.
New government bodies to censor online speech
If passed into law, the Online Harms Act will create a new Digital Safety Commission to enforce compliance with new regulations created by the federal cabinet. This Digital Safety Commission will have the power to regulate nearly any person or entity operating as a “social media service” in Canada. Any person or social media service found to have permitted “harmful content” would face penalties. The severity of the penalties would be established by the federal cabinet. The creators and users of online content will self-censor to avoid the risk of running afoul of the new regulations and government-imposed censorship. The Online Harms Act provides that an Order of the Digital Safety Commission may be converted into an Order of the Federal Court and enforced like a Court Order. This could result in people operating social media services being fined and imprisoned for contempt of court if they refuse to censor Canadians’ speech.
Pre-emptive punishment for crimes not committed
The Online Harms Act, if passed into law, will add section 810.012 to the Criminal Code, which will permit pre-emptive violations of personal liberty when no crime has been committed. This repudiates centuries of legal tradition that rightly reserved punishment for what a person had done, not for what a person might do. Under this new provision, a complainant can assert to a provincial court that they “fear” that someone will promote genocide, hate or antisemitism. If the judge believes that there are “reasonable grounds” to justify the fear, the court can violate the liberty interests of the accused citizen by requiring her or him to do any or all of the following:
- wear an ankle bracelet (electronic monitoring device)
- obey a curfew and stay at home, as determined by the judge
- abstain from alcohol, drugs, or both
- provide bodily substances (e.g. blood, urine) to confirm abstinence from drugs or alcohol
- not communicate with certain designated persons
- not go to certain places, as determined by the judge
- surrender her or his legally owned and legally required firearms
In other words: a citizen who has not committed any crime can be subjected to one or more (or all) of the above conditions just because someone fears that that person might commit a speech crime in future. Further, if the person who has committed no crime fails to agree to these court-ordered violations of her or his personal liberty, she or he could be sentenced to up to two years in prison.
Our criminal justice system is not supposed to function this way. Violating the liberty of citizens through pre-emptive punishment, when no crime has been committed (and quite possibly when no crime will be committed), is a radical departure from centuries of common law tradition. The respect that our legal system has for individual rights and freedoms means that an accused person is presumed innocent until proven guilty by way of a fair trial, held before an independent and impartial court. We do not punish the innocent, nor do we restrict their liberty based on what they might do. The mere fear that harmful expression may occur is not a legitimate basis for court-ordered imprisonment or other conditions that violate personal liberty.
Life imprisonment for words spoken
For the existing Criminal Code offence of advocating for genocide, the Online Harms Act would raise the maximum penalty from five years in jail to life imprisonment. Free societies recognize the distinction between speech and actions. The Online Harms Act blurs that distinction.
Considering the inherent difficulty in determining whether a person has actually “advocated for genocide,” the punishment of a five-year prison term is already an adequate deterrent for words alone.
Federal cabinet can censor speech without input from Parliament
The Online Harms Act, if passed into law, would give new powers to the federal cabinet to pass regulations (which have the same force of law as legislation passed by Parliament) that place prohibitions or obligations on social media services. This includes passing regulations that impose fines or other consequences (e.g., the removal of a licence or the shutting down of a website) for non-compliance. New regulations can be created by the federal cabinet in its sole discretion, and do not need to be debated, voted on or approved by Parliament. Parliamentary proceedings are public. Any political party, or even one single MP, can raise public awareness about a Bill that she or he disagrees with, and can mobilize public opposition to that Bill. Not so with regulations, which are deliberated in secret by the federal cabinet, and that come into force without any public consultation or debate.
Apart from a federal election held once every four years, there is no meaningful way to hold cabinet to account for the draconian censorship of social media services by way of regulations and the harsh penalties that may be imposed for hosting “harmful content.” The federal cabinet can also decide what number of “users” the “social media service” needs to have in order to trigger federal regulation of content, or the federal cabinet can simply designate a social media service as regulated, regardless of the number of its users.
New censorship powers for Canadian Human Rights Commission
The Online Harms Act, if passed into law, will give the Canadian Human Rights Commission new powers to prosecute and punish offensive but non-criminal speech by Canadians if, in the subjective opinion of unelected and unaccountable bureaucrats, they deem someone’s statement to be “hateful.” The Online Harms Act will empower Canadians offended by non-criminal expression to file complaints against their fellow citizens.
Those who are prosecuted by the Human Rights Commission cannot defend themselves by establishing that their supposedly “hateful” statement is true, or that they had reasonable grounds for believing that their statement was true.
Those found guilty by the Canadian Human Rights Tribunal can be required to pay as much as $50,000 to the government, plus up to $20,000 to the person(s) designated as “victims” by the Canadian Human Rights Tribunal. These significant financial penalties will discourage or eliminate necessary discussion on controversial but important issues in our society.
Advocates for censorship often stress the fact that human rights prosecutions are not criminal. It is true that those found guilty of violating vague speech codes by the Canadian Human Rights Tribunal do not suffer the consequences of a criminal record. However, those who are prosecuted for expressing their beliefs face the difficult choice of having to spend tens of thousands of dollars on legal bills or having to issue an abject apology. Regardless of whether they choose to defend themselves against the complaint or not, they may still be ordered to pay up to $20,000 to the offended party or up to $50,000 to the government, or up to $70,000 to both.
Many Canadians will continue to exercise their Charter-protected freedom of expression, but many will self-censor to avoid the risk of being prosecuted by the Canadian Human Rights Commission.
Anonymous complaints: no right to face one’s accuser
The Online Harms Act, if passed into law, will allow complaints to be filed against Canadians in secret, such that the citizen who is prosecuted by the Canadian Human Rights Commission loses the ancient and well-founded right to face and question one’s accuser. This repudiates centuries of common law tradition requiring the legal process to be public and transparent.
The pretext for eliminating this necessary and long-standing legal protection is that some complainants might be subjected to “threats, intimidation or discrimination.” This ignores the fact that threats and intimidation are already Criminal Code offences, and any illegal discrimination can be addressed by way of a new and separate complaint. Those filing complaints about expression should be accountable for their decision to do so; this is an inherent and necessary component of both criminal and civil legal proceedings.
No need to establish that someone was harmed
If the Online Harms Act is passed into law, the Canadian Human Rights Commission will not even require a victim in order to prosecute a citizen for what she or he has said. For example, a man in Vancouver can file an anonymous complaint against a woman in Nova Scotia who made disparaging online remarks about a mosque in Toronto, regardless of whether that mosque’s members were harmed, or even offended, by the post. No actual victims are required for the Canadian Human Rights Commission to find guilt or to impose penalties. Nor does a victim need to prove that he or she suffered loss or damage; feeling offended by alleged “hate” is all that is needed to become eligible for financial compensation.
Conclusion
For reasons set out here above, the Online Harms Act will harm freedom of expression in Canada if it is passed into law. Many Canadians will self-censor to avoid being prosecuted by the Canadian Human Rights Commission. Canadians who do not self-censor, by practicing courage and by continuing to exercise their Charter-protected freedom of expression, will still see their online expression removed from the internet by the operators of social media websites and platforms. These operators will seek to avoid running afoul of Mr. Trudeau’s new regulations. Everyone will live in fear of the Digital Safety Commission.
The Justice Centre urges all Members of Parliament to vote against this legislation.
2025 Federal Election
Election Security Briefing Confirms CCP-Linked Operation Boosted Carney


 Dan Knight
Dan Knight
While Beijing boosts Mark Carney on WeChat, federal officials downplay foreign interference, dodge accountability, and protect the very narrative propped up by the CCP.
As Canadians prepare to head to the polls on April 28, 2025, the federal government is working overtime to project an image of preparedness in the face of growing foreign interference, digital disinformation, and mounting public skepticism.
This week’s National Election Security Briefing—one in a series leading up to the vote—was framed as a gesture of transparency and reassurance. Led by Lauren Kempton, the session brought together senior bureaucrats from Canada’s intelligence, cybersecurity, and diplomatic corps. Among them: Allan Sutherland from the Privy Council Office, Vanessa Lloyd of the SITE Task Force, Bridget Walsh from the Canadian Centre for Cyber Security, and Larissa Galarza from Global Affairs.
They were joined virtually by officials from the RCMP, CSIS, and other federal agencies, forming what was presented as a united front against threats to Canada’s democratic process.
This briefing follows last week’s announcement of a new Candidate Security Program, offering private, unarmed security details to protect political candidates from intimidation. It’s a telling sign of the times—when running for office in Canada now comes with real, documented threats from foreign powers.
And if you thought foreign interference was yesterday’s problem, what came next confirmed: it’s not just back—it’s more sophisticated, more aggressive, and more deeply embedded than ever.
The WeChat Election: CCP Bots, Mark Carney, and the Digital Hijacking of Canadian Democracy
The latest federal election security briefing confirmed what many suspected but few in government are willing to say out loud: the Chinese Communist Party is actively trying to shape Canadian politics—and their current project of interest is Mark Carney.
Intelligence services revealed that a state-linked WeChat account called Youli-Youmian, tied directly to the CCP’s Central Political and Legal Affairs Commission, launched an information operation targeting Chinese-Canadian communities. The timing was not subtle. Two major spikes in activity occurred—on March 10 and again on March 25, right in the heart of the federal election campaign. The platform used was WeChat, a messaging app with over a billion users and a long record of CCP censorship, surveillance, and narrative control.
The operation focused on Mark Carney. He was the centerpiece. The content wasn’t one-sided, but it was manipulative. It praised him for being “tough” on the United States—exactly the kind of posture the CCP likes to see in Western leaders. At the same time, it seeded doubts about his experience and readiness to lead. The strategy is transparent: elevate the figure they believe will be most useful, then control the temperature of public perception around him.
The operation was not organic. Intelligence officials described it as “coordinated inauthentic behavior”—mass posting of identical headlines across outlets, bot-driven sharing, engineered engagement. This wasn’t a handful of users with strong opinions. It was algorithmic warfare.
The bureaucrats behind the briefing bent over backwards to downplay the impact. They said the campaign was “contained to one platform” and argued that Canadians have access to diverse information, so the overall electoral process remains “free and fair.” But that’s not the point. The CCP doesn’t need to control the entire media ecosystem. It only needs to shape perception where it counts—and in targeted communities, with targeted narratives, it’s clearly trying to do just that.
The Liberal Party was only briefed on the situation on April 6—after the second spike in activity. That’s weeks after the operation had already gained traction. What happened during that time? Carney’s campaign moved forward without addressing any of it. And now we know why. Whether he’s aware of it or not, the CCP sees value in propping him up—at least in the right communities, with the right messaging. If that doesn’t send alarm bells ringing, it should.
This isn’t speculation. It’s documented. It’s active. And it’s part of a larger pattern. The same interference networks have previously targeted Conservative MPs like Michael Chong, Erin O’Toole, and Kenny Chiu. They’ve gone after Chrystia Freeland too. But the recent attention to Carney marks something new—not just an attempt to tear down opponents, but to sculpt the image of a candidate who just might serve certain foreign interests, directly or indirectly.
The Chinese Communist Party doesn’t operate on party loyalty. It operates on leverage. And this operation—whether Carney asked for it or not—is a sign that Beijing believes his leadership could be shaped to their advantage.
The Canadian government can claim “no impact” all it wants. But influence isn’t always measured by votes—it’s measured by narrative, tone, and who ends up in the spotlight looking just a little more “strong” or “stable” through the right lens. Beijing’s lens.
The CCP’s Safe Bet: Mark Carney
And now, after days of playing cleanup behind a polished podium, the government rolls out a Q&A session to assure us that “nothing’s wrong,” “everything’s under control,” and that the CCP’s operation to shape the election isn’t a big deal because—get this—it only ran on one platform.
Let’s be blunt: the CCP isn’t playing to win headlines on Twitter. They’re not interested in going viral on Facebook. They’re targeting WeChat—because that’s where Chinese-Canadian voters live, talk, and form political opinions. And in that space, Beijing amplified Mark Carney—not because he’s “tough,” not because he’s competent, but because he’s good for China.
Canada has become a proxy battleground in a new Cold War between the West and the Chinese Communist Party. And Carney? He’s the CCP’s safe bet. Let’s not forget: this is the man whose financial career includes a quarter-billion-dollar loan from the Bank of China while chairing Brookfield Asset Management. The same man who’s never disclosed his full assets, despite now leading a party that’s still pretending foreign interference is just noise on the margins.
And now, in classic bureaucratic fashion, SITE and the government tell us they “don’t speculate on intent.” They claim the CCP is just sowing discord. That their approach is “party-agnostic.” That they weren’t trying to help Carney, just “pollute the digital environment.”
Give me a break. You don’t call someone a “tough opponent” to the U.S. and a “rock star” in a state-linked campaign unless you’re trying to boost their image. You don’t run coordinated bot amplification to spread content about one candidate because you’re bored and trying to “confuse people.” This wasn’t confusion. This was elevation.
And what did the government do? They flagged the content. They told Tencent about it. And then they backed off—because they don’t require any action. The PRC is running soft propaganda on a Canadian election platform, and Ottawa’s solution is: “Well, we told them. Hopefully they fix it.”
What’s worse? When asked about it directly, the government refused to name Carney as the beneficiary. They said they don’t want to “amplify the content” by repeating it. So let’s get this straight: Beijing gets to run a pro-Carney campaign, but Canadians aren’t even allowed to know the details?
That’s not protecting democracy. That’s protecting a narrative.
The truth is, Mark Carney is not being elevated because he’s good for Canadians. He’s being elevated because he’s safe for Beijing. The Liberals know it. The bureaucrats know it. And so far, no one in power has had the spine to stop it—because China’s interference benefits the very political class that claims to oppose it.
So when they talk about “safeguarding our democracy,” ask yourself: who are they really safeguarding it from? Because right now, it’s not from foreign influence—it’s from accountability.
Invite your friends and earn rewards
2025 Federal Election
Poilievre Will Bring in ‘One and Done’ Resource Approvals, and Ten Specific Projects Including LNG Canada Phase II

From Energy Now
Conservative Leader Pierre Poilievre announced that he will create a new ‘One and Done’ rule for resource projects: a one-stop shop, with one simple application and one environmental review. Poilievre also announced that he will rapidly approve 10 projects that have been stuck for years in the slow federal approval process. That will include Phase II of LNG Canada, a massive natural gas liquefaction project in Northern British Columbia. Many other projects will also be encouraged, all with an aim to bolster Canada’s economic independence against the Americans.
ONE-AND-DONE RULE will:
- Create a ‘One Stop Shop’ – A single office called the Rapid Resource Project Office will handle all regulatory approvals across all levels of government, so businesses don’t waste years navigating bureaucratic chaos and coordinating between multiple departments with different processes. We will cooperate with provincial governments to get all approvals into this single office.
- One application. End duplication – There will be one application and one environmental review per project, ensuring efficiency without sacrificing environmental standards. Instead of multiple overlapping studies that stall projects, governments will work together to deliver a single, effective review.
- One-year maximum wait times for approvals with a target of six months. There will be a target goal of decisions on applications in six months, with an upper time limit of one year, giving businesses certainty, cutting delays, and getting shovels in the ground faster.
“After the Lost Liberal decade, Canada is poorer, weaker, and more dependent on the United States than ever before, especially as a market for our natural resources,” said Poilievre. “My ‘One-and-Done’ rule will quickly and safely unleash Canada’s natural resources by rapidly approving the projects Canadians need more of now: mines, roads, LNG terminals, hydro projects, and nuclear power stations, so we can stand on our own two feet and stand up to the Americans.”
When completed, LNG Canada Phase II will double LNG output from 14 million to 28 million tonnes annually, creating hundreds of jobs in construction, operations and maintenance, and generating new revenues to fund the social programs that Canadians depend on. A new Conservative Government will also repeal C-69, the No Pipelines–No Development Law, and lift the cap on Canadian energy that would prevent LNG Canada Phase II from ever proceeding. Mark Carney has confirmed he will keep both C-69 and the cap in place.
Conservatives will also establish the Canadian Indigenous Opportunities Corporation (CIOC), to offer loan guarantees for local Indigenous-led resource projects.
A new Conservative government will also rapidly review nine other projects to find the hold-ups and accelerate federal decisions to get industry moving, workers working, and dollars flowing back to Canada. The full list of projects is at the end of this release.
Mark Carney and Steven Guilbeault’s “keep-it-in-the-ground” ideology–which maintains Bill C-69, the energy production cap, and the industrial carbon tax–will continue to stifle development in Canada, leading to job losses and increased reliance on foreign imports. Carney has said that “more than 80 per cent of current fossil fuel reserves … would need to stay in the ground.”
“The choice is clear: a fourth Liberal term that will keep our resources in the ground and keep us weak and vulnerable to Trump’s threats, or a strong new Conservative government that will approve projects, unleash our economy, bring jobs and dollars home, and put Canada First—For a Change.”
Some of the priority projects a Poilievre government will work with proponents and First Nations to approve:
- LNG Canada Phase II Expansion Project (BC): Aims to double LNG output but faces power supply challenges and output limitations related to the emissions cap.
- Suncor Base Mine Extension (Alberta): Expansion of an existing mine anticipated to produce 225,000 barrels per day of bitumen froth. Under assessment with the IAAC since 2020.
- Rook 1 Uranium Mine (Saskatchewan): A development-stage uranium project expected to be a major source of low-cost uranium. Approval process started in 2019 with the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission.
- Springpole Lake Gold (Ontario): A proposed gold and silver mine with an on-site metal mill. Under assessment with the IAAC since 2018.
- Upper Beaver Gold Mine (Ontario): A proposed underground and gold and copper mine. Under assessment with the IAAC since 2021.
- Northern Road Link (Ontario): A proposed all-season, multi-use road in northern Ontario. Under assessment with the IAAC since 2023.
- Crawford Nickel Project (Ontario): A proposed nickel-cobalt mine with an on-site metal mill. Under assessment with the IAAC since 2022.
- Troilus Gold and Copper Mine (Quebec): A proposed gold and copper mine. Under assessment with the IAAC since 2022.
- Sorel-Tracy Port Terminal (Quebec): A proposed new port terminal in the industrial-port area of Sorel-Tracy. Under assessment with the IAAC since 2022.
- Cape Ray Gold and Silver Mine (Newfoundland): A proposed gold and silver mine with a milling complex. Under assessment with the IAAC since 2017.
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoLiberals Replace Candidate Embroiled in Election Interference Scandal with Board Member of School Flagged in Canada’s Election Interference Inquiry
-
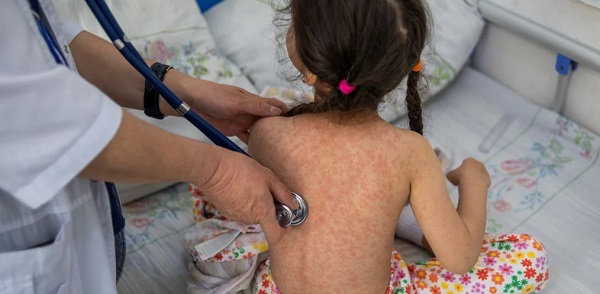
 Courageous Discourse1 day ago
Courageous Discourse1 day agoEurope Had 127,350 Cases of Measles in 2024
-

 2025 Federal Election2 days ago
2025 Federal Election2 days agoPierre Poilievre Declares War on Red Tape and Liberal Decay in Osoyoos
-

 Podcasts22 hours ago
Podcasts22 hours agoTrump’s Tariffs: The US, Canada, and the rest of the world
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoIs Canada’s Federation Fair?
-

 2025 Federal Election22 hours ago
2025 Federal Election22 hours agoMark Carney Comes to B.C. and Delivers a Masterclass in Liberal Arrogance
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days ago5 Stories the Media Buried This Week
-

 International2 days ago
International2 days agoBiden Lied About Everything, Including Nuclear Risk, During Ukraine Operation






