Health
52-year-old grandfather the latest Canadian to choose euthanasia while waiting for cancer treatment
From LifeSiteNews
Dan Quayle’s wife believes that she could still have her husband today if he’d gotten the treatment he needed. In fact, wait times for cancer patients in Canada who are literally dying while waiting for treatment keep getting worse.
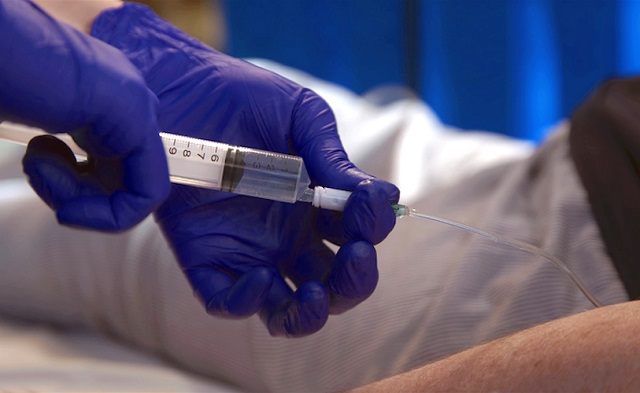
On October 7, 2023, Dan Quayle – a British Columbian, not the former vice president of the United States – turned 52. He was hoping to be told that he could begin chemotherapy after being diagnosed with esophageal cancer. It was not to be. “After 10 weeks in hospital, Quayle, a gregarious grandfather who put on his best silly act for his two grandkids, was in so much pain, unable to eat or walk, he opted for a medically assisted death on Nov. 24,” the National Post reported. “This was despite assurances from doctors that chemotherapy had the potential to prolong his life by a year.”
Throughout the agonizing wait, his family “prayed he would change his mind or get an 11th-hour call that chemo had been scheduled,” but were instead told consistently by the hospital that they were “backlogged.” The family is speaking out now “following the stories of two Vancouver Island women who went public with their decisions to seek treatment in the U.S. to avoid delays in B.C.” – and Dan’s wife believes that she could still have her husband today if he’d gotten the treatment he needed. In fact, wait times for cancer patients who are literally dying while waiting for treatment keep getting worse.
When Dan Quayle died by lethal injection, he still hadn’t been given a timeline for when he might get chemotherapy. It reminds me of the posthumously published obituary written by a Winnipeg woman who chose to die by assisted suicide after being refused the treatments she needed: “I could have had more time if I had more help.”
Indeed, one of the reasons Quayle felt that a lethal injection was his only option is because he didn’t have the financial resources to get help that was available elsewhere – but as a price. “If we had more money, we could have gone to the States,” his wife told the National Post sadly. “But we’re just regular people.”
She is likely referring to the two Vancouver Island women who decided to go public with their own experiences with the BC health care system. Global News published one story with the headline “B.C. woman gets surgery in U.S., says wait times at home could have cost her life” about Allison Ducluzeau, who paid $200,000 for surgery in the United States after she was told by a BC oncologist that she was not a candidate for the treatment that saved her life. After successfully getting treatment in the U.S., she recently got married – and is appalled by how she was treated in BC. In fact, she wasn’t offered life-saving treatment – but she was offered assisted suicide.
“There’s a lot of promises I’m hearing,” she told Global News. “But, you know, we need boots-on-the-ground action right now. What can you do to shorten these wait times? How can you prioritize cases so that people with aggressive stage four cancer get seen by someone and when they do get seen, they get offered treatment and not MAID like I was the first time?”
Another woman, 43-year-old Kristin Logan of Campbell River, was diagnosed with Stage 4 ovarian cancer – but faced a three or four month wait for treatment in British Columbia. She went to Washington State for chemotherapy, instead – she could afford it because the treatment was covered due to her dual citizenship and veteran status. When the health minister responded to her case by saying that the system “doesn’t always get it right,” she responded with fury: “To suggest that the system merely ‘doesn’t always get it right’ is a gross understatement, bordering on denial. Our healthcare system isn’t tripping over minor hurdles; it’s plummeting off a cliff. We’re not dealing with ‘occasional misses’; we’re grappling with a chronically diseased system where inefficiency and neglect have become the norm.”
What does this mean? It means that people are dying on waitlists – and while they suffer, often horribly, they are offered assisted suicide when they are their most vulnerable. And if the Trudeau Liberals get their way, in March of next year the floodgates will open and assisted suicide will also be available to those suffering with mental illness. Waitlists for mental health assistance and psychiatric care are even longer – I know people who have waited for years merely for an appointment. Many Canadians simply do not have access to this care. And so not only will Canadians die on waitlists; many will be offered assisted suicide while they are on waitlists, and many will, out of desperation, say yes.
Health
RFK Jr. promises to identify cause of autism ‘epidemic’ by September

From LifeSiteNews
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. explained that autism rates continue to climb, and are now expected to impact 1 in 31 children, up from ‘1 in 10,000 when I was a kid.’
Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. said that his agency has undertaken a multinational study involving “hundreds of scientists around the world” to identify the causes of the growing incidence of autism in children.
“We’ve launched a massive testing and research effort that’s going to involve hundreds of scientists from around the world,” Kennedy told President Trump during Thursday’s White House Cabinet meeting. “By September, we will know what has caused the autism epidemic, and we’ll be able to eliminate those exposures.”
Kennedy explained that autism rates continue to climb, and are now expected to impact 1 in 31 children, up from “1 in 10,000 when I was a kid.”
“It’s a horrible statistic,” Trump said of the latest autism rate figures. “There’s got to be something artificial out there that’s doing this.”
“There will be no bigger news conference than when you come up with that answer,” predicted the president.
As recently as 2000, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) research showed that 1 in 150 children were diagnosed with autism.
While many mainstream autism researchers adhere to theories that the rising rate of autism is due to “increased awareness” and an evolving, broadening definition of autism, Kennedy holds to that belief that the cause will be found primarily in environmental factors, eating habits, and currently accepted standard medical protocols.
“We’re going to look at vaccines, but we’re going to look at everything. Everything is on the table, our food system, our water, our air, different ways of parenting, all the kind of changes that may have triggered this epidemic,” the HHS head told Fox News.
“It is an epidemic,” Kennedy insisted. “Epidemics are not caused by genes. Genes can provide a vulnerability, but you need an environmental toxin.”
“We know that it is an environmental toxin that is causing this cataclysm,” said Kennedy, “and we are going to identify it.”
Kennedy is known for vehemently opposing vaccines, a stance he adopted after the mothers of vaccine-injured children implored him to look into the research linking thimerosal to neurological injuries, including autism. He went on to found Children’s Health Defense, an organization with the stated mission of “ending childhood health epidemics by eliminating toxic exposure,” largely through vaccines.
The federal government spent more than $300 million on autism research in 2023, according to a report by The Hill.
Health
RFK Jr. Shuts Down Measles Scare in His First Network Interview as HHS Secretary

 The Vigilant Fox
The Vigilant Fox
CBS’s Jon LaPook tried to hype the measles panic, but Kennedy calmly dismantled the narrative and set the record straight.
The following is a streamlined and editorialized version of a thread that originally appeared on the American Values X page. It was edited and republished with permission. Click here to read the original thread.
HHS Secretary RFK Jr. recently set the record straight in an interview with CBS News’ chief medical correspondent, Dr. Jon LaPook. He pushed back on the claim that a second child had died from measles, exposing the narrative as not just misleading, but flat-out false.
But before that happened, Kennedy addressed the current measles outbreak and ongoing concerns about vaccine safety. He revealed that new safety trials are finally in motion.
“We don’t know the risks of many of these products,” he said. “They’re not adequately safety-tested.” He explained that “many of the vaccines are tested for only 3-4 days with NO placebo group.”
Kennedy made it clear this isn’t about banning vaccines—it’s about transparency. “I’ve always said … I’m not gonna take people’s vaccines away from them,” he said. “I’m gonna make sure that we have good science so that people can make an informed choice.” He added, “We are doing that science today.”
Kennedy was asked about Daisy Hildebrand, the young girl in Texas whose funeral he attended. Her death had been cited in headlines as proof of a growing measles crisis.
“It was very nice to be able to meet the parents in person and spend the whole day with them and share their lives with them and get to know their community,” he said. “The community was very welcoming and loving towards me.”
Kennedy described the experience warmly: “The Mennonite community was beautiful to me.” He added, “I went to a large lunch with the whole community and you had boys and girls sitting together and nobody was on a cell phone.”
That’s when Kennedy dropped the real bombshell: the child didn’t die from measles.
“The child whose funeral I attended this week was hospitalized three times from other illnesses,” he said. “She got measles and she got over the measles, according to her parents.” He added, “I saw the medical report on it today and the thing that killed her was not the measles, but it was a bacteriological infection.”
And it wasn’t the first time the media misled the public. Last month, another child’s death was falsely blamed on measles. But the truth is that it was a case of catastrophic medical error.
“Her death is the result of an egregious medical error,” CHD’s Mary Holland told Steve Bannon. “This girl wound up in the hospital because she did have some difficulty breathing, and instead of giving her breathing care, you’ll understand from the specialists with me that she got inaccurate, wrong-headed medical care, and that’s why she died.”
She added, “She did not die from measles. She died from a medical error, the third leading cause of death in this country.”
Thanks for reading. If you value the work being published here, upgrading your subscription is the most powerful way to support it. The more this Substack earns, the more we can expand the team, improve quality, and create the best reader experience possible.
For the full experience, upgrade your subscription.
-

 Also Interesting2 days ago
Also Interesting2 days agoMortgage Mayhem: How Rising Interest Rates Are Squeezing Alberta Homeowners
-

 Alberta2 days ago
Alberta2 days agoAlberta takes big step towards shorter wait times and higher quality health care
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoStocks soar after Trump suspends tariffs
-

 COVID-192 days ago
COVID-192 days agoBiden Admin concealed report on earliest COVID cases from 2019
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoTrump raises China tariffs to 125%, announces 90-day pause for countries who’ve reached out to negotiate
-
 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoScott Bessent Says Trump’s Goal Was Always To Get Trading Partners To Table After Major Pause Announcement
-

 2025 Federal Election1 day ago
2025 Federal Election1 day agoResearchers Link China’s Intelligence and Elite Influence Arms to B.C. Government, Liberal Party, and Trudeau-Appointed Senator
-

 Energy2 days ago
Energy2 days agoTrump signs four executive orders promoting coal industry










